Abstract
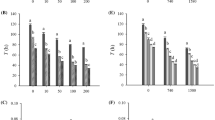
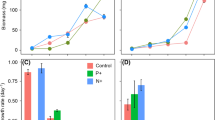
The harmful dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi is responsible for the mortality of aquatic animals. However, the mechanism behind these toxic effects has not been fully determined. Herein, the toxic effects of K. mikimotoi on the growth performance, antioxidative responses, physiological activities, and energetic substance contents of rotifer Brachionus plicatilis were assessed. Rotifers were exposed to Nannochloropsis salina (Eustigmatophyceae), K. mikimotoi, and a mixture of N. salina and K. mikimotoi with biomass ratio proportions of 3:1, 1:1, and 1:3, respectively. Results indicated that K. mikimotoi negatively affected the population growth, survival, and specific growth rates of rotifers within 24 h. The level of reactive oxygen species (ROS), the content of malondialdehyde, and the activity of amylase increased. However, the total antioxidant capacity level, pepsase, cellulase, alkaline phosphatase, xanthine oxidase, and lactate dehydrogenase activities, and glycogen and protein contents decreased with increasing proportions of K. mikimotoi. The mixture of 50% N. salina and 50% K. mikimotoi promoted the increase in glutamic–pyruvic transaminase activity and triglyceride content. These findings underscore ROS-mediated antioxidative responses, physiological responses, and energetic substance content changes in B. plicatilis work together to affect population dynamics inhibition of rotifers by K. mikimotoi.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Tawwab M, Shukry M, Farrag FA, EI-Shafai NM, Dawood MAO, Abdel-Latif HMR (2021) Dietary sodium butyrate nanoparticles enhanced growth, digestive enzyme activities, intestinal histomorphometry, and transcription of growth-related genes in Nile tilapia juveniles. Aquaculture 536:736467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736467
Anand PSS, Kohli MPS, Roy SD, Sundaray JK, Kumar S, Sinha A, Pailan GH, Sukham MK (2014) Effect of dietary supplementation of periphyton on growth, immune response and metabolic enzyme activities in Penaeus monodon. Aquacult Res 46:2277–2288. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12385
Basti L, Nagai S, Go J, Okano S, Nagai K, Watanabe R, Suzuki T, Tanaka Y (2015) Differential inimical effects of Alexandrium spp. and Karenia spp. on cleavage, hatching, and two larval stages of Japanese pearl oyster Pinctada fucata martensii. Harmful Algae 43:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2014.12.004
Chen B, Wang K, Guo H, Lin H (2021) Karenia mikimotoi blooms in coastal waters of China from 1998 to 2017. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 249:107034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2020.107034
Chen H, Tang X, Zhou B, Xu N, Wang Y (2016) Mechanism of Deca-BDE-induced apoptosis in Neuro-2a cells: Role of death-receptor pathway and reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway. J Environ Sci 46:241–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.02.015
Chen H, Wang J, Zhuang Y, Yu W, Liu G (2022) Reduced fitness and elevated oxidative stress in the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicus exposed to the toxic dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi. Antioxidants 11:2299. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112299
Cheng CH, Ma HL, Deng YQ, Feng J, Jie YK, Guo ZX (2021) Oxidative stress, cell cycle arrest, DNA damage and apoptosis in the mud crab (Scylla paramamosain) induced by cadmium exposure. Chemosphere 263:128277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128277
Cheng CH, Ma HL, Su YL, Deng YQ, Feng J, Xie JW, Chen XL, Guo ZX (2019) Ammonia toxicity in the mud crab (Scylla paramamosain): The mechanistic insight from physiology to transcriptome analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 179:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.04.033
Cho K, Ueno M, Liang Y, Kim D, Oda T (2022) Generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by harmful algal bloom (HAB)–forming phytoplankton and their potential impact on surrounding living organisms. Antioxidants 11:206. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020206
Coggins BL, Collins JW, Holbrook KJ, Yampolsky LY (2017) Antioxidant capacity, lipid peroxidation, and lipid composition changes during long-term and short-term thermal acclimation in Daphnia. J Comp Physiol B 187:1091–1106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-017-1090-9
Conlin SM, Tudor MS, Shim J, Gosse JA, Neilson A, Hamlin HJ (2018) Elevated nitrate alters the metabolic activity of embryonic zebrafish. Environ Pollut 235:180–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.12.069
Dang LX, Li Y, Liu F, Zhang Y, Yang WD, Li HY, Liu JS (2015) Chemical response of the toxic dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi against grazing by three species of zooplankton. J Eukaryot Microbiol 62:470–480. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12201
Diamantino TC, Almeida E, Soares AMVM, Guilhermino L (2001) Lactate dehydrogenase activity as an effect criterion in toxicity tests with Daphnia magna straus. Chemosphere 45:553–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00029-7
Dorantes-Aranda JJ, Seger A, Mardones JI, Nichols PD, Hallegraeff GM (2015) Progress in understanding algal bloom-mediated fish kills: the role of superoxide radicals, phycotoxins and fatty acids. PLoS ONE 10:e0133549. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0133549
Dube PN, Shwetha A, Hosetti BB (2014) Impact of copper cyanide on the key metabolic enzymes of freshwater fish Catla catla (Hamilton). Biotechnol Anim Husband 30:499–508. https://doi.org/10.2298/BAH1403499D
Durigon EG, Almeida APG, Jerônimo GT, Baldisserotto B, Emerenciano MGC (2019) Digestive enzymes and parasitology of Nile tilapia juveniles raised in brackish biofloc water and fed with different digestible protein and digestible energy levels. Aquaculture 506:35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.03.022
Graff JR, Milligan AJ, Behrenfeld MJ (2012) The measurement of phytoplankton biomass using flow-cytometric sorting and elemental analysis of carbon. Limnol Oceanogr: Methods 10:910–920. https://doi.org/10.4319/lom.2012.10.910
Han Q, Wang Y, Lv T, Han Q, Jiang X (2017) Effects of dietary lipids on the growth performance, survival, and digestive enzymes of juvenile cuttlefish, Sepia lycidas. J World Aquacult Soc 48:963–971. https://doi.org/10.1111/jwas.12446
Higo S, Maung-Saw-Htoo-Thaw Yamatogi T, Ishida N, Hirae S, Koike K (2017) Application of a pulse-amplitude-modulation (PAM) fluorometer reveals its usefulness and robustness in the prediction of Karenia mikimotoi blooms: a case study in Sasebo Bay, Nagasaki, Japan. Harmful Algae 61:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2016.11.013
Jia R, Han C, Lei JL, Liu BL, Huang B, Huo HH, Yin ST (2015) Effects of nitrite exposure on haematological parameters, oxidative stress and apoptosis in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquat Toxicol 169:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.09.016
Kanta P, Ghosh T, Kaur A, Muthukumarappa T (2021) An innovative and cost-effective way to estimate alkaline phosphatase activity in in vitro cellular model systems. Int J Biochem Mol Biol 12:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.09.016
Kim D, Wencheng L, Matsuyama Y, Cho K, Yamasaki Y, Takeshita S, Yamaguchi K, Oda T (2019) Extremely high level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in a newly isolated strain of the dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi. Eur J Phycol 54:632–640. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670262.2019.1632936
Kok JWK, Leong SCY (2019) Nutrient conditions and the occurrence of a Karenia mikimotoi (Kareniaceae) bloom within East Johor Straits. Singapore. Reg Stud Mar Sci 27:100514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2019.100514
Krebs CJ (1994) Ecology: the Experimental Analysis of Distribution and Abundance, 4th edn. Harper Collins College Publishers, New York
Kwiterovich PO (2000) The metabolic pathways of high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, and triglycerides: a current review. Am J Cardiol 86:5–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9149(00)01461-2
Lampert W, Trubetskova I (1996) Juvenile growth rate as a measure of fitness in Daphnia. Funct Ecol 10:631–635. https://doi.org/10.2307/2390173
Li X, Yan T, Lin J, Yu R, Zhou M (2017) Detrimental impacts of the dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi in Fujian coastal waters on typical marine organisms. Harmful Algae 61:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2016.11.011
Li X, Yan T, Yu R, Zhou M (2019) A review of Karenia mikimotoi: bloom events, physiology, toxicity and toxic mechanism. Harmful Algae 90:101702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2019.101702
Li X, Yan T, Zhang Q, Yu R, Zhou M (2020) Inhibition to crucial enzymes in the lethal effects of the dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi on the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Mar Environ Res 157:104866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2019.104866
Li Y, Yu J, Sun T, Liu C, Sun Y, Wang Y (2018) Using the marine rotifer Brachionus plicatilis as an endpoint to evaluate whether ROS-dependent hemolytic toxicity is involved in the allelopathy induced by Karenia mikimotoi. Toxins 10:439. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110439
Liang Y, Guo H, Liao Q, Zhang X, Huang K (2020) Growth performance, phenotypic traits, and antioxidant responses of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis under different proportions of Phaeocystis globosa. Ecotox Environ Safe 202:110963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110963
Liang Y, Su Y, Ouyang K, Chen X, Yang J (2017) Effects of microcystin-producing and mucrocystin-free Microcystis aeruginosa on enzyme activity and nitrite content in the rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:10430–10442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8704-3
Liang Y, Yang X, Wang Y, Liu R, Gu H, Mao L (2021a) Influence of polystyrene microplastics on rotifer (Brachionus calyciflorus) growth, reproduction, and antioxidant responses. Aquat Ecol 55:1097–1111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-021-09885-y
Liang Y, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Liu R, Qi J, Lin Y, Zhang T, Jiang Q (2021b) Use of physiological activities to estimate the population growth of rotifer (Brachionus calyciflorus) under the stress of toxic Microcystis and nitrite. Chemosphere 285:131419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131419
Lin J, Yan T, Zhang Q, Zhou M (2016) Impact of several harmful algal bloom (HAB) causing species, on life history characteristics of rotifer Brachionus plicatilis Müller. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 34:642–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-016-5065-6
Lin JN, Song JJ, Yan T, Zhang QC, Zhou MJ (2015) Large-scale dinoflagellate bloom species Prorocentrum donghaiense and Karenia mikimotoi reduce the survival and reproduction of copepod Calanus sinicus. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 95:1071–1079. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315415000533
Lyu K, Yu B, Li D, Gu L, Yang Z (2022) Increased food availability reducing the harmful effects of microplastics strongly depends on the size of microplastics. J hazard Mater 437:129375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129375
Mills S, Alcántara-Rodríguez JA, Ciros-Pérez J, Gómez A, Hagiwara A, Galindo KH, Jersabek CD, Malekzadeh-Viayeh R, Leasi F, Lee JS, Mark Welch DB, Papakostas S, Riss S, Segers H, Serra M, Shiel R, Smolak R, Snell TW, Stelzer CP, Tang CQ, Wallace RL, Fontaneto D, Walsh EJ (2017) Fifteen species in one: deciphering the Brachionus plicatilis species complex (Rotifera, Monogononta) through DNA taxonomy. Hydrobiologia 796:39–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2725-7
Neely T, Campbell L (2006) A modified assay to determine hemolytic toxin variability among Karenia clones isolated from the Gulf of Mexico. Harmful Algae 5:592–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2005.11.006
Niu X, Xu S, Yang Q, Xu X, Zheng M, Li X, Guan W (2021) Toxic effects of the dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi on zebrafish (Danio rerio) larval behavior. Harmful Algae 103:101996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2021.101996
Olsen Y, Reitan KI, Vadstein O (1993) Dependence of temperature on loss rates of rotifers, lipids and ω3 fatty acids in starved Brachionus plicatilis cultures. Hydrobiologia 255:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00025815
Sibly RM, Hone J (2002) Population growth rate and its determinants: an overview. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 357:1153–1170. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2002.1117
Snell TW, Janssen CR (1995) Rotifers in ecotoxicology: a review. Hydrobiologia 313–314:231–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00025956
Sun S, Fu H, Zhu J, Ge X, Wu X, Qiao H, Jin S, Zhang W (2018) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of lactate dehydrogenase from the oriental river prawn Macrobrachium nipponense in response to hypoxia. Int J Mol Sci 19:1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071990
Wang B, Guo Y, Zhou B, Zhang H, Cui X, Sun Y, Wang Y (2021) A possible speculation on the involvement of ROS and lysosomes mediated mitochondrial pathway in apoptosis of rotifer Brachionus plicatilis with BDE-47 exposure. Sci Total Environ 787:147315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147315
Wang H, Tang X, Sha J, Chen H, Sun T, Wang Y (2015) The reproductive toxicity on the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis induced by BDE-47 and studies on the effective mechanism based on antioxidant defense system changes. Chemosphere 135:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.090
Xu A, Shang-Guan J, Li Z, Gao Z, Huang YC, Chen Q (2020) Effects of dietary asafoetida (Ferula sinkiangensis K. M. Shen) levels on feeding attraction activity, growth performance, healthiness, and digestive enzyme activity in juvenile Lateolabrax japonicus. Fish Physiol Biochem 46:1991–2003. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00849-x
Yamasaki Y, Kim D, Matsuyama Y, Oda T, Honjo T (2004) Production of superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide by the red tide dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi. J Biosci Bioeng 97:212–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1389-1723(04)70193-0
Yang W, Zhang N, Cui W, Xu Y, Li H, Liu J (2011) Effects of co-existing microalgae and grazers on the production of hemolytic toxins in Karenia mikimotoi. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 29:1155–1163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-011-0274-5
You S, Wang G, Zhou F, Wu H, Han Y, Xue W, Ma Y, Zhang C, Zhou L, Yan F, Fu C, Dong A (2022) Chapter 8–Antihyperuricemic peptides: A review focused on xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities. Studies Nat Products Chem 74:279–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91099-6.00013-X
Yu Z, Wu X, Zheng L, Dai Z, Wu L (2020) Effect of acute exposure to ammonia and BFT alterations on Rhynchocypris lagowski: Digestive enzyme, inflammation response, oxidative stress and immunological parameters. Environ Toxicol Phar 78:103380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2020.103380
Zhang H, Ju Q, Pang S, Wei N, Zhang Y (2021) Recent progress of fluorescent probes for the detection of alkaline phosphatase (ALP): A review. Dyes Pigments 194:109569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2021.109569
Zou Y, Kim D, Yagi M, Yamasaki Y, Kurita J, Iida T, Matsuyama Y, Yamaguchi K, Oda T (2013) Application of LDH-release assay to cellular-level evaluation of the toxic potential of harmful algal species. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 77:345–352. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.120764
Zou Y, Yamasaki Y, Matsuyama Y, Yamaguchi K, Honjo T, Oda T (2010) Possible involvement of hemolytic activity in the contact-dependent lethal effects of the dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi on the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Harmful Algae 9:367–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2010.01.005
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: 42206217), the Fund of Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Marine Ecological Conservation and Restoration, China (Grant number: EPR2020004), the Open–End Funds of Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Marine Biotechnology, Jiangsu Ocean University, China (Grant number: HS2021001), and the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of NUIST, China (Grant numbers: 2018r040 and 2020r062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL: Investigation, Conceptualization, Methodology, Visualization, Writing-original draft, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing-review & editing. JY: Methodology, Visualization. ZN: Data curation, Software, Validation. JZ: Methodology. HG: Project administration, Supervision, Writing-review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the use of animals were followed by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Y., Yang, J., Ni, Z. et al. Dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi on the growth performance, antioxidative responses, and physiological activities of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Ecotoxicology 32, 768–781 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-023-02686-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-023-02686-z