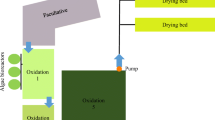
Abstract
Water pollution is one of the major challenges and is of serious concern in the world. Toxicities generated by industrial activities severely deteriorate aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems during their uncontrolled discharge and accentuate water scarcity problems. An adequate treatment of released effluents seems to be mandatory. This study investigated the effect of synthetic textile wastewater (STWW) before and after an innovative algal–bacterial treatment occurred under anoxic–aerobic conditions on growth and mineral contents of radish plants. The health risk assessment was performed after the consumption of irrigated plants by rats. Results revealed a significant reduction in heavy metals content in plants irrigated with treated STWW, and rats fed with these plants showed normal health status. Rats fed with plants irrigated with raw STWW showed a disturbance of their homeostasis. The innovative treatment using algal–bacteria under anoxic–aerobic conditions succeeds to reduce the toxicity of raw STWW and provide an alternative water resource able to tackle water shortage.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Abdel-Shafy, H. I., & Mansour, M. S. M. (2016). A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egyptian Journal of Petroleum, 25, 107–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2015.03.011
Aebi, H. (1984). Catalase in Vitro. Methods in Enzymology, 105, 121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Akhkha, A., Al-Radaddi, E. S., & Al-Shoaibi, A. K. (2019). The impact of treated and untreated municipal sewage water on growth and physiology of the desert plant Calotropis procera. Journal of Taibah University for Science. https://doi.org/10.1080/16583655.2019.1605650
Ali, H., Khan, E., & Ilahi, I. (2019). Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. Journal of Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6730305
Amin, K. A., Abdel Hameid, H., & Abd Elsttar, A. H. (2010). Effect of food azo dyes tartrazine and carmoisine on biochemical parameters related to renal, hepatic function and oxidative stress biomarkers in young male rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 48, 2994–2999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.07.039
Bansal, A. K., Bansal, M., Soni, G., & Bhatnagar, D. (2005). Modulation of N-nitrosodiethylamine induced oxidative stress by vitamin E in rat erythrocytes. Human and Experimental Toxicology, 24, 297–302. https://doi.org/10.1191/0960327105ht533oa
Belhaj, D., Jerbi, B., Medhioub, M., Zhou, J., Kallel, M., & Ayadi, H. (2016). Impact of treated urban wastewater for reuse in agriculture on crop response and soil ecotoxicity. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 15877–15887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5672-3
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Camera, E., Mastrofrancesco, A., Fabbri, C., Daubrawa, F., Picardo, M., Sies, H., & Stahl, W. (2009). Astaxanthin, canthaxanthin and β-carotene differently affect UVA-induced oxidative damage and expression of oxidative stress-responsive enzymes. Experimental Dermatology, 18, 222–231. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0625.2008.00790.x
Cheng, C. W., Chen, L. Y., Chou, C. W., & Liang, J. Y. (2015). Investigations of riboflavin photolysis via coloured light in the nitro blue tetrazolium assay for superoxide dismutase activity. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 148, 262–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.04.028
Comittee for the update of the Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals (2011) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. 8, 1–220.
Dhaouefi, Z., Toledo-Cervantes, A., Ghedira, K., Chekir-Ghedira, L., & Muñoz, R. (2019). Decolorization and phytotoxicity reduction in an innovative anaerobic/aerobic photobioreactor treating textile wastewater. Chemosphere, 234, 356–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.106
Dringen, R., Gutterer, J. M., & Hirrlinger, J. (2000). Glutathione metabolism in brain metabolic interaction between astrocytes and neurons in the defense against reactive oxygen species. European Journal of Biochemistry, 267, 4912–4916. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01597.x
Eaton, A.D., Clesceri, L.S., Greenberg, A.E., 2005. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, twenty-first ed. American Public Health Association/ AmericanWater Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington, DC.European Directive.
Eke, D., & Çelik, A. (2016). Curcumin prevents perfluorooctane sulfonate-induced genotoxicity and oxidative DNA damage in rat peripheral blood. Drug and Chemical Toxicology, 39, 97–103. https://doi.org/10.3109/01480545.2015.104160
Fenga, C., Gangemi, S., Teodoro, M., Rapisarda, V., Golokhvast, K., Docea, A. O., Tsatsakis, A. M., & Costa, C. (2017). 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine as a biomarker of oxidative DNA damage in workers exposed to low-dose benzene. Toxicology Reports, 4, 291–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2017.05.008
Ferronato, N., & Torretta, V. (2019). Waste mismanagement in developing countries: A review of global issues. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16, 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16061060
Flohe, L., & Gunzler, W. A. (1984). Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods in Enzymology, 105, 114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05015-1
Hampel, M., Blasco, J., & Segner, H. (2015). Molecular and cellular effects of contamination in aquatic ecosystems. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 17261–17266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5565-5
Hao, M. L., Pan, N., Zhang, Q. H., & Wang, X. H. (2015). Therapeutic efficacy of chlorogenic acid on cadmium-induced oxidative neuropathy in a murine model. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 9, 1887–1894. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2367
INNORPI, Institut National de la Normalisation et de la Propriété Industrielle. (1989). Protection de l’environnement, utilisation des eaux usées traitées à des fins agricoles. Spécifications Physico-Chimiques Et Biologiques, NT, 106(03), 2p.
Jackson, M. L. (1973). Soil chemical analysis. Prentice-Hall Inc.
Jagota, S. K., & Dani, H. M. (1982). A new colorimetric technique for the estimation of vitamin C using Folin phenol reagent. Analytical Biochemistry, 127, 178–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(82)90162-2
Jan, A., Azam, M., Siddiqui, K., Ali, A., Choi, I., & Haq, Q. (2015). Heavy metals and human health: Mechanistic insight into toxicity and counter defense system of antioxidants. Intenational Journal of Molecular Science, 16, 29592–29630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226183
Journal Officiel de la République Tunisienne, 2018. Arrêté du ministre des affaires locales et de l’environnement et du ministre de l’industrie et des petites et moyennes entreprises du 26 mars 2018, fixant les valeurs limites des rejets d’effluents dans le milieu récepteur, NT106.02 : 822 - 837.
Kamble, S., Ahmed, M. Z., Ramabhimaiaha, S., & Patil, P. (2013). Anti-inflammatory activity of Raphanus Sativus in acute and chronic experimental models in albino rats. Biomedical & Pharmacology Journal, 6, 315–320. https://doi.org/10.1300/BPJ/420
Lellis, B., Fávaro-Polonio, C. Z., Pamphile, J. A., & Polonio, J. C. (2019). Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. Biotechnology Research and Innovation, 3, 275–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biori.2019.09.001
Lemiere, S., Cossu-Leguille, C., Bispo, A., Jourdain, M. J., Lanhers, M. C., Burnel, D., & Vasseur, P. (2004). Genotoxicity related to transfer of oil spill pollutants from mussels to mammals via food. Environmental Toxicology, 19, 387–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2004.10.015
Lushchak, V. I. (2012). Glutathione homeostasis and functions: Potential targets for medical interventions. Journal of Amino Acids. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/736837
Maddineni, S., Nichenametla, S., Sinha, R., Wilson, R. P., & Richie, J. P. (2013). Methionine restriction affects oxidative stress and glutathione-related redox pathways in the rat. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 238(4), 392–399. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370213477988
Man, Y. B., Chow, K. L., Zhang, F., Lei, K. M., Leung, A. O. W., Mo, W. Y., & Wong, M. H. (2021). Protecting water birds of wetlands: Using toxicological tests and ecological risk assessment, based on metal/loid (s) of water, sediment and biota samples. Science of the Total Environment, 78, 146317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146
Moron, M.S., Depierre, J.W., Mannervik, B., 1979. Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochimica et Biophysica acta (BBA)-General Subjects. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4165(79)90289-7.
Onakpa, M. M., Njan, A. A., & Kalu, O. C. (2018). A review of heavy metal contamination of food crops in Nigeria. Annals of Global Health, 84, 488–494. https://doi.org/10.29024/aogh.2314
Pan, H., Feng, J., He, G.-X., Cerniglia, C. E., & Chen, H. (2012). Evaluation of impact of exposure of Sudan azo dyes and their metabolites on human intestinal bacteria. Anaerobe, 18, 445–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2012.05.002
Poreba, R., Gac, P., Poreba, M., & Andrzejak, R. (2011). Environmental and occupational exposure to lead as a potential risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Environmental Toxicology Pharmacology., 31, 267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2010.12.002
Rodrigues, C. S. D., Madeira, L. M., & Boaventura, R. A. R. (2014). Synthetic textile dyeing wastewater treatment by integration of advanced oxidation and biological processes–Performance analysis with costs reduction. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2, 1027–1039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2014.03.019
Singh, N. P., McCoy, M. T., Tice, R. R., & Schneider, E. L. (1988). A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Experimental Cell Research, 175, 184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4827(88)90265-0
Tsai, H. J., Wu, P. Y., Huang, J. C., & Chen, S. C. (2021). Environmental pollution and chronic kidney disease. International Journal of Medical Sciences, 18, 1121–1129.
Tsuda, S., Matsusaka, N., Madarame, H., Miyamae, Y., Ishida, K., Satoh, M., Sekihashi, K., Sasaki, Y.F., 2000. The alkaline single cell electrophoresis assay with eight mouse organs: results with 22 mono-functional alkylating agents (including 9 dialkyl N-nitrosoamines) and 10 DNA crosslinkers. Mutation Research Genetic. 467, 83–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1383-5718(00)00014-0.
Tutun H., Ahu Kahraman H., Aluc, Y., Avci, T., Ekici, H., (2019) Investigation of some metals in honey samples from West Mediterranean region of Turkey. Veterinary Research Forum. 10, 181 – 186. https://doi.org/10.30466/vrf.2019.96726.2312.
Uddin, A. B. M. H., Khalid, R. S., Alaama, M., Abdualkader, A. M., Kasmuri, A., & Abbas, S. A. (2016). Comparative study of three digestion methods for elemental analysis in traditional medicine products using atomic absorption spectrometry. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology, 7, 6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-016-0085-6
Vairetti, M., Di Pasqua, L. G., Cagna, M., Richelmi, P., Ferrigno, A., & Berardo, C. (2021). Changes in glutathione content in liver diseases: An update. Antioxidants, 10, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030364
Wagner, M., Bolm-Audorff, U., Hegewald, J., Fishta, A., Schlattmann, P., Schmitt, J., & Seidler, A. (2015). Occupational polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure and risk of larynx cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 72, 226–233. https://doi.org/10.1136/oemed-2014-102317
Walter, G. L. (2013). Interpretation of clinical pathology results in non-clinical toxicology testing. Haschek and Rousseaux’s Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-415759-0.00029-7
Zasoski, R. J., & Burau, R. G. (1977). A rapid nitric-perchloric acid digestion method for multi-element tissue analysis. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 8, 425–436. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103627709366735
Zheng, S., Yang, Y., Wen, C., Liu, W., Cao, L., Feng, X., & Yang, F. (2021). Effects of environmental contaminants in water resources on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Environment International, 154, 106555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.10655
Acknowledgements
The Centre National de Recherche en Sciences des Matériaux Borj Cedria, Tunisia is specially acknowledged for the ICP-AES analysis.
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZD performed the experiments, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript; AL, RK made contribution to in vivo studies; IBT and DE helped in biochemical analysis, and LCG conducted and supervised the experimentation and reviewed the manuscript for its final approval. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All experiments obtained the explicit approval of the Tunisian Ethics Animal Committee.
Consent to participate
All authors declare that they have participated in the study and in the development of the manuscript.
Consent for publication
All authors declare that they have read the final version and give their consent for the article to be published in EGAH.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhaouefi, Z., Lahmar, A., Khlifi, R. et al. Evaluation of eventual toxicities of treated textile wastewater using anoxic–aerobic algal–bacterial photobioreactor. Environ Geochem Health 44, 4285–4297 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01187-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01187-4