Abstract
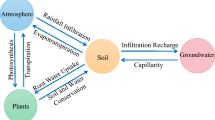
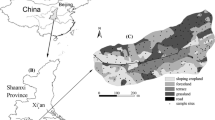
Coal mine in arid and semi-arid area is one of the most severely degraded ecosystems on the earth. The continuous decrease in groundwater level caused by coal mining will inevitably affect biogeochemical environment of the vadose zone, and then lead to the replacement of surface vegetation. Yimin open-pit coal mine was taken as an example to reveal the relationship between the groundwater depth and soil water content (SWC), soil salt content, soil electrical conductivity (SEC), soil organic matter (SOM), soil available potassium (SAK), soil available nitrogen (SAN), vegetation coverage, aboveground biomass and species richness. The results show that, the change of groundwater depth can affect soil properties and then change the characteristics of surface vegetation, and the change of surface vegetation can also react on soil properties. Vegetation coverage and aboveground biomass are negatively correlated with groundwater depth, and positively correlated with SWC, SEC, SOM and SAK. The shallow groundwater table is conducive to the accumulation of SOM, so that the surface biomass and vegetation coverage are high. The higher the surface biomass, the more the SAN is absorbed. Under natural conditions, the relative strength of biological nitrogen fixation and plant absorption determine the content of SAN. In the research area, when the depth of groundwater is less than 0.4 m will cause soil salinization, then lead to low species richness; Species richness is exponentially correlated with groundwater depth and decreases with the increase in groundwater depth.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data in this study are from field sampling data and groundwater survey data, which are all available data.
References
Badiane, A., Ndour, N. Y. B., Guèye, F., Faye, S., Ndoye, I., & Mass, D. (2012). Effects of different inputs of organic matter on the response of plant production to a soil water stress in Sahelian region. Natural Science, 4(12), 969–975.
Bai, S. H., Dempsey, R., Reverchon, F., Blumfield, T. J., Ryan, S., & Cernusak, L. A. (2017). Effects of forest thinning on soil-plant carbon and nitrogen dynamics. Plant and Soil, 411(1/2), 437–449.
Barre, P., Durand, H., Chenu, C., Meunier, P., Montagne, D., Castel, G., Billiou, D., Soucemarianadin, L., & Cecillon, L. (2017). Geological control of soil organic carbon and nitrogen stocks at the landscape scale. Geoderma, 285, 50–56.
Brunet, J., Falkengren-Grerup, U., & Tyler, G. (1996). Herb layer vegetation of south Swedish beech and oak forests: Effects of management and soil acidity during one decade. Forest Ecology and Management, 88(3), 259–272.
Cao, G. D., Chen, J. H., Xia, J., Zhu, H. W., Jiang, Y. C., Zhang, X., & Wang, S. M. (2013). Analysis of soil physical properties under different vegetation types in the alluvial fan area of Manas river watershed. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(1), 195–204.
Cappellazzi, S., & Morgan, C. (2020). Assessing soil health: soil nitrogen cycling. Crops & Soils, 54(1), 26–30.
Celentano, D., Rousseau, G. X., Engel, V. L., Zelarayán, M., Oliveira, E. C., Araujo, A. C. M., & de Moura, E. G. (2017). Degradation of riparian forest affects soil properties and ecosystem services provision in eastern amazon of Brazil. Land Degradation and Development, 28, 482–493.
Chen, Y., Li, W., Xu, C., Ye, Z., & Chen, Y. (2015). Desert riparian vegetation and groundwater in the lower reaches of the Tarim River basin. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(2), 547–558.
Cui, G., Lu, Y., Zheng, C., Liu, Z., & Sai, J. (2019). Relationship between soil salinization and groundwater hydration in Yaoba oasis. Northwest China Water, 11(1), 175.
Damar, H., Ziadi, N., Lafond, J., & Parent, L. E. (2021). Long-term impact of fertilizer sources on cyclic P budget and soil P status under ley farming system. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 119(2), 165–180.
Fan, Y. X., Xie, L., Chen, S. D., et al. (2015). Effects of temperature and humidity on soil microbial biomass nitrogen at different altitudes in the Wuyi Mountains of Southeast China. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 10(2), 9–15.
Fang, A., Bao, M., Chen, W., & Dong, J. (2021). Assessment of surface ecological quality of grassland mining area and identification of its impact range. Natural Resources Research, 30(5), 3819–3837.
Janssens, F., Peeters, A., Tallowin, J. R. B., Bakker, J. P., Bekker, R. M., Fillat, F., & Oomes, M. J. M. (1998). Relationship between soil chemical factors and grassland diversity. Plant and Soil, 202(1), 69–78.
Jiang, M. (1982). Potassium fixation and release from potassium minerals in soil. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 03, 44–49.
Jin, X. M., Schaepman, M. E., Clevers, J. G., Su, Z. B., & Hu, G. (2011). Groundwater depth and vegetation in the Ejina area, China. Arid Land Research and Management, 25(2), 194–199.
Jingting, H., Guangcai, H., & Zhengping, T. (2008). Vegetation ecological areas of the Ordos Plateau, China and their hydrogeological significance. Geological Bulletin of China, 08(2008), 1330–1334.
Kath, J., Powell, S., Reardon-Smith, K., El Sawah, S., Jakeman, A. J., Croke, B. F., & Dyer, F. J. (2015). Groundwater salinization intensifies drought impacts in forests and reduces refuge capacity. Journal of Applied Ecology, 52(5), 1116–1125.
Kopeć, D., Michalska-Hejduk, D., & Krogulec, E. (2013). The relationship between vegetation and groundwater levels as an indicator of spontaneous wetland restoration. Ecological Engineering, 57, 242–251.
Li, H. X., Cui, Y. L., Ma, X. B., et al. (2019). Moisture migration characteristics in vadose zones in Weining Plain. Arid Land Geography, (04), 845–853.
Liang, C. H., Wei, L. P., & Luo, L. (2002). Advance in research on mechanisms of potassium releasing and fixing in soils. Advances in Earth Science, 05, 679–684.
Ma, F., Ma, H. L., Qiu, H., & Yang, H. Y. (2015). Effects of water levels and the additions of different nitrogen forms on soil net nitrogen transformation rate and N2O emission in subtropical. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26(2), 379–387.
Masoud, N., Saghar, F.-S., & Sepaskhah, A. R. (2020). Application of SALTMED and HYDRUS-1D models for simulations of soil water content and soil salinity in controlled groundwater depth. Journal of Arid Land, 12(3), 447–461.
Meijiao, L. U., Jie, D., Gao, G., et al. (2014). Spatial variation characteristics of chloride, nitrate and sulfate in soil system Northeast China. Pratacultural Science, 31(11), 2042–2049.
Pandey, C. B., Singh, G. B., Singh, S. K., & Singh, R. K. (2010). Soil nitrogen and microbial biomass carbon dynamics in native forests and derived agricultural land uses in a humid tropical climate of India. Plant and Soil, 333(1), 453–467.
Peng, L., Huang, J., & Yuan, L. (2020). Biological mobilization of potassium from soil by thirteen Suillus species and ectomycorrhizal Pinus massoniana Lamb seedlings. European Journal of Soil Science, 71(4), 740–751.
Shao, S., He, H. B., Zhang, W., Zhao, Y., & Zhang, X. D. (2017). Soil organic matter formation and origin: A review. Journal of Jilin Normal University (natural Science Edition), 38(1), 126–130.
Shaogang, D., Zhibin, J., Baiwei, L., Zhiyi, W., & Dingding, W. (2013). Study on eco-hydrogeological evolution in underground mining coal of arid areas: Taking the coal mine in Ordos as the example. Engineering Investigation and Surveying, 41(02), 45–48.
Shen, Z., Zhang, Q., Chen, D., & Singh, V. P. (2021). Varying effects of mining development on ecological conditions and groundwater storage in dry region in inner Mongolia of China. Journal of Hydrology, 597, 125759.
Sheng, X. B., & Zhao, Y. P. (1997). Effects of grassland biomass on soil organic matter. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 06, 244–245.
Shouse, P. J., Ayars, J. E., & Šimůnek, J. (2011). Simulating root water uptake from a shallow saline groundwater resource. Agricultural Water Management, 98(5), 784–790.
Shu, R. X., Doyle, A., Holden, P. A., & Schimel, J. P. (2008). Drying and rewetting effects on C and N mineralization and microbial activity in surface and subsurface California grassland soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40(9), 2281–2289.
Silva, R. C., Baird, R., Degryse, F., & McLaughlin, M. J. (2018). Slow and fast-release boron sources in potash fertilizers: Spatial variability, nutrient dissolution and plant uptake. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 82(6), 1437–1448.
Sommer, B., & Froend, R. (2014). Phreatophytic vegetation responses to groundwater depth in a drying mediterranean-type landscape. Journal of Vegetation Science, 25(4), 1045–1055.
Turner, S., Meyer-Stüve, S., Schippers, A., Guggenberger, G., Schaarschmidt, F., Wild, B., Richter, A., Dohrmann, R., & Mikutta, R. (2017). Microbial utilization of mineral-associated nitrogen in soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 104, 185–196.
Wang, H. Y., Gai, X. P., Zhai, L. M., & Liu, H. (2016). Effect of biochar on soil nitrogen cycling: A review. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(19), 5998–6011.
Wang, Q., & Zhao, M. (2017). Effects of coal resources’ exploitation on the water resource and vegetation in arid and semi-arid region. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 28(3), 77–81.
Wang, Y., Chen, M., Yan, L., Hu, Y., Deng, W., & Zhou, F. (2019). Critical depth of groundwater recharge for vegetation in semi-arid areas. IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science, 237(3), 032091.
Xia, M., Dong, S., Chen, Y., & Liu, H. (2021). Study on evolution of groundwater-lake system in typical prairie open-pit coal mine area. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00890-6
Yang, Z., Li, W., Li, X., & He, J. (2019). Quantitative analysis of the relationship between vegetation and groundwater buried depth: A case study of a coal mine district in Western China. Ecological Indicators, 102, 770–782.
Yuanzhi, X. U., Guizhang, Z. H., & Nisha, M. U. (2019). Review on factors affecting the process of water movement in vadose zone. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, 40(02), 37–41.
Zelm, R. V., Schipper, A. M., Rombouts, M., Snepvangers, J., & Huijbregts, M. A. (2011). Implementing groundwater extraction in life cycle impact assessment: Characterization factors based on plant species richness for the Netherlands. Environmental Science and Technology, 45(2), 629–635.
Zhang, B. W., Tan, X., Wang, S., Chen, M., Chen, S., Ren, T., Xia, J., Bai, Y., Huang, J., & Han, X. (2017). Asymmetric sensitivity of ecosystem carbon and water processes in response to precipitation change in a semi-arid steppe. Functional Ecology, 31(6), 1301–1311.
Zhang, D., Fan, M., Liu, H., Wang, R., Zhao, J., Yang, Y., Cui, R., & Chen, A. (2019). Effects of shallow groundwater table fluctuations on nitrogen in the groundwater and soil profile in the nearshore vegetable fields of Erhai Lake, southwest China. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 20(1), 42–51.
Zhang, H., & Wang, X. S. (2020). The impact of groundwater depth on the spatial variance of vegetation index in the Ordos Plateau, China: A Semivariogram analysis. Journal of Hydrology, 588, 125096.
Zhang, W., Xiao, H., Yang, B., Dong, K., Ruan, H., Zheng, A., Shen, C., & Cao, G. (2016). Effects of soil fauna on seasonal variations of soil N mineralization under different land use type. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (natural Sciences Edition), 40(6), 20–26.
Zhang, X., Guan, T., Zhou, J., Cai, W., Gao, N., Du, H., Jiang, L., Lai, L., & Zheng, Y. (2018). Groundwater depth and soil properties are associated with variation in vegetation of a desert riparian ecosystem in an arid area of China. Forests, 9(1), 34.
Zhao, N., & Li, X. G. (2017). Effects of aspect-vegetation complex on soil nitrogen mineralization and microbial activity on the Tibetan Plateau. CATENA, 155, 1–9.
Zuo, Q., & Wang, S. (2021). Regulation mechanism of biotic and abiotic factors on the nitrogen mineralization of forest soil. Journal of Zhejiang A and F University, 38(03), 613–623.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (41562020). We are also thanks to our all laboratory colleagues and research staff members for their constructive advice and help.
Funding
The study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (41562020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SD contributed to conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing original draft, writing review and editing and visualization. BL contributed to Conceptualization, validation, resources, supervision, project administration. MM contributed to english editing, picture beautification and investigation. MX contributed to investigation, software and formal analysis. CW contributed to investigation, methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Animal and human rights
No animals were involved in the study.
Consent to participate
No human participants were involved in this study.
Consent for publication
No human participants were involved in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, S., Liu, B., Ma, M. et al. Effects of groundwater level decline to soil and vegetation in arid grassland: a case study of Hulunbuir open pit coal mine. Environ Geochem Health 45, 1793–1806 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01292-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01292-y