Abstract
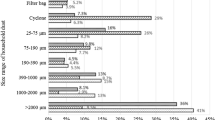
Comprehensive studies on emerging contaminants like volatile methyl siloxanes in settled dust from different micro-environments are still limited. In this study, concentrations and distribution of cyclic volatile methyl siloxanes (CVMSs) including D3, D4, D5, and D6 were examined in indoor dust samples collected from various micro-environments in northern and central Vietnam. Concentrations of total CVMSs in the dust samples ranged from 86.0 to 5890 (median 755) ng/g and decreased in the order: waste processing workshops (median 1560; range 329–5890) > common houses (650; 115–1680) > university classrooms (480; 86.0–1540) > vehicle repair shops (295; 126–1950) ng/g. This observation suggests that informal waste processing activities are sources of CVMSs. Among the studied CVMSs, D5 was the most predominant compound (41 ± 14%), followed by D6 (26 ± 13%), D4 (23 ± 12%), and D3 (11 ± 11%). Moderate positive correlations between D3/D4, D4/D5, and D5/D6 were found. Median daily intake doses of D3, D4, D5, and D6 through dust ingestion were 0.016, 0.051, 0.11, and 0.054 ng/kg/d, respectively, which were comparable to water consumption and markedly lower than the air inhalation pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Anh, H. Q., Nguyen, H. M. N., Do, T. Q., Tran, K. Q., Minh, T. B., & Tran, T. M. (2021). Air pollution caused by phthalates and cyclic siloxanes in Hanoi, Vietnam: Levels, distribution characteristics, and implications for inhalation exposure. Science of the Total Environment, 760, 143380.
Cheng, J., Tang, Z., Ma, Y., Yin, H., Meng, T., & Sun, J. (2021). Methyl siloxanes in soils from a large silicone-manufacturing site, China: Concentrations, distributions and potential human exposure. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43, 3871–3881.
Cincinelli, A., Martellini, T., Scodellini, R., Scopetani, C., Guerranti, C., & Katsoyiannis, A. (2020). Cyclic and Linear Siloxanes in Indoor Environments Occurrence and Human Exposure. In V. Honem & N. Ratola (Eds.), Volatile methylsiloxanes in the environment. The handbook of environmental chemistry 89 (pp. 1–32). Springer.
Gaj, K. (2020). Properties, potential toxicity, and transformations of VMSs in the environment. In V. Honem & N. Ratola (Eds.), Volatile methylsiloxanes in the environment. The handbook of environmental chemistry 89 (pp. 1–32). Springer.
Gallego, E., Teixidor, P., Roca, F. J., & Perales, J. F. (2020). Levels of volatile methyl siloxanes in outdoor air. In V. Honem & N. Ratola (Eds.), Volatile methylsiloxanes in the environment. The handbook of environmental chemistry 89 (pp. 201–226). Springer.
Genualdi, S., Harner, T., Cheng, Y., MacLeod, M., Hansen, K. M., van Egmond, R., Shoeib, M., & Lee, S. C. (2011). Global distribution of linear and cyclic volatile methyl siloxanes in air. Environmental Science and Technology, 45, 3349–3354.
Guo, J., Zhou, Y., Cui, J., Zhang, B., & Zhang, J. (2019). Assessment of volatile methylsiloxanes in environmental matrices and human plasma. Science of the Total Environment, 668, 1175–1182.
Hoang, A. Q., Le, T. M., Nguyen, H. M. N., Le, H. Q., Vu, N. D., Chu, N. C., Dang, G. H. M., Minh, T. B., Takahashi, S., & Tran, T. M. (2021). Phthalic acid esters (PAEs) in workplace and house dust from Vietnam: Concentrations, profiles, emission sources, and exposure risk. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16851-6
Horii, Y., & Kannan, K. (2020). Main uses and environmental emissions of volatile methylsiloxanes. In V. Honem & N. Ratola (Eds.), Volatile methylsiloxanes in the environment. The handbook of environmental chemistry 89 (pp. 33–70). Springer.
Kierkegaard, A., & McLachlan, M. S. (2013). Determination of linear and cyclic volatile methylsiloxanes in air at a regional background site in Sweden. Atmospheric Environment, 80, 322–329.
Liu, N., Xu, L., & Cai, Y. (2018). Methyl siloxanes in barbershops and residence indoor dust and the implication for human exposures. Science of the Total Environment, 618, 1324–1330.
Lu, Y., Yuan, T., Yun, S. H., Wang, W., Wu, Q., & Kannan, K. (2010). Occurrence of cyclic and linear siloxanes in indoor dust from China, and implications for human exposures. Environmental Science and Technology, 44, 6081–6087.
Lucattini, L., Poma, G., Covaci, A., de Boer, J., Lamoree, M. H., & Leonards, P. E. G. (2018). A review of semi-volatile organic compounds (SVOCs) in the indoor environment: Occurrence in consumer products, indoor air and dust. Chemosphere, 201, 466–482.
Nguyen, H. M. N., Khieu, H. T., Ta, N. A., Le, H. Q., Nguyen, T. Q., Do, T. Q., Hoang, A. Q., Kannan, K., & Tran, T. M. (2021). Distribution of cyclic volatile methylsiloxanes in drinking water, tap water, surface water, and wastewater in Hanoi, Vietnam. Environmental Pollution, 285, 117260.
Tran, T. M., Abualnaja, K. O., Asimakopoulos, A. G., Covaci, A., Gevao, B., Johnson-Respetro, B., Kumosani, T. A., Malarvannan, G., Minh, T. B., Moon, H. B., Nakata, H., Sinha, R. K., & Kannan, K. (2015). A survey of cyclic and linear siloxanes in indoor dust and their implications for human exposures in twelve countries. Environment International, 78, 39–44.
Tran, T. M., Hoang, A. Q., Le, S. T., Minh, T. B., & Kannan, K. (2019). A review of contamination status, emission sources, and human exposure to volatile methyl siloxanes (VMSs) in indoor environments. Science of the Total Environment, 691, 584–594.
Tran, T. M., Minh, T. B., Kumosani, T. A., & Kannan, K. (2016). Occurrence of phthalate diesters (phthalates), p-hydroxybenzoic acid esters (parabens), bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (BADGE) and their derivatives in indoor dust from Vietnam: Implications for exposure. Chemosphere, 144, 1553–1559.
Tran, T. M., Tran-Lam, T. T., Mai, H. H. T., Bach, L. H. T., Nguyen, H. M. N., Trinh, H. T., Dang, L. T., Minh, T. B., Quan, T. C., & Hoang, A. Q. (2021). Parabens in personal care products and indoor dust from Hanoi, Vietnam: Temporal trends, emission sources, and non-dietary exposure through dust ingestion. Science of the Total Environment, 761, 143274.
Tran, T. M., Trinh, H. T., Anh, H. Q., Le, T. V., Le, S. N., & Minh, T. B. (2020). Characterization of triclosan and triclocarban in indoor dust from home micro-environments in Vietnam and relevance of non-dietary exposure. Science of the Total Environment, 732, 139326.
Tran, T. M., Tu, M. B., & Vu, N. D. (2018). Cyclic siloxanes in indoor environments from hair salons in Hanoi, Vietnam: Emission sources, spatial distribution, and implications for human exposure. Chemosphere, 212, 330–336.
US EPA. (2017). Update for chapter 5 of the exposure factors handbook. Soil and dust ingestion. https://www.epa.gov/expobox/exposure-factors-handbook-chapter-5. Accessed 10 June 2021.
Xu, L., Shi, Y., Liu, N., & Cai, Y. (2015). Methyl siloxanes in environmental matrices and human/fat from both general industries and residential areas in China. Science of the Total Environment, 505, 454–463.
Xu, L., Shi, Y., Wang, T., Dong, Z., Su, W., & Cai, Y. (2012). Methyl siloxanes in environmental matrices around a siloxane production facility, and their distribution and elimination in plasma of exposed population. Environment Science and Technology, 46, 11718–11726.
Xu, S., & Kropscott, B. (2013). Octanol/air partition coefficients of volatile methylsiloxanes and their temperature dependence. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 58, 136–142.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AQH (Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing–Original draft preparation); HTT (Formal analysis); HMNN (Formal analysis); TQN (Formal analysis); TXN (Formal analysis); TVD (Formal analysis); TBM (Conceptualization, Resources); TMT (Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing–Review and editing, Project investigator).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Before entering any home or workshop, we have received permission from the owner.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoang, A.Q., Trinh, H.T., Nguyen, H.M.N. et al. Assessment of cyclic volatile methyl siloxanes (CVMSs) in indoor dust from different micro-environments in northern and central Vietnam. Environ Geochem Health 45, 1711–1722 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01298-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01298-6