Abstract
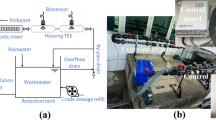
A bioelectrochemical sensor (BES) was constructed for toxicity assessment of copper in contaminated domestic sewage. Electrochemically active bacteria (EAB), whose growth was supported by the bioenergy generated from an in situ metallurgical process, functioned as the sensing elements. The external resistance of metallurgical BES was optimized based on linear sweep voltammetry analysis. The stabilized BES was utilized to monitor the copper toxicity in real wastewater. During the less than 1-h sensing period, copper concentration ranging from 1 to 5 mg L−1 could be detected. A power output of around 100 Wh (kg Cu)−1 and metallic copper resource were obtained simultaneously. This study demonstrated that the highly active EAB species enriched in metallurgical BES could be a promising candidate for rapid and reliable evaluation of copper toxicity in real domestic wastewater.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abourached, C., Catal, T., & Liu, H. (2014). Efficacy of single-chamber microbial fuel cells for removal of cadmium and zinc with simultaneous electricity production. Water Research, 51, 228–233.
Bourgeois, W., Burgess, J. E., & Stuetz, R. M. (2001). On-line monitoring of wastewater quality: A review. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 76(4), 337–348.
Cheng, S. A., Wang, B. S., & Wang, Y. H. (2013). Increasing efficiencies of microbial fuel cells for collaborative treatment of copper and organic wastewater by designing reactor and selecting operating parameters. Bioresource Technology, 147, 332–337.
ElMekawy, A., Hegab, H. M., Pant, D., & Saint, C. P. (2017). Bio-analytical applications of microbial fuel cell based-biosensors for onsite water quality monitoring. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 124(1), 302–313.
Feng, C. J., Hu, A. Y., Chen, S. H., & Yu, C. P. (2013). A decentralized wastewater treatment system using microbial fuel cell techniques and its response to a copper shock load. Bioresource Technology, 143, 76–82.
Gajaraj, S., & Hu, Z. Q. (2014). Integration of microbial fuel cell techniques into activated sludge wastewater treatment processes to improve nitrogen removal and reduce sludge production. Chemosphere, 117, 151–157.
Ha, P. T., Moon, H., Kim, B. H., Ng, H. Y., & Chang, I. S. (2010). Determination of charge transfer resistance and capacitance of microbial fuel cell through a transient response analysis of cell voltage. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 25(7), 1629–1634.
He, Z. (2013). Microbial fuel cells: Now let us talk about energy. Environmental Science and Technology, 47(1), 332–333.
Jia, H., Yang, G., Ngo, H. H., Guo, W. S., Zhang, H. W., Gao, F., et al. (2017). Enhancing simultaneous response and amplification of biosensor in microbial fuel cell-based upflow anaerobic sludge bed reactor supplemented with zero-valent iron. Chemical Engineering Journal, 327, 1117–1127.
Jiang, Y., Liang, P., Liu, P. P., Yan, X. X., Bian, Y. H., & Huang, X. (2017). A cathode-shared microbial fuel cell sensor array for water alert system. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42(7), 4342–4348.
Jiang, Y., Liang, P., Zhang, C. Y., Bian, Y. H., Yang, X. F., Huang, X., et al. (2015). Enhancing the response of microbial fuel cell based toxicity sensors to Cu(II) with the applying of flow-through electrodes and controlled anode potentials. Bioresource Technology, 190, 367–372.
Kim, M., Hyun, M. S., Gadd, G. M., Kim, G. T., Lee, S. J., & Kim, H. J. (2009). Membrane-electrode assembly enhances performance of a microbial fuel cell type biological oxygen demand sensor. Environmental Technology, 30(4), 329–336.
Kumlanghan, A., Liu, J., Thavarungkul, P., Kanatharana, P., & Mattiasson, B. (2007). Microbial fuel cell-based biosensor for fast analysis of biodegradable organic matter. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 22(12), 2939–2944.
Li, T., Wang, X., Zhou, L., An, J. K., Li, J. H., Li, N., et al. (2016). Bioelectrochemical sensor using living biofilm to in situ evaluate flocculant toxicity. ACS Sensors, 1(11), 1374–1379.
Liu, R., Gao, C. Y., Zhao, Y. G., Wang, A. J., Lu, S. S., Wang, M., et al. (2012). Biological treatment of steroidal drug industrial effluent generation in the microbial fuel cells. Bioresource Technology, 123, 86–91.
Logan, B. E. (2007). Microbial fuel cells. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley.
Logan, B. E. (2009). Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 7(5), 375–381.
Logan, B. E., & Elimelech, M. (2012). Membrane-based processes for sustainable power generation using water. Nature, 488(7411), 313–319.
Madoni, P., & Romeo, M. G. (2006). Acute toxicity of heavy metals towards freshwater ciliated protists. Environmental Pollution, 141(1), 1–7.
McCarty, P. L., Bae, J., & Kim, J. (2011). Domestic wastewater treatment as a net energy producer—Can this be achieved? Environmental Science and Technology, 45(17), 7100–7106.
MEP. (2002). Discharge standard of pollutants for municipal wastewater treatment plant (GB 18918-2002)—Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP) of China.
Modin, O., Wang, X., Wu, X., Rauch, S., & Fedje, K. K. (2012). Bioelectrochemical recovery of Cu, Pb, Cd, and Zn from dilute solutions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 235–236, 291–297.
Modin, O., & Wilén, B. M. (2012). A novel bioelectrochemical BOD sensor operating with voltage input. Water Research, 46(18), 6113–6120.
NEA. (2015). Qualifying criteria for highly efficient water pollution. Singapore: National Environment Agency (NEA).
Perfus-Barbeoch, L., Leonhardt, N., Vavasseur, A., & Forestier, C. (2002). Heavy metal toxicity: Cadmium permeates through calcium channels and disturbs the plant water status. Plant Journal, 32(4), 539–548.
Seidl, M., Huang, V., & Mouchel, J. M. (1998). Toxicity of combined sewer overflows on river phytoplankton: The role of heavy metals. Environmental Pollution, 101(1), 107–116.
Shen, Y. J., Wang, M., Chang, I. S., & Ng, H. Y. (2013). Effect of shear rate on the response of microbial fuel cell toxicity sensor to Cu(II). Bioresource Technology, 136, 707–710.
Stein, N. E., Hamelers, H. M. V., van Straten, G., & Keesman, K. J. (2012). On-line detection of toxic components using a microbial fuel cell-based biosensor. Journal of Process Control, 22(9), 1755–1761.
Stein, N. E., Keesman, K. J., Hamelers, H. V. M., & van Straten, G. (2011). Kinetic models for detection of toxicity in a microbial fuel cell based biosensor. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 26(7), 3115–3120.
Tao, H. C., Zhang, L. J., Gao, Z. Y., & Wu, W. M. (2011). Copper reduction in a pilot-scale membrane-free bioelectrochemical reactor. Bioresource Technology, 102(22), 10334–10339.
Thomas, Y. R. J., Picot, M., Carer, A., Berder, O., Sentieys, O., & Barriere, F. (2013). A single sediment-microbial fuel cell powering a wireless telecommunication system. Journal of Power Sources, 241, 703–708.
Tront, J. M., Fortner, J. D., Plotze, M., Hughes, J. B., & Puzrin, A. M. (2008). Microbial fuel cell biosensor for in situ assessment of microbial activity. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 24(4), 586–590.
Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Xu, R., Sun, Z., & Jie, Z. (2010). An innovative reactor-type biosensor for BOD rapid measurement. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 25(7), 1705–1709.
Zhang, L. J., Gao, Y., Lai, L. K., & Li, S. F. Y. (2015). Whole-cell-based identification of electrochemically active bacteria in microbial fuel cells by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 29(23), 2211–2218.
Zhang, L. J., Tao, H. C., Wei, X. Y., Lei, T., Li, J. B., Wang, A. J., et al. (2012). Bioelectrochemical recovery of ammonia–copper(II) complexes from wastewater using a dual chamber microbial fuel cell. Chemosphere, 89(10), 1177–1182.
Zhou, T. Y., Han, H. W., Liu, P., Xiong, J., Tian, F. K., & Li, X. K. (2017). Microbial fuels cell-based biosensor for toxicity detection: A review. Sensors, 17(10), 2230. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102230.
Zhang, Y. F., & Angelidaki, I. (2011). Submersible microbial fuel cell sensor for monitoring microbial activity and BOD in groundwater: Focusing on impact of anodic biofilm on sensor applicability. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 108(10), 2339–2347.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National University of Singapore, National Research Foundation and Economic Development Board (SPORE, COY-15-EWI-RCFSA/N197-1) and Ministry of Education (R-143-000-519-112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Li, S.F.Y. & Tao, H. Toxicity assessment of copper by electrochemically active bacteria in wastewater. Environ Geochem Health 41, 81–91 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0105-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0105-0