Abstract
Heavy metals in soil are harmful to natural biodiversity and human health, and it is difficult to estimate the effects accurately. To reduce pollution and manage risk in coal-mining regions, it is essential to evaluate risks for heavy metals in soil. The present study reviews the levels of 21 metals (Nb, Zr, Ag, Ni, Na, K, Mg, Rb, Zn, Ca, Sr, As, Cr, Fe, Pb, Cd, Co, Hg, Cu, Mn and Ti) in soils around Barapukuria coal-mining vicinity, Bangladesh which were reported in literature. An integrated approach for risk assessments with the positive matrix factorization (PMF) model, source-oriented ecological and health hazards were applied for the study. The contents of Rb, Ca, Zn, Pb, As, Ti, Mn, Co, Ag, Zr, and Nb were 1.63, 1.10, 1.97, 14.12, 1.20, 3.13, 1.22, 3.05, 3.85, 5.48, and 7.21 times greater than shale value. About 37%, 67%, 12%, and 85% of sampling sites posed higher risks according to the modified contamination factor, Nemerow pollution index, Nemerow integrated risk index, and mean effect range median quotient, respectively. Five probable metal sources were computed, including industrial activities to coal mining (17%), agricultural activities (33%), atmospheric deposition (19%), traffic emission (16%), and natural sources (15%). Modified Nemerow integrated risk index reported that agricultural activities, industrial coal mining activities, and atmospheric deposition showed moderate risk. Health hazards revealed that cancer risk values computed by the PMF-HHR model with identified sources were higher than the standard value (1.0E−04) for children, adult male, and female. Agricultural activities showed higher cancer risks to adult male (39%) and children (32%) whereas traffic emission contributed to female (25%). These findings highlight the ecological and health issues connected to potential sources of metal contamination and provide useful information to policymakers on how to reduce such risks.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Abliz, A., Shi, Q., Keyimu, M., & Sawut, R. (2018). Spatial distribution, source, and risk assessment of soil toxic metals in the coal-mining region of northwestern China. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11, 793.
Adetunji, A. T., Adeyinka, G. C., & Neji, P. A. (2020). Assessment of the selected heavy metals contamination of fossil fuel (Coal) within Okaba, Onyeama and Ribadu Mining Sites, Nigeria. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 00(00), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1807973
Agyeman, P. C., Kingsley, J., Kebonye, N. M., Ofori, S., Borůvka, L., Vašát, R., & Kočárek, M. (2022). Ecological risk source distribution, uncertainty analysis, and application of geographically weighted regression cokriging for prediction of potentially toxic elements in agricultural soils. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 164, 729–746.
Ahmad, N., Niamatullah, Hussain, J., Ahmad, I., & Asif, M. (2020). Estimation of health risk to humans from heavy metals in soil of coal mines in Harnai, Balochistan. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 102(16), 3894–3905.
Anaman, R., Peng, C., Jiang, Z., Liu, X., Zhou, Z., Guo, Z., & Xiao, X. (2022). Identifying sources and transport routes of heavy metals in soil with different land uses around a smelting site by GIS based PCA and PMF. Science of the Total Environment, 823, 153759.
Ao, M., Sun, S., Deng, T., Zhang, F., Liu, T., Tang, Y., et al. (2022). Natural source of Cr (VI) in soil: The anoxic oxidation of Cr (III) by Mn oxides. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 433, 128805.
Arisekar, U., Shakila, R. J., Shalini, R., Jeyasekaran, G., Keerthana, M., Arumugam, N., et al. (2022). Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals using geochemical normalization factors in the aquatic sediments. Chemosphere, 294, 133708.
Basak, B. B., Sarkar, B., Biswas, D. R., Sarkar, S., Sanderson, P., & Naidu, R. (2017). Bio-intervention of naturally occurring silicate minerals for alternative source of potassium: Challenges and opportunities. Advances in Agronomy, 141, 115–145.
Bhuiyan, M. A. H., Parvez, L., Islam, M. A., Dampare, S. B., & Suzuki, S. (2010). Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173(1–3), 384–392.
Bu, Q., Li, Q., Zhang, H., Cao, H., Gong, W., Zhang, X., et al. (2020). Concentrations, spatial distributions, and sources of heavy metals in surface soils of the coal mining city Wuhai, China, 2020.
Bushra, A., Zakir, H. M., Sharmin, S., Quadir, Q. F., Rashid, M. H., Rahman, M. S., & Mallick, S. (2022). Human health implications of trace metal contamination in topsoils and brinjal fruits harvested from a famous brinjal-producing area in Bangladesh. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 1–14.
Carrillo, K. C., Drouet, J. C., Rodríguez-Romero, A., Tovar-Sánchez, A., Ruiz-Gutiérrez, G., & Fuente, J. R. V. (2021). Spatial distribution and level of contamination of potentially toxic elements in sediments and soils of a biological reserve wetland, northern Amazon region of Ecuador. Journal of Environmental Management, 289, 112495.
Chakraborty, B., Bera, B., Roy, S., Adhikary, P. P., & Sengupta, D. (2021). Assessment of non-carcinogenic health risk of heavy metal pollution: Evidences from coal mining region of eastern India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28, 47275–47293.
Chari, N. R., Lin, Y., Lin, Y. S., & Silver, W. L. (2021). Interactive effects of temperature and redox on soil carbon and iron cycling. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 157, 108235.
Chen, X., Jiang, S., Palmer, M. R., Schertl, H.-P., Cambeses, A., Hernández-Uribe, D., et al. (2022a). Tourmaline chemistry, boron, and strontium isotope systematics trace multiple melt–fluid–rock interaction stages in deeply subducted continental crust. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 340, 120–140.
Chen, Z., Ding, Y., Jiang, X., Duan, H., Ruan, X., Li, Z., & Li, Y. (2022b). Combination of UNMIX, PMF model and Pb-Zn-Cu isotopic compositions for quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in suburban agricultural soils. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 234, 113369.
Croffie, M. E. T., Williams, P. N., Fenton, O., Fenelon, A., & Daly, K. (2022). Rubidium measured by XRF as a predictor of soil particle size in limestone and siliceous parent materials. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 22(3), 818–830.
Cui, X., Geng, Y., Li, T., Zhao, R., Li, X., & Cui, Z. (2021). Field application and effect evaluation of different iron tailings soil utilization technologies. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 173, 105746.
de Souza Oliveira, N., Schiavo, J. A., Pereira, M. G., da Silva Coêlho, R., Ozório, J. M. B., & de Moraes, E. M. V. (2022). Pedogenesis of soils with accumulation of organic carbon in the subsurface horizons in a saline lake in the Pantanal wetland of Nhecolândia, Brazil. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 117, 103816.
Deng, D., Wu, Y., Sun, Y., Ren, B., & Song, L. (2022). Pollution characteristics and spatial distribution of heavy metals in coal-bearing sandstone soil: A case study of coal mine area in Southwest China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(11), 6493.
Dominech, S., Albanese, S., Guarino, A., & Yang, S. (2022). Assessment on the source of geochemical anomalies in the sediments of the Changjiang river (China), using a modified enrichment factor based on multivariate statistical analyses. Environmental Pollution, 313, 120126.
Du, S., Lu, Q., Liu, L., Wang, Y., & Li, J. (2022). Rhodococcus qingshengii facilitates the phytoextraction of Zn, Cd, Ni, and Pb from soils by Sedum alfredii Hance. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 424, 127638.
Fan-xin, Q. I. N., Chao-fu, W. E. I., & Shou-qin, Z. (2016). Soil heavy metal (loid) s and risk assessment in vicinity of a coal mining area from southwest Guizhou, China. Journal of Central South University, 23(1), 63–73.
Fardushe, R. S., Hoque, M. M., & Roy, S. (2014). Assessment of soil and water quality of Barapukuria coal mining site, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Bangladesh Journal of Scientific Research, 27(1), 63–73.
Fei, X., Lou, Z., Xiao, R., Ren, Z., & Lv, X. (2020). Contamination assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil through the synthesis of PMF and GeogDetector models. Science of the Total Environment, 747, 141293.
Feng, X., Wang, Q., Sun, Y., Zhang, S., & Wang, F. (2022). Microplastics change soil properties, heavy metal availability and bacterial community in a Pb-Zn-contaminated soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 424, 127364.
Fural, Ş, Kükrer, S., Cürebal, İ, & Aykır, D. (2022). Ecological degradation and non-carcinogenic health risks of potential toxic elements: A GIS-based spatial analysis for Doğancı Dam (Turkey). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(4), 1–18.
Ge, D., Yuan, H., Xiao, J., & Zhu, N. (2019). Insight into the enhanced sludge dewaterability by tannic acid conditioning and pH regulation. Science of the Total Environment, 679, 298–306.
Goswami, A. P., & Kalamdhad, A. S. (2022). Mobility and risk assessment of heavy metals in benthic sediments using contamination factors, positive matrix factorisation (PMF) receptor model, and human health risk assessment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30, 7056–7074.
Guo, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, W., Zhao, J., Yu, S., Jia, H., et al. (2022). Incorporating in vitro bioaccessibility into human health risk assessment of heavy metals and metalloid (As) in soil and pak choi (Brassica chinensis L.) from greenhouse vegetable production fields in a megacity in Northwest China. Food Chemistry, 373, 131488.
Halim, M. A., Majumder, R. K., & Zaman, M. N. (2015). Paddy soil heavy metal contamination and uptake in rice plants from the adjacent area of Barapukuria coal mine, northwest Bangladesh. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(6), 3391–3401.
Han, J., Liang, L., Zhu, Y., Xu, X., Wang, L., Shang, L., et al. (2022). Heavy metal (loid) s in farmland soils on the Karst Plateau, Southwest China: An integrated analysis of geochemical baselines, source apportionment, and associated health risk. Land Degradation & Development, 33(10), 1689–1703.
Hong, Y., Chen, S., Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Yu, L., Liu, Y., et al. (2018). Rapid identification of soil organic matter level via visible and near-infrared spectroscopy: Effects of two-dimensional correlation coefficient and extreme learning machine. Science of the Total Environment, 644, 1232–1243.
Hossain, M., Paul, S. K., & Hasan, M. (2015). Environmental impacts of coal mine and thermal power plant to the surroundings of Barapukuria, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(4), 1–11.
Hossen, M. A., Chowdhury, A. I. H., Mullick, M. R. A., & Hoque, A. (2021). Heavy metal pollution status and health risk assessment vicinity to Barapukuria coal mine area of Bangladesh. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 16, 100469.
Huang, C., Cai, L., Xu, Y., Wen, H., Jie, L., Hu, G., et al. (2022a). Quantitative analysis of ecological risk and human health risk of potentially toxic elements in farmland soil using the PMF model. Land Degradation & Development, 33(11), 1954–1967.
Huang, C. C., Cai, L. M., Xu, Y. H., Jie, L., Chen, L. G., Hu, G. C., et al. (2022b). A comprehensive exploration on the health risk quantification assessment of soil potentially toxic elements from different sources around large-scale smelting area. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(3), 1–17.
Huang, G., Wang, X., Chen, D., Wang, Y., Zhu, S., Zhang, T., et al. (2022c). A hybrid data-driven framework for diagnosing contributing factors for soil heavy metal contaminations using machine learning and spatial clustering analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 129324.
Huang, Y., Li, K., Liu, H., Yuan, X., Li, M., Xiong, B., et al. (2022d). Distribution, sources and risk assessment of PAHs in soil from the water level fluctuation zone of Xiangxi Bay, Three Gorges Reservoir. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 44(8), 2615–2628.
Ilić, P., Ilić, S., Markić, D. N., Bjelić, L. S., Popović, Z., Radović, B., et al. (2022). Ecological risk of toxic metal contamination in soil around coal mine and thermal power plant. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 31(5), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/148071
Jiang, S., Liu, Y., & Shu, Y. (2022a). Biochar and exogenous calcium assisted alleviation of Pb phytotoxicity in water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica Forsk) cultivated in Pb-spiked soil. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 44(1), 207–219.
Jiang, S., Zeng, J., Zhang, X., Zhou, S., Wang, L., Xu, S., & Lu, Q. (2022b). Association of urinary rubidium concentrations with hypertension risk and blood pressure levels: A cross-sectional study in China. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 71, 126936.
Jingsen, F. A. N., Yuzhuang, S. U. N., Xinyu, L. I., Cunliang, Z., Duanxin, T., & Longyi, S. (2013). Pollution of organic compounds and heavy metals in a coal gangue dump of the Gequan Coal Mine , China, 241–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-013-0628-0
Khan, M. H. R., Seddique, A. A., Rahman, A., & Shimizu, Y. (2017). Heavy metals contamination assessment of water and soils in and around Barapukuria coal mine area, Bangladesh. American Journal of Environmental Protection, 6(4), 80–86.
Khatun, J., Intekhab, A., & Dhak, D. (2022). Effect of uncontrolled fertilization and heavy metal toxicity associated with arsenic (As), lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd), and possible remediation. Toxicology, 477, 153274.
Knysh, I., & Karabyn, V. (2014). Heavy metals distribution in the waste pile rocks of chervonogradska mine of the lviv-volyn Coal Basin (Ukraine). Pollution Research, 33(4), 663–670.
Kumar, V., Bharti, P. K., Talwar, M., Tyagi, A. K., & Kumar, P. (2017). Studies on high iron content in water resources of Moradabad district (UP), India. Water Science, 31(1), 44–51.
Lei, M., Li, K., Guo, G., & Ju, T. (2022). Source-specific health risks apportionment of soil potential toxicity elements combining multiple receptor models with Monte Carlo simulation. Science of the Total Environment, 817, 152899.
Li, H., Xu, W., Dai, M., & Wang, Z. (2019). Assessing heavy metal pollution in paddy soil from coal mining area, Anhui, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 518.
Li, P., Hua, P., Zhang, J., & Krebs, P. (2022a). Ecological risk and machine learning based source analyses of trace metals in typical surface water. Science of The Total Environment, 838, 155944.
Li, T., Yu, X., Li, M., Rong, L., Xiao, X., & Zou, X. (2023). Ecological insight into antibiotic resistome of ion-adsorption rare earth mining soils from south China by metagenomic analysis. Science of the Total Environment, 872, 162265.
Li, W., Shi, Y., Zhu, D., Wang, W., Liu, H., Li, J., et al. (2021a). Fine root biomass and morphology in a temperate forest are influenced more by the nitrogen treatment approach than the rate. Ecological Indicators, 130, 108031.
Li, X., Bing, J., Zhang, J., Guo, L., Deng, Z., Wang, D., & Liu, L. (2022b). Ecological risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments of a river–reservoir system. Science of The Total Environment, 842, 156683.
Li, Y., Chen, H., Song, L., Wu, J., Sun, W., & Teng, Y. (2021b). Effects on microbiomes and resistomes and the source-specific ecological risks of heavy metals in the sediments of an urban river. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 409, 124472.
Liang, J., Feng, C., Zeng, G., Gao, X., & Zhong, M. (2017). Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in surface soils in a typical coal mine city, Lianyuan, China. Environmental Pollution, 225, 681–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.03.057
Liu, J., Lu, B., Poulain, A. J., Zhang, R., Zhang, T., Feng, X., & Meng, B. (2022a). The underappreciated role of natural organic matter bond Hg (II) and nanoparticulate HgS as substrates for methylation in paddy soils across a Hg concentration gradient. Environmental Pollution, 292, 118321.
Liu, L., Xu, X., Han, J., Zhu, J.-M., Li, S., Liang, L., et al. (2022b). Heavy metal (loid) s in agricultural soils in the world’s largest barium-mining area: Pollution characteristics, source apportionment, and health risks using PMF model and Cd isotopes. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 166, 669–681.
Liu, W.-J., Liu, C.-Q., Zhao, Z.-Q., Xu, Z.-F., Liang, C.-S., Li, L., & Feng, J.-Y. (2013). Elemental and strontium isotopic geochemistry of the soil profiles developed on limestone and sandstone in karstic terrain on Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China: Implications for chemical weathering and parent materials. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 67, 138–152.
Liu, X., Gu, S., Yang, S., Deng, J., & Xu, J. (2021a). Heavy metals in soil-vegetable system around E-waste site and the health risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 779, 146438.
Liu, Y., Wu, T., White, J. C., & Lin, D. (2021b). A new strategy using nanoscale zero-valent iron to simultaneously promote remediation and safe crop production in contaminated soil. Nature Nanotechnology, 16(2), 197–205.
Liu, Z., Zheng, J., Liu, W., Liu, X., Chen, Y., Ren, X., et al. (2020). Identification of the key host phases of Cr in fresh chromite ore processing residue (COPR). Science of the Total Environment, 703, 135075.
Liu, Z., Xu, J., Liu, M., Yin, Z., Liu, X., Yin, L., & Zheng, W. (2023). Remote sensing and geostatistics in urban water-resource monitoring: A review. Marine and Freshwater Research, 74(9–10), 747–765.
Lu, T., Wang, W., Liu, L., Wang, L., Hu, J., Li, X., & Qiu, G. (2022). Remediation of cadmium-polluted weakly alkaline dryland soils using iron and manganese oxides for immobilized wheat uptake. Journal of Cleaner Production, 365, 132794.
Ma, W., Sun, T., Xu, Y., Zheng, S., & Sun, Y. (2022). In-situ immobilization remediation, soil aggregate distribution, and microbial community composition in weakly alkaline Cd-contaminated soils: A field study. Environmental Pollution, 292, 118327.
Mazumder, P., Das, A., Khwairakpam, M., & Kalamdhad, A. S. (2021). A comprehensive insight into ecological risk assessment and remediation of metal contaminated coal mine soil: Towards a cleaner and sustainable environment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 324, 129185.
Mazur, P., Gozdowski, D., & Wójcik-Gront, E. (2022). Soil electrical conductivity and satellite-derived vegetation indices for evaluation of phosphorus, potassium and magnesium content, pH, and delineation of within-field management zones. Agriculture, 12(6), 883.
Miao, L., & Niu, Y. (2022). Coal mine electrical safety management and accident prevention based on neural network and signal processing. Journal of computational methods in sciences and engineering, (Preprint), 1–10.
Moustafa, A. A., Abdelbasir, S. M., Ashmawy, A. M., Ghayad, I. M., & El-Zomrawy, A. A. (2022). A novel ionic liquid for improvement of lead-acid battery performance and protection of its electrodes against corrosion. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 292, 126764.
Nakagawa, K., Imura, T., & Berndtsson, R. (2022). Distribution of heavy metals and related health risks through soil ingestion in rural areas of western Japan. Chemosphere, 290, 133316.
Neckel, A., Pinto, D., Adelodun, B., & Dotto, G. L. (2022). An analysis of nanoparticles derived from coal fly ash incorporated into concrete. Sustainability, 14(7), 3943.
Nfor, B., Fai, P. B. A., Tamungang, S. A., Fobil, J. N., & Basu, N. (2022). Soil contamination and bioaccumulation of heavy metals by a tropical earthworm species (Alma nilotica) at informal E-waste recycling sites in Douala, Cameroon. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 41(2), 356–368.
Okoye, E. A., Ezejiofor, A. N., Nwaogazie, I. L., Frazzoli, C., & Orisakwe, O. E. (2022). Heavy metals and arsenic in soil and vegetation of Niger Delta, Nigeria: Ecological risk assessment. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 6, 100222.
Oladoye, P. O., Olowe, O. M., & Asemoloye, M. D. (2022). Phytoremediation technology and food security impacts of heavy metal contaminated soils: A review of literature. Chemosphere, 288, 132555.
Ozturk, A., & Arici, O. K. (2021). Carcinogenic-potential ecological risk assessment of soils and wheat in the eastern region of Konya (Turkey). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(12), 15471–15484.
Peng, J., Zhang, S., Han, Y., Bate, B., Ke, H., & Chen, Y. (2022). Soil heavy metal pollution of industrial legacies in China and health risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 816, 151632.
Proshad, R., Dey, H. C., Ritu, S. A., Baroi, A., Khan, M. S. U., Islam, M., & Idris, A. M. (2022a). A review on toxic metal pollution and source-oriented risk apportionment in road dust of a highly polluted megacity in Bangladesh. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 45, 2729–2762.
Proshad, R., Islam, M., & Idris, A. M. (2022b). Uncertainty analysis in receptor model with sources identification and risks apportionment of toxic metal (oid) s in agricultural soils around industrial areas in Bangladesh. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 233(8), 1–26.
Qin, F., Wei, C., Zhong, S., Huang, X., Pang, W., & Jiang, X. (2016). Soil heavy metal (loid) s and risk assessment in vicinity of a coal mining area from southwest Guizhou, China. Journal of Central South University, 23(9), 2205–2213.
Qin, Z., Jin, J., Liu, L., Zhang, Y., Du, Y., Yang, Y., & Zuo, S. (2023). Reuse of soil-like material solidified by a biomass fly ash-based binder as engineering backfill material and its performance evaluation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 402, 136824.
Raj, D., Kumar, A., & Kumar, S. (2019). Evaluation of toxic metal(loid)s concentration in soils around an open-cast coal mine (Eastern India). Environmental Earth Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8657-6
Ran, H., Deng, X., Guo, Z., Hu, Z., An, Y., Xiao, X., et al. (2022). Pollution characteristics and environmental availability of toxic elements in soil from an abandoned arsenic-containing mine. Chemosphere, 303, 135189.
Rehman, A. U., Nazir, S., Irshad, R., Tahir, K., ur Rehman, K., Islam, R. U., & Wahab, Z. (2021). Toxicity of heavy metals in plants and animals and their uptake by magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 321, 114455.
Ren, C., Zhang, Q., Wang, H., & Wang, Y. (2021). Characteristics and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of groundwater in Hutuo River alluvial-pluvial fan, China, based on PMF model. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(8), 9647–9656.
Reza, S. K., Baruah, U., Singh, S. K., & Das, T. H. (2015). Geostatistical and multivariate analysis of soil heavy metal contamination near coal mining area, Northeastern India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(9), 5425–5433.
Sattar, A., Naveed, M., Ali, M., Zahir, Z. A., Nadeem, S. M., Yaseen, M., et al. (2019). Perspectives of potassium solubilizing microbes in sustainable food production system: A review. Applied Soil Ecology, 133, 146–159.
Sawut, R., Tiyip, T., Abliz, A., Kasim, N., Nurmemet, I., & Sawut, M. (2017). Using regression model to identify and evaluate heavy metal pollution sources in an open pit coal mine area, Eastern Junggar China. Environmental Earth Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7035-5
Sheng, D., Meng, X., Wen, X., Wu, J., Yu, H., & Wu, M. (2022). Contamination characteristics, source identification, and source-specific health risks of heavy metal(loid)s in groundwater of an arid oasis region in Northwest China. Science of the Total Environment, 841, 156733.
Shi, C., He, H., Xia, Z., Gan, H., Xue, Q., Cui, Z., & Chen, J. (2022a). Heavy metals and Pb isotopes in a marine sediment core record environmental changes and anthropogenic activities in the Pearl River Delta over a century. Science of the Total Environment, 814, 151934.
Shi, W., Li, T., Feng, Y., Su, H., & Yang, Q. (2022b). Source apportionment and risk assessment for available occurrence forms of heavy metals in Dongdahe Wetland sediments, southwest of China. Science of The Total Environment, 815, 152837.
Shi, X.-M., Liu, S., Song, L., Wu, C.-S., Yang, B., Lu, H.-Z., et al. (2022c). Contamination and source-specific risk analysis of soil heavy metals in a typical coal industrial city, central China. Science of the Total Environment, 836, 155694.
Shi, X., Liu, S., Song, L., Wu, C., Yang, B., Lu, H., et al. (2022d). Science of the total environment contamination and source-specific risk analysis of soil heavy metals in a typical coal industrial city, central China. Science of the Total Environment, 836, 155694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155694
Siddique, M. A. B., Alam, M. K., Islam, S., Diganta, M. T. M., Akbor, M. A., Bithi, U. H., et al. (2020). Apportionment of some chemical elements in soils around the coal mining area in northern Bangladesh and associated health risk assessment. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 14, 100366.
Siddiqui, A. U., Jain, M. K., & Masto, R. E. (2020). Pollution evaluation, spatial distribution, and source apportionment of trace metals around coal mines soil: The case study of eastern India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 10822–10834.
Singh, K. N., & Narzary, D. (2021). Heavy metal tolerance of bacterial isolates associated with overburden strata of an opencast coal mine of Assam (India). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(44), 63111–63126.
Škrbić, B. D., Buljovčić, M., & Antić, I. (2022). Comprehensive assessment of heavy elements and evaluation of potential human health risk in the urban environment: a case study from Novi Sad, Serbia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 38551–38566
Song, T., Das, D., Hu, Q., Yang, F., & Zhang, J. (2021). Alternate wetting and drying irrigation and phosphorus rates affect grain yield and quality and heavy metal accumulation in rice. Science of the Total Environment, 752, 141862.
Sun, J., Zhao, M., Huang, J., Liu, Y., Wu, Y., Cai, B., et al. (2022). Determination of priority control factors for the management of soil trace metal (loid) s based on source-oriented health risk assessment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 423, 127116.
Tang, J., Tang, H., Sima, W., Wang, H., Zou, D., Qiu, B., et al. (2022). Heavy metal pollution level and potential ecological risk assessment of sludge landfill. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 41(3), e13795.
Tang, Z., Chai, M., Cheng, J., Jin, J., Yang, Y., Nie, Z., & Huang, Q. (2017). Ecotoxicology and environmental safety contamination and health risks of heavy metals in street dust from a coal- mining city in eastern China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 138, 83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.11.003
Teng, Y., Liu, L., Zheng, N., Liu, H., Wu, L., & Yue, W. (2022). Application of different indices for soil heavy metal pollution risk assessment comparison and uncertainty: A case study of a copper mine tailing site. Minerals, 12(9), 1074.
Van Hoang, N., Van, D. T., & Hoa, P. L. (2020). Heavy metal contamination of soil based on pollution, geo-accumulation indices and enrichment factor in Phan Me coal mine area, Thai Nguyen province, Vietnam. Vietnam Journal of Earth Sciences, 42(2), 105–117.
Wang, J., Hu, X., Shi, T., He, L., Hu, W., & Wu, G. (2022a). Assessing toxic metal chromium in the soil in coal mining areas via proximal sensing: Prerequisites for land rehabilitation and sustainable development. Geoderma, 405, 115399.
Wang, N., Guan, Q., Sun, Y., Wang, B., Ma, Y., Shao, W., & Li, H. (2021a). Predicting the spatial pollution of soil heavy metals by using the distance determination coefficient method. Science of the Total Environment, 799, 149452.
Wang, S., Zhou, P., Luo, B., & Ye, S. (2022b). Stoichiometric characteristics of medium‐and micro‐elements (Ca, Mg, Fe, and Mn) in soil aggregates as affected by stand age in Chinese fir plantations. Land Degradation & Development, 33(18), 3991–4003.
Wang, X., & Wang, H. (2022). Risk assessment of coal mine safety production management activities based on FMEA-BN. Journal of Computational Methods in Sciences and Engineering, 22(1), 123–136.
Wang, Y., Guo, G., Zhang, D., & Lei, M. (2021b). An integrated method for source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils and model uncertainty analysis. Environmental Pollution, 276, 116666.
Wang, Z., Zhou, W., Jiskani, I. M., Luo, H., Ao, Z., & Mvula, E. M. (2022c). Annual dust pollution characteristics and its prevention and control for environmental protection in surface mines. Science of the Total Environment, 825, 153949.
Wu, Y., Liu, Q., Ma, J., Zhao, W., Chen, H., & Qu, Y. (2022). Antimony, beryllium, cobalt, and vanadium in urban park soils in Beijing: Machine learning-based source identification and health risk-based soil environmental criteria. Environmental Pollution, 293, 118554.
Xiang, M., Li, Y., Yang, J., Lei, K., Li, Y., Li, F., et al. (2021). Heavy metal contamination risk assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metal contents in soil and crops. Environmental Pollution, 278, 116911.
Xiang, Q., Yu, H., Chu, H., Hu, M., Xu, T., Xu, X., & He, Z. (2022). The potential ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals using self-organizing map. Science of the Total Environment, 843, 156978.
Xu, D., Li, J., Liu, J., Qu, X., & Ma, H. (2022). Advances in continuous flow aerobic granular sludge: A review. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 163, 27–35.
Xu, D. M., & Fu, R. B. (2022). The mechanistic insights into the leaching behaviors of potentially toxic elements from the indigenous zinc smelting slags under the slag dumping site scenario. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 437, 129368.
Xu, D., Zhu, D., Deng, Y., Sun, Q., Ma, J., & Liu, F. (2023a). Evaluation and empirical study of Happy River on the basis of AHP: a case study of Shaoxing City (Zhejiang, China). Marine and Freshwater Research, 74(9–10), 838–850.
Xu, H., Croot, P., & Zhang, C. (2021a). Discovering hidden spatial patterns and their associations with controlling factors for potentially toxic elements in topsoil using hot spot analysis and K-means clustering analysis. Environment International, 151, 106456.
Xu, J., Gui, H., Chen, J., Li, C., Li, Y., Zhao, C., & Guo, Y. (2021b). A combined model to quantitatively assess human health risk from different sources of heavy metals in soils around coal waste pile. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 27(9–10), 2235–2253.
Xu, R., Wang, Y., Sun, Y., Wang, H., Gao, Y., Li, S., et al. (2023b). External sodium acetate improved Cr (VI) stabilization in a Cr-spiked soil during chemical-microbial reduction processes: Insights into Cr (VI) reduction performance, microbial community and metabolic functions. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 251, 114566.
Yan, T., Zhao, W., Yu, X., Li, H., & Gao, Z. (2022). Evaluating heavy metal pollution and potential risk of soil around a coal mining region of Tai ’ an City. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 61(3), 2156–2165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.08.013
Yang, B., Qiu, H., Zhang, P., He, E., Xia, B., Liu, Y., et al. (2022a). Modeling and visualizing the transport and retention of cationic and oxyanionic metals (Cd and Cr) in saturated soil under various hydrochemical and hydrodynamic conditions. Science of the Total Environment, 812, 151467.
Yang, H., Wang, F., Yu, J., Huang, K., Zhang, H., & Fu, Z. (2021). An improved weighted index for the assessment of heavy metal pollution in soils in Zhejiang, China. Environmental Research, 192, 110246.
Yang, J., Sun, Y., Wang, Z., Gong, J., Gao, J., Tang, S., et al. (2022b). Heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils of a typical volcanic area: Risk assessment and source appointment. Chemosphere, 304, 135340.
Yang, M., Zhao, A., Ke, H., & Chen, H. (2023). Geo-environmental factors’ influence on the prevalence and distribution of dental fluorosis: Evidence from Dali County, Northwest China. Sustainability, 15(3), 1871.
Yang, X., Shaheen, S. M., Wang, J., Hou, D., Ok, Y. S., Wang, S.-L., et al. (2022c). Elucidating the redox-driven dynamic interactions between arsenic and iron-impregnated biochar in a paddy soil using geochemical and spectroscopic techniques. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 422, 126808.
Yang, X., Lei, S., Zhao, Y., & Cheng, W. (2022d). Use of hyperspectral imagery to detect affected vegetation and heavy metal polluted areas: A coal mining area, China. Geocarto International, 37(10), 2893–2912.
Yin, L., Wang, L., Ge, L., Tian, J., Yin, Z., Liu, M., & Zheng, W. (2023). Study on the thermospheric density distribution pattern during geomagnetic activity. Applied Sciences, 13(9), 5564.
Zakir, H. M. (2017). Assessment of Metallic Pollution along with Geochemical Baseline of Soils at Barapukuria Open Coal Mine Area in Dinajpur, Bangladesh, (October). https://doi.org/10.3233/AJW-170038.
Zeng, W., Wan, X., Wang, L., Lei, M., Chen, T., & Gu, G. (2022). Apportionment and location of heavy metal (loid) s pollution sources for soil and dust using the combination of principal component analysis, Geodetector, and multiple linear regression of distance. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 438, 129468.
Zerizghi, T., Guo, Q., Tian, L., Wei, R., & Zhao, C. (2022). An integrated approach to quantify ecological and human health risks of soil heavy metal contamination around coal mining area. Science of the Total Environment, 814, 152653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152653
Zhang, B., Guo, B., Zou, B., Wei, W., Lei, Y., & Li, T. (2022a). Retrieving soil heavy metals concentrations based on GaoFen-5 hyperspectral satellite image at an opencast coal mine, Inner Mongolia, China. Environmental Pollution, 300, 118981.
Zhang, H., Zhang, F., Song, J., Leong, M., & Kung, H. (2021a). Pollutant source, ecological and human health risks assessment of heavy metals in soils from coal mining areas in Xinjiang, China. Environmental Research, 202, 111702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111702
Zhang, T., Sun, F., Lei, Q., Jiang, Z., Luo, J., Lindsey, S., et al. (2022b). Quantification of soil element changes in long-term agriculture: A case study in Northeast China. CATENA, 208, 105766.
Zhang, Y., Gui, H., Huang, Y., Yu, H., Li, J., Wang, M., et al. (2021b). Characteristics of soil heavy metal contents and its source analysis in affected areas of Luning Coal Mine in Huaibei Coalfield. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 30(2), 1465–1476. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/125515
Zhang, Z., Ma, J., Wang, Z., Zhang, L., He, X., Zhu, G., et al. (2021c). Rubidium isotope fractionation during chemical weathering of granite. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 313, 99–115.
Zhao, G., Ma, Y., Liu, Y., Cheng, J., & Wang, X. (2022a). Source analysis and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils around heavy metal industry in Anxin County. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 1–17.
Zhao, H., Lan, X., Yu, F., Li, Z., Yang, J., & Du, L. (2022b). Comprehensive assessment of heavy metals in soil-crop system based on PMF and evolutionary game theory. Science of the Total Environment, 849, 157549.
Zhou, L., Zhao, X., Meng, Y., Fei, Y., Teng, M., Song, F., & Wu, F. (2022). Identification priority source of soil heavy metals pollution based on source-specific ecological and human health risk analysis in a typical smelting and mining region of South China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 242, 113864.
Zhou, W., Yang, H., Xie, L., Li, H., Huang, L., Zhao, Y., & Yue, T. (2021). Hyperspectral inversion of soil heavy metals in Three-River Source Region based on random forest model. CATENA, 202, 105222.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to the reviewers of the manuscript for their valuable comments and suggestions during the review process.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through small group Research Project under grant number RGP1/120/44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
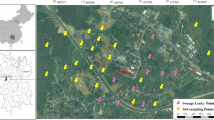
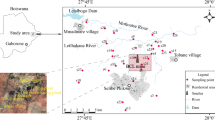
KC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft. RP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Software, Writing—original draft. MI: Draw—spatial map, Writing—review and editing. AMI: Writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicting interests stated by the authors. The items employed in this study are routinely used in our field of study and nation. There is no financial and non-financial interests interest arise among the authors.
Ethical approval
All of the investigations were carried out in compliance with the principles of national and international guidelines. Present study does not involve human participants. The manuscript has not been submitted or published in any form, in part or in whole.
Consent for publication
All of the authors have read and approved the paper for submission of publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chandra, K., Proshad, R., Islam, M. et al. An integrated overview of metals contamination, source-specific risks investigation in coal mining vicinity soils. Environ Geochem Health 45, 7425–7458 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01672-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01672-y