Abstract
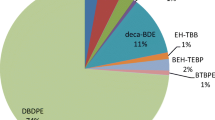
The aim of this study was to assess the pollution profiles of various typical brominated flame retardants in water and surface sediment near a typical electronic waste dismantling region in southern China. We found that polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), 2,4,6-tribromophenol (TBP), pentabromophenol (PeBP), tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA), and bisphenol A (BPA) were ubiquitous in the water and sediment samples collected in the study region. In water, Σ19PBDEs (sum of all 20 PBDE congeners studied except BDE-209, which was below the detection limit) levels ranged from 0.31 to 8.9 × 102 ng L−1. TBP, PeBP, TBBPA, and BPA concentrations in the water samples ranged from not being detectable (nd—under the detection limit) to 3.2 × 102 (TBP), from nd to 37 (PeBP), from nd to 9.2 × 102 (TBBPA) and from nd–8.6 × 102 ng L−1 (BPA). In sediment, Σ19PBDEs ranged from nd to 5.6 × 103 ng g−1, while BDE-209 was the predominant congener, with a range of nd to 3.5 × 103 ng g−1. Tri- to hepta-BDE concentrations were significantly (p < 0.01) correlated with each other, except for BDE-71 and BDE-183, and octa- to nona-BDEs concentrations were significantly (p < 0.05) correlated with each other, except for BDE-208. BDE-209 was not significantly correlated with tri- to nona-BDEs. Risk assessments indicated that the water and sediment across the sampling sites posed no estrogenic risk. However, different eco-toxicity risk degrees at three trophic levels did exist at most sampling sites.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaee, M., Arias, P., Sjödin, A., & Bergman, Å. (2003). An overview of commercially used brominated flame retardants, their applications, their use patterns in different countries/regions and possible modes of release. Environment International, 29(6), 683–689.
An, T. C., Chen, J. X., Li, G. Y., Ding, X. J., Sheng, G. Y., Fu, J. M., et al. (2008). Characterization and the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 immobilized hydrophobic montmorillonite photocatalysts degradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 209). Catalysis Today, 139(1–2), 69–76.
An, T. C., Zhang, D. L., Li, G. Y., Mai, B. X., & Fu, J. M. (2011a). On-site and off-site atmospheric PBDEs in an electronic dismantling workshop in south China: Gas-particle partitioning and human exposure assessment. Environmental Pollution, 159(12), 3529–3535.
An, T. C., Zu, L., Li, G. Y., Wan, S. G., Mai, B. X., & Wong, P. K. (2011b). One-step process for debromination and aerobic mineralization of tetrabromobisphenol-A by a novel Ochrobactrum sp. T isolated from an e-waste recycling site. Bioresource Technology, 102(19), 9148–9154.
Arbeli, Z., & Ronen, Z. (2003). Enrichment of a microbial culture capable of reductive debromination of the flame retardant tetrabromobisphenol-A, and identification of the intermediate metabolites produced in the process. Biodegradation, 14(6), 385–395.
Binelli, A., Sarkar, S. K., Chatterjee, M., Riva, C., Parolini, M., Bhattacharya, B. D., et al. (2007). Concentration of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in sediment cores of Sundarban mangrove wetland, northeastern part of Bay of Bengal (India). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54(8), 1220–1229.
Bjorklund, J. A., Thuresson, K., Cousins, A. P., Sellstrom, U., Emenius, G., & de Wit, C. A. (2012). Indoor air is a significant source of tri-decabrominated diphenyl ethers to outdoor air via ventilation systems. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(11), 5876–5884.
Bradley, P. W., Wan, Y., Jones, P. D., Wiseman, S., Chang, H., Lam, M. H., et al. (2011). PBDEs and methoxylated analogues in sediment cores from two Michigan, USA, inland lakes. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 30(6), 1236–1242.
Chen, S. J., Feng, A. H., He, M. J., Chen, M. Y., Luo, X. J., & Mai, B. X. (2013). Current levels and composition profiles of PBDEs and alternative flame retardants in surface sediments from the Pearl River Delta, southern China: Comparison with historical data. Science of the Total Environment, 444, 205–211.
Chen, S. J., Luo, X. J., Lin, Z., Luo, Y., Li, K. C., Peng, X. Z., et al. (2007). Time trends of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediment cores from the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Environmental Science and Technology, 41(16), 5595–5600.
EU Commission. (1996). Technical guidance document in support of commission directive 93/67/EEC on risk assessment for new notified substances and commission regulation (EC) No. 1488/94 on risk assessment for existing substances. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg, pp. 328–334.
EU Commission. (2003). Technical guidance document on risk assessment in support of commission Directive 93/67/EEC on risk assessment for new notified substances and commission regulation (EC) No 1488/94 on risk assessment for existing substances. Directive 98/8/EC of the European parliament and of the council concerning the placing of biocidal products on the market. Part II. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg
Cristale, J., García Vázquez, A., Barata, C., & Lacorte, S. (2013a). Priority and emerging flame retardants in rivers: Occurrence in water and sediment, Daphnia magna toxicity and risk assessment. Environment International, 59, 232–243.
Cristale, J., Katsoyiannis, A., Sweetman, A. J., Jones, K. C., & Lacorte, S. (2013b). Occurrence and risk assessment of organophosphorus and brominated flame retardants in the River Aire (UK). Environmental Pollution, 179, 194–200.
de Wit, C. A., Herzke, D., & Vorkamp, K. (2010). Brominated flame retardants in the Arctic environment—Trends and new candidates. Science of the Total Environment, 408(15), 2885–2918.
Di Toro, D. M., Zarba, C. S., Hansen, D. J., Berry, W. J., Swartz, R. C., Cowan, C. E., et al. (1991). Technical basis for establishing sediment quality criteria for nonionic organic chemicals using equilibrium partitioning. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 10(12), 1541–1583.
Du, W. C., Ji, R., Sun, Y. Y., Zhu, J. G., Wu, J. C., & Guo, H. Y. (2013). Fate and ecological effects of decabromodiphenyl ether in a field lysimeter. Environmental Science and Technology, 47(16), 9167–9174.
Feng, A. H., Chen, S. J., Chen, M. Y., He, M. J., Luo, X. J., & Mai, B. X. (2012). Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) and tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in riverine and estuarine sediments of the Pearl River Delta in southern China, with emphasis on spatial variability in diastereoisomer- and enantiomer-specific distribution of HBCD. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(5), 919–925.
Fujii, Y., Nishimura, E., Kato, Y., Harada, K. H., Koizumi, A., & Haraguchi, K. (2014). Dietary exposure to phenolic and methoxylated organohalogen contaminants in relation to their concentrations in breast milk and serum in Japan. Environment International, 63, 19–25.
Ginebreda, A., Muñoz, I., de Alda, M. L., Brix, R., López-Doval, J., & Barceló, D. (2010). Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceuticals in rivers: Relationships between hazard indexes and aquatic macroinvertebrate diversity indexes in the Llobregat River (NE Spain). Environment International, 36(2), 153–162.
Gorga, M., Martinez, E., Ginebreda, A., Eljarrat, E., & Barcelo, D. (2013). Determination of PBDEs, HBB, PBEB, DBDPE, HBCD, TBBPA and related compounds in sewage sludge from Catalonia (Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 444, 51–59.
He, M. J., Luo, X. J., Yu, L. H., Wu, J. P., Chen, S. J., & Mai, B. X. (2013). Diasteroisomer and enantiomer-specific profiles of hexabromocyclododecane and tetrabromobisphenol A in an aquatic environment in a highly industrialized area, South China: Vertical profile, phase partition, and bioaccumulation. Environmental Pollution, 179, 105–110.
Huang, H. W., Chang, B. V., & Lee, C. C. (2014a). Reductive debromination of decabromodiphenyl ether by anaerobic microbes from river sediment. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 87, 60–65.
Huang, D. Y., Zhao, H. Q., Liu, C. P., & Sun, C. X. (2014b). Characteristics, sources, and transport of tetrabromobisphenol A and bisphenol A in soils from a typical e-waste recycling area in South China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(9), 5818–5826.
Jin, S. W., Yang, F. X., Xu, Y., Dai, H. P., & Liu, W. P. (2013). Risk assessment of xenoestrogens in a typical domestic sewage-holding lake in China. Chemosphere, 93(6), 892–898.
Kitamura, S., Suzuki, T., Sanoh, S., Kohta, R., Jinno, N., Sugihara, K., et al. (2005). Comparative study of the endocrine-disrupting activity of bisphenol A and 19 related compounds. Toxicological Sciences, 84(2), 249–259.
Kuramochi, H., Kawamoto, K., Miyazaki, K., Nagahama, K., Maeda, K., Li, X. W., et al. (2008). Determination of physicochemical properties of tetrabromobisphenol A. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27(12), 2413–2418.
La Guardia, M. J., Hale, R. C., & Harvey, E. (2006). Detailed polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) congener composition of the widely used penta-, octa-, and deca-pbde technical flame-retardant mixtures. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(20), 6247–6254.
Labadie, P., Tlili, K., Alliot, F., Bourges, C., Desportes, A., & Chevreuil, M. (2010). Development of analytical procedures for trace-level determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and tetrabromobisphenol A in river water and sediment. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 396(2), 865–875.
Law, R. J., Alaee, M., Allchin, C. R., Boon, J. P., Lebeuf, M., Lepom, P., & Stern, G. A. (2003). Levels and trends of polybrominated diphenylethers and other brominated flame retardants in wildlife. Environment International, 29(6), 757–770.
Lee, H. J., An, S., & Kim, G. B. (2014). Background level and composition of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in creek and subtidal sediments in a rural area of Korea. Science of the Total Environment, 470–471, 1479–1484.
Lee, I. S., Kim, K. S., Kim, S. J., Yoon, J. H., Choi, K. H., Choi, S. D., & Oh, J. E. (2012). Evaluation of mono- to deca-brominated diphenyl ethers in riverine sediment of Korea with special reference to the debromination of DeBDE209. Science of the Total Environment, 432, 128–134.
Li, Y., Lin, T., Chen, Y., Hu, L., Guo, Z., & Zhang, G. (2012a). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in sediments of the coastal East China Sea: Occurrence, distribution and mass inventory. Environmental Pollution, 171, 155–161.
Li, F. J., Wang, J. J., Nastold, P., Jiang, B. Q., Sun, F. F., Zenker, A., et al. (2014). Fate and metabolism of tetrabromobisphenol A in soil slurries without and with the amendment with the alkylphenol degrading bacterium Sphingomonas sp strain TTNP3. Environmental Pollution, 193, 181–188.
Li, G. Y., Zu, L., Wong, P. K., Hui, X., Lu, Y., Xiong, J. K., & An, T. C. (2012b). Biodegradation and detoxification of bisphenol A with one newly-isolated strain Bacillus sp. GZB: Kinetics, mechanism and estrogenic transition. Bioresource Technology, 114, 224–230.
Liu, F., Liao, C. Y., Fu, J. J., Lv, J. G., Xue, Q. Z., & Jiang, G. B. (2014). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides in rice hull from a typical e-waste recycling area in southeast China: Temporal trend, source, and exposure assessment. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36(1), 65–77.
Liu, J., Wang, Y. F., Jiang, B. Q., Wang, L. H., Chen, J. Q., Guo, H. Y., & Ji, R. (2013). Degradation, metabolism, and bound-residue formation and release of tetrabromobisphenol a in soil during sequential anoxic-oxic incubation. Environmental Science and Technology, 47(15), 8348–8354.
Lopez, P., Brandsma, S. A., Leonards, P. E. G., & De Boer, J. (2009). Methods for the determination of phenolic brominated flame retardants, and by-products, formulation intermediates and decomposition products of brominated flame retardants in water. Journal of Chromatography A, 1216(3), 334–345.
Malik, R. N., Mehboob, F., Ali, U., Katsoyiannis, A., Schuster, J. K., Moeckel, C., & Jones, K. C. (2014). Organo-halogenated contaminants (OHCs) in the sediments from the Soan River, Pakistan: OHCs (adsorbed TOC) burial flux, status and risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 481, 343–351.
Marcus, M. D., Covington, S., Liu, B., & Smith, N. R. (2010). Use of existing water, sediment, and tissue data to screen ecological risks to the endangered Rio Grande silvery minnow. The Science of the Total Environment, 409(1), 83–94.
Mariani, G., Canuti, E., Castro-Jiménez, J., Christoph, E. H., Eisenreich, S. J., Hanke, G., et al. (2008). Atmospheric input of POPs into Lake Maggiore (Northern Italy): PBDE concentrations and profile in air, precipitation, settling material and sediments. Chemosphere, 73[Suppl 1], S114–S121.
Möller, A., Xie, Z., Sturm, R., & Ebinghaus, R. (2011). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and alternative brominated flame retardants in air and seawater of the European Arctic. Environmental Pollution, 159(6), 1577–1583.
Moon, H. B., Choi, M., Yu, J., Jung, R. H., & Choi, H. G. (2012). Contamination and potential sources of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in water and sediment from the artificial Lake Shihwa, Korea. Chemosphere, 88(7), 837–843.
Nakajima, A., Saigusa, D., Tetsu, N., Yamakuni, T., Tomioka, Y., & Hishinuma, T. (2009). Neurobehavioral effects of tetrabromobisphenol A, a brominated flame retardant, in mice. Toxicology Letters, 189(1), 78–83.
Nouira, T., Risso, C., Chouba, L., Budzinski, H., & Boussetta, H. (2013). Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in surface sediments from Monastir Bay (Tunisia, Central Mediterranean): Occurrence, distribution and seasonal variations. Chemosphere, 93(3), 487–493.
National Industrial Chemicals Notification and Assessments Scheme (NICNAS). (2001). PBFRs, P.F.R. Priority Existing Chemical Assessment Report No. 20. NICNAS/Australian Government, Marrickville.
Polo, M., Llompart, M., Garcia-Jares, C., Gomez-Noya, G., Bollain, M. H., & Cela, R. (2006). Development of a solid-phase microextraction method for the analysis of phenolic flame retardants in water samples. Journal of Chromatography A, 1124(1–2), 11–21.
Reistad, T., Mariussen, E., & Fonnum, F. (2005). The effect of a brominated flame retardant, tetrabromobisphenol-A, on free radical formation in human neutrophil granulocytes: The involvement of the MAP kinase pathway and protein kinase C. Toxicological Sciences, 56, 95–104.
Ronen, Z., & Abeliovich, A. (2000). Anaerobic-aerobic process for microbial degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66(6), 2372–2377.
Sánchez-Avila, J., Tauler, R., & Lacorte, S. (2012). Organic micropollutants in coastal waters from NW Mediterranean Sea: Sources distribution and potential risk. Environment International, 46, 50–62.
Shi, Z. X., Jiao, Y., Hu, Y., Sun, Z. W., Zhou, X. Q., Feng, J. F., et al. (2013). Levels of tetrabromobisphenol A, hexabromocyclododecanes and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in human milk from the general population in Beijing, China. Science of the Total Environment, 452–453, 10–18.
Staples, C. A., Dome, P. B., Klecka, G. M., Oblock, S. T., & Harris, L. R. (1998). A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of bisphenol A. Chemosphere, 36(10), 2149–2173.
Sun, C., Chang, W., Ma, W., Chen, C., & Zhao, J. (2013a). Photoreductive debromination of decabromodiphenyl ethers in the presence of carboxylates under visible light irradiation. Environmental Science and Technology, 47(5), 2370–2377.
Sun, Y., Huang, H., Sun, Y., Wang, C., Shi, X. L., Hu, H. Y., et al. (2013b). Ecological risk of estrogenic endocrine disrupting chemicals in sewage plant effluent and reclaimed water. Environmental Pollution, 180, 339–344.
Takigami, H., Suzuki, G., Hirai, Y., & Sakai, Si. (2009). Brominated flame retardants and other polyhalogenated compounds in indoor air and dust from two houses in Japan. Chemosphere, 76(2), 270–277.
Tang, Z. W., Huang, Q. F., Cheng, J. L., Yang, Y. F., Yang, J., Guo, W., et al. (2014). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soils, sediments, and human hair in a plastic waste recycling area: A neglected heavily polluted area. Environmental Science and Technology, 48(3), 1508–1516.
Wang, X. W., Xi, B. D., Huo, S. L., Deng, L., Pan, H. W., Xia, X. F., et al. (2013). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers occurrence in major inflowing rivers of Lake Chaohu (China): Characteristics, potential sources and inputs to lake. Chemosphere, 93(8), 1624–1631.
Wong, C. S. C., Duzgoren-Aydin, N. S., Aydin, A., & Wong, M. H. (2007). Evidence of excessive releases of metals from primitive e-waste processing in Guiyu. China. Environmental Pollution, 148(1), 62–72.
Xing, G. H., Chan, J. K. Y., Leung, A. O. W., Wu, S. C., & Wong, M. H. (2009). Environmental impact and human exposure to PCBs in Guiyu, an electronic waste recycling site in China. Environment International, 35(1), 76–82.
Yu, Z. Q., Liao, R., Li, H. R., Mo, L. G., Zeng, X. Y., Sheng, G. Y., & Fu, J. M. (2011). Particle-bound Dechlorane Plus and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in ambient air around Shanghai, China. Environmental Pollution (Barking, Essex: 1987), 159(10), 2982–2988.
Zhang, D. L., An, T. C., Qiao, M., Loganathan, B. G., Zeng, X. Y., Sheng, G. Y., & Fu, J. M. (2011). Source identification and health risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with electronic dismantling in Guiyu town, South China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192(1), 1–7.
Zhang, X. L., Luo, X. J., Chen, S. J., Wu, J. P., & Mai, B. X. (2009). Spatial distribution and vertical profile of polybrominated diphenyl ethers, tetrabromobisphenol A, and decabromodiphenylethane in river sediment from an industrialized region of South China. Environmental Pollution, 157(6), 1917–1923.
Zhao, X., Zhang, H., Ni, Y., Lu, X., Zhang, X., Su, F., et al. (2011). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments of the Daliao River Estuary, China: Levels, distribution and their influencing factors. Chemosphere, 82(9), 1262–1267.
Zu, L., Li, G. Y., An, J. B., Li, J. J., & An, T. C. (2013). Kinetic optimization of biodegradation and debromination of 2,4,6-tribromophenol using response surface methodology. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 76, 18–23.
Acknowledgments
This is contribution No. 1971 from GIGCAS. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from NSFC (41373103 and U1201234) and Earmarked Fund of SKLOG (SKLOG2011A02). The authors also express their thanks to Yong Huang for his help in collecting samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, J., An, T., Zhang, C. et al. Pollution profiles and risk assessment of PBDEs and phenolic brominated flame retardants in water environments within a typical electronic waste dismantling region. Environ Geochem Health 37, 457–473 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9658-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9658-8