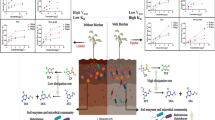
Abstract
Soil contamination with petroleum hydrocarbons affects plants and rhizospheric microorganisms. Microbial activity participates in important biochemical processes that stimulate, together with plants, the modification of toxic compounds for organisms. A nine-month experiment was set up to study the effect over time of oil on plant height (cm), formation of new plants, plant matter production (gravimetry), and population of rhizospheric microorganisms (serial dilution) in the sedge Eleocharis palustris. Removal of total petroleum hydrocarbons (soxhlet and gravimetry) from the soil was also evaluated. The means of the evaluated variables registered significant statistical differences (Duncan, p < 0.05) regarding the age of the plant and the amount of crude oil. There was a high correlation between oil and plant height (0.848) and with new plants (0.994). 60 mg oil dose promoted the greatest statistical difference in the amounts of roots and plant biomass (p < 0.05). E. palustris exposed to 60 and 75 mg of oil stimulated high densities of microalgae, actinomycetes, fungi, hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria and Pseudomonas spp; the overall ratio was 2:1 relative to natural attenuation. Plant and microorganism variables evaluated registered physiological and microbiological hormetic indices ≥1, showing a positive linear relationship. Natural attenuation was more efficient in removing crude oil. We conclude that E. palustris is tolerant to oil exposure. It is suggested to combine it with natural attenuation for the optimization of soils contaminated with crude oil.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu GO, Dike PO (2008) A study of natural attenuation processes involved in a microcosm model of a crude oil-impacted wetland sediment in the Niger Delta. Bioresour Technol 99(11): 4761–4767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.09.06
Afzal M, Rehman K, Shabir G, Tahseen R, ljaz A, Hashmat JA, Brix H (2019) Large-scale remediation of oil contaminated water using floating treatment wetlands. npj Clean Water 2(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-018-0025-7
Agarry SE, Oghenejoboh KM, Latinwo GK, Owabor CN (2018) Biotreatment of petroleum refinery wastewater in vertical surface-flow constructed wetland vegetated with Eichhornia crassipes: lab-scale experimental and kinetic modelling. Environ Technol 41(14):1793–1813. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1549106
Agathokleous E, Calabrese EJ (2020a) A global environmental health perspective and optimisation of stress. Sci. Total Environ 704:135263. https://doi.org/10.1016/jscitotenv.2019.135263
Agathokleous E, Calabrese EJ (2020b) Environmental toxicology and ecotoxicology: How clean is clean? Rethinking dose-response analysis. Sci Total Environ 746:138769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138769
Agathokleous E, Barcelo D, Tsatsakis A, Calabrese JE (2020) Hydrocarbon-induced hormesis: 101 years of evidence at the margin. Environ Pollut 265:114846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114846
Alanbary SRN, Abdullah SRS, Al-Baldawi IAW, Hasan HA, Anuar N, Othman AR, Suja F (2019) Phytotoxicity of contaminated sand containing crude oil sludge on Ludwigia octovalvis. J Ecol Eng 20(11):246–255. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/113189
Al-Baldawi AI, Abdullah SRS, Anuar N, Suja F, Mushrifah I (2015) Phytodegradation of total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) in diesel-contaminated water using Scirpus grossus. Ecol Eng 74:463–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.11.007
Al-Mansoory AF, Idris M, Abdullah SRS, Anaur N (2017) Phytoremediation of contaminated soils containing gasoline using Ludwigia octovalvis (Jacq.) in greenhouse pots. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(13):11998–12008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5261-5
Al-Mansoory AF, Idris M, Abdullah SRS, Anuar N, Kurniawan BS (2021) Response and capability of Scirpus mucronatus (L.) in phytotreating petrol-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 269(128760):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128760
Atlas MR, Bartha R (2002) Ecología Microbiana y Microbiología Ambiental. Pearson Educación S.A. Madrid, España
Azcón-Bieto J, Talón M (2013) Fundamentos de Fisiología Vegetal. McGraw-Hill. Interamericana de España, S.L, Madrid, España
Brady CN, Weil RR (2008) The nature and properties of soils. Pearson. Prentice Hall, New Jersey, Columbus Ohio, USA
Calabrese EJ (2013) Hormetic mechanisms. Crit Rev Toxicol 43(7):580e606. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408444.2013.808172
Calabrese EJ, Blain RB (2009) Hormesis and plant biology. Environ Pollut 157(1):42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.07.028
Calabrese EJ, Agathokleous E (2020) Theodosius Dobzhansky’s view on biology and evolution v.2.0: “Nothing in biology makes sense except in light of evolution and evolution’s dependence on hormesis mediated acquired resilience that optimizes biological performance and numerous diverse short and longer term protective strategies”. Environ Res 186:109559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109559
Calabrese EJ, Agathokleous E (2021) Accumulator plants and hormesis. Environ Pollut 274:116526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116526
Cao Z, Liu X, Zhang X, Chen L, Liu S, Hu Y (2012) Short-term effects of diesel fuel on rhizosphere microbial community structure of native plants in Yangtze estuarine wetland. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(6):2179–2185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0720-0
Cedergreen N, Streibig JC, Kudsk P, Mathiassen SK, Duke SO (2007) The occurrence of hormesis in plants and algae. Dose-Response 5(2):150–162. https://scholarworks.umass.edu/dose_response/vol5/iss2/8
Dagher DJ, de la Providencia IE, Pitre FE, St-Arnaud M, Hijri M (2019) Plant identity shaped rhizospheric microbial communities more strongly than bacterial bioaugmentation in petroleum hydrocarbon-polluted sediments. Front Microbiol 10:2144. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02144
Durenne B, Druarta P, Blondela A, Fauconnier ML (2018) How cadmium affects the fitness and the glucosinolate content of oilseed rape plantlets. Environ Exp Bot 155:185–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.06.008
Eichert T, Fernández V (2012) Uptake and release of elements by leaves and other aerial plant parts. In: Marschner P (ed.) Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, p 71-84 https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-384905-2.00004-2 Corpus ID: 88795032
Escaso SF, Martínez GJL, Planelló CMR (2010) Fundamentos Básicos de Fisiología Vegetal y Animal. Pearson Educación, S.A, Madrid, España
Etchevers BJD (1992) Manual de métodos para análisis de suelos, plantas agua y fertilizantes. Análisis rutinarios en estudios y programas de fertilidad. Laboratorio de Fertilidad, Centro de Edafología. Colegio de Postgraduados en Ciencias Agrícolas. Montecillos. edo, México
Fan D, Wang S, Guo Y, Liu J, Agathokleous E, Zhu Y, Han J (2021) The role of bacterial communities in shaping Cd-induced hormesis in ‘living’ soil as a function of land-use change. J Hazard Mater 409:124996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124996
Fleeger JW, Carman K, Riggio A, Mendelssohn I, Lin Q, Hou A, Deis L, Zengel S (2015) Recovery of salt marsh benthic microalgae and meiofauna following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill linked to recovery of Spartina alterniflora. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 536:39–54. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps11451
Fodelianakis S, Antoniou E, Mapelli F, Magagnini M, Nikolopoulou M, Marasco R, Barbato M, Tsiola A, Tsikopouloue I, Giaccaglia L, Mahjoubi M, Jaouani A, Amer R, Husseinj E, Al-Horani FA, Benzhal F, Blaghenl M, Malkawu IH, Abdel-Fattahi Y, Cherif A, Daffonchio D, Kalogerakis N (2015) Allochthonous bioaugmentation in ex situ treatment of crude oil-polluted sediments in the presence of an effective degrading indigenous microbiome. J Hazar Mater 287:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.01.03
Fu J, Huang B (2001) Involvement of antioxidants and lipid peroxidation in the adaptation of two cool season grasses to localized drought stress. Environ Exp Bot 45(2):105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0098-8472(00)00084-8
Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T (2005) Pseudomonadales Orla-Jensen 1921, 270AL. In: Brenner DJ et al. (eds.) Bergey’s Manual® of Systematic Bacteriology. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-28022-7-9
George E, Host W, Neumann E (2012) Adaptation of Plants to Adverse Chemical Soil Conditions. In: Marschener P (ed.) Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, USA, p 409–455
Gerba PC, Pepper LI (2015) Drinking Water Treatment and Distribution. In: Pepper LI, Gerba PCh, Gentry JT (eds.) Environmental Microbiology. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, p 663-642
González-Moscoso M, Rivera-Cruz MC, Delgadillo-Martínez J, Lagunes-Espinoza LC (2017) Growth analysis and plant production of Leersia hexandra Swartz in tropic wet mexican in fuction on petroleum and surfactant. Polibotánica 43:177–196. https://doi.org/10.18387/polibotanica.43.8
González-Moscoso M, Rivera-Cruz MC, Trujillo-Narcía A (2019) Decontamination of soil containing oil by natural attenuation, phytoremediation and chemical desorption. Int J Phytoremediat 21(8):768–776. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2019.1566879
Hauser AS (2006) Eleocharis palustris. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). https://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/plants/graminoid/elepal/all.html [2021, November 17]
Iturbe R, Flores C, Castro A, Torres LG (2007) Sub-soil contamination due to oil spills in zones surrounding oil pipeline-pump stations and oil pipeline right-of-ways in Southwest-Mexico. Environ Monit Assess 133(1-3):387–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9593-y
Jacques RJS, Bento FM, Antoniolli ZI, Camargo FAO (2007) Biorremediação de solos contaminados com hidrocarbonetos aromáticos policíclicos. Ciência Rural 37(4):1192–1201
Jeffrey AA (2002) Catalase activity, hydrogen peroxide content and thermotolerance of pepper leaves. Sci Hort 95(4):277–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4238(02)00076-6
Jia L, Liu Z, Chen W, Ye Y, Yu S, He XY (2015) Hormesis effects induced by cadmium on growth and photosynthetic performance in a hyperaccumulator, Lonicera japonica. Thunb. J Plant Growth Regul 34(1):13–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-014-9433-1
Johnson LF, Curl EA (1972) Methods for research on the ecology of soil-borne plant pathogens. Burgess Publishing Company. Minneapolis, MN, USA
Labud V, García C, Hernández T (2007) Effect of hydrocarbon pollution on the microbial properties of a sandy and a clay soil. Chemosphere 66(10):1863–1871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.08.021
Ławniczak L, Woozniak-Karczewska M, Loibner AP, Heipieper HJ, Chrzanowski L (2020) Microbial degradation of hydrocarbons-basic principles for bioremediation: A review. Molecules 25(4):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25040856
Lynch J, Marschner P, Rengel Z (2012) Effect of Interna and External Factors on Root Growth and Development. In: Marschner P (ed.) Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, p 331-346
Madigan MT, Martinko JM, Bender KS, Buckley DH, Stahl DA (2015) Brock. Biología de los Microorganismos. 14a. (ed.) Pearson Educación SA, Madrid, España
Maier MR, Gentry JT (2015) Microorganisms and organic Pollutants. In: Pepper LI, Gerba PCH, Gentry JT (eds.) Environmental Microbiology. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, p 377–413
Marschner P (2012) Rhizosphere Biology. In: Marschner P (ed.) Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, p 369–373
Marschner P, Rengel Z (2012) Nutrient Availability in Soil. In: Marschner P (ed.) Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, p 315–330
Mitsch JW, Gosselink GJ (2015) Wetlands. John Wileg &Sons. Inc, Hobeken. Fifth (edt). New Jersey USA. Mommer JSL, Visser WJE (2005) Underwater photosynthesis in flooded terrestrial plants: A matter of leaf plasticity. Ann Bot 96:581–589. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mci212
Moubasher HA, Hegazy AK, Mohamed NH, Moustafa YM, Kabiel HF, Hamad AA (2015) Phytoremediation of soils polluted with crude petroleum oil using Bassia scoparia and its associated rhizosphere microorganisms. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 98:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2014.11.019
Neumann G, Römheld V (2012) Rhizosphere Chemistry in Relation to Plant Nutrition. In: Marschner P (ed.) Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, p 347–368
Ogle D, Tilley D, St. John L (2012) Plant Guide for common spikerush (Eleocharis palustris). USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, Aberdeen Plant Materials Center. Aberdeen, Idaho 83210. https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_PLANTMATERIALS/publications/idpmcfs11627.pdf
Orocio-Carrillo JA, Rivera-Cruz MC, Aranda-Ibañez M, Trujillo-Narcía A, Hernández-Gálvez G, Mendoza-López MR (2019) Hormesis under oil-induced stress in Leersia hexandra Sw. used as phytoremediator in clay soils of the Mexican humid tropic. Ecotoxicology 28(9):1063–1074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-019-02106-1
Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (1982) Nitrogen total. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeny DR (Eds.) Methods of Soil Analy-sis. Part 2. Chemical and Mi-crobiological Properties. 2nd ed. ASA. SSSA. Madison, WI, EUSA. p 595–629
Pentreath V, González E, Barquín M, Ríos SM, Perales S (2015) Bioensayo de toxicidad aguda con plantas nativas para evaluar un derrame de petróleo. Revista de Salud Ambiental. Sociedad Española de Sanidad Ambiental 15(1):4–12
Pepper LI, Gentry JT (2015) Microorganisms Found in the Environment. In: Pepper LI, Gerba PCH, Gentry TJ (eds.) Environmental Microbiology. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, p 9-34
Rastogi S, Ratna S, Said BO, Kumar R (2021) Physiological and Molecular Aspects of Retrieving Environmental Stress in Plants by Microbial Interactions. In: Sharma A (ed.) Microbes and Signaling Biomolecules Against Plant Stress, Rhizosphere Biology. Academic Press Singapore, Pte Ltd, p. 107- 125. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7094-0-6
Rebetzke G, Read J, Barbour M, Condon A, Rawson H (2000) A hand-held porameter for rapid assessment of leaf conductance in wheat. Crop Sci 40(1):277–280. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2000.401277x
Rivera-Cruz MC, Trujillo-Narcía, Trujillo- Rivera EA, Arias-Trinidad A, Mendoza-López MR (2016) Natural attenuation of weathered oil using aquatic plants in a farm in Southeast Mexico. Int J Phytoremediat 18(9):877–884. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2016.1156632
Rodríguez-Rodríguez N, Rivera-Cruz MC, Trujillo-Narcía A, Almaráz-Suárez JJ, Salgado-García S (2016) Spatial distribution of oil and biostimulation through the rhizosphere of Leersia hexandra in degraded soil. Water Air Soil Poll 227(9):319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3030-9
Rodríguez-Uribe ML, Peña-Cabriales JJ, Rivera-Cruz MC, Délano-Frier JD (2021) Native bacteria isolated from weathered petroleum oil-contaminated soils in Tabasco, Mexico, accelerate the degradation petroleum hydrocarbons in saline soil microcosms. Environ Technol Innov 23:101781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101781
Salisbury FB, Ross CW (2000) Fisiología de las Plantas: Desarrollo de las Plantas y Fisiología Ambiental. Thomson Editores, Madrid, España
SAS (Statiscal Analysis Systems) (2005) “User’s guide”, versión 9.1.3. SAS Institute, Inc, Cary, NC, p 664
Segura J (2008) Citoquininas. In: Azcón-Bieto J, Talón M (eds.) Fundamentos de Fisiología Vegetal. MacGraw-Hill interamericana de España, S.A.U. Barcelona España
Shukry MW, Al-Hawas GHS, Al-Moaik RMS, El-Bendar MA (2013) Effect of petroleum crude oil on mineral nutrient elements and soil properties of jojoba plant (Simmondsia chinensis). Acta Bot Hung 55(1-2):117–133. https://doi.org/10.1556/ABot.55.2013.1-2.8
Smith LJ, Collins PH, Crump RA, Bailey LV (2015) Management of Soil Biota and Their Processes. In: Paul A (ed.) Soil Microbiology, Ecology, and Biochemistry. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, p 539–572
Tang J, Wang M, Wang F, Sun Q, Zhou Q (2011) Eco-toxicity of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated sand. J Environ Sci 23(5):845–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(10)60517-7
Tondera K, Shang K, Vincent G, Chazarenc F, Hu Y, Brisson J (2020) Effect of plant species and nutrient loading rates in treatment wetlands for polluted river water under a subtropical climate. Water Air Soil Pollut 231(9):480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04830-5
USEPA-3540C (1996) Soxhlet extraction organics. SW-846 test methods for evaluating solid waste physical/chemical methods. http://www.epa.gov/wast es/hazard/testmethods/sw846/pdfs/3540c.pdf [Accessed 2021 Jun 10]
Vázquez-Luna M, Montiel-Flores A, Vázquez-Luna D, Herrera-Tenorio MF (2011) Impacto del petróleo crudo en suelo sobre la microbiota de vida libre fijadora de nitrógeno. Trop Subtrop Agroecosystems 13(3):511–523
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and aprosed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37(1):29–38. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-193401000-00003
Yanto DHY, Tachibana S (2014) Enhanced biodegradation of asphalt in the presence of Tween® surfactants, Mn2+ and H2O2 by Pestalotiopsis sp in liquid medium and soil. Chemosphere 103:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.11.044
Acknowledgements
Karla Chavez thanks the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT) of Mexico for the scholarship no. 1031784 granted during his Master of Sciences studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chávez-Álvarez, K., del Carmen Rivera-Cruz, M., Aceves-Navarro, L.A. et al. Physiological and microbiological hormesis in sedge Eleocharis palustris induced by crude oil in phytoremediation of flooded clay soil. Ecotoxicology 31, 1241–1253 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-022-02583-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-022-02583-x