Abstract
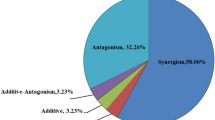
Information on joint toxicity is limited. To clarify the joint toxicity and the interactions among toxicants on different aquatic organisms, we investigated the acute toxicity of cadmium and sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, two chemicals with high concerns in Chinese waters, on the immobilization of Daphnia magna (D. magna) and the swimming behavior of Danio rerio (D. rerio). Our results illustrated that cadmium and sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate expressed a synergistic effect on the immobilization of D. magna; and an antagonistic effect on the swimming speed D. rerio, but a synergistic effect on its vertical position in the water column. Based on the observed data, we found the independent action model was more appropriate than the concentration addition model in the prediction of their joint toxicity. Our results gave an example of the joint toxicity investigation, and aided to comprehensive the toxicity action mode of chemical mixtures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
AIST (2013) AIST-MeRAM software, the Advanced Industrial Science and Technology. http://en-meram.aist-riss.jp/download/. Accessed 15 Sept 2015
Barry MJ (2012) Application of a novel open-source program for measuring the effects of toxicants on the swimming behavior of large groups of unmarked fish. Chemosphere 86:938–944. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.11.011
Bjerregaard HF (2001) Effect of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) on ion transport and intracellular calcium in kidney distal epithelial cells (A6). Toxicol In Vitro 15:531–537
Brown TJ et al. (2016) World Mineral Production (2010–2014). British Geological Survey (BGS). http://www.bgs.ac.uk/mineralsUK/statistics/worldStatistics.html. Accessed 17 Mar 2016
Cheng LB, Hu DZ, Yao MZ (1992) The synthesis and applicaiton of fine chemical products. Press of Dalian university of technology, Dalian, China
Chon T-S, Ji CW, Park Y-S, SE J (2009) Behavioral methods in ecotoxicology. In: Jrgensen S, Chon T-S, Recknagel FE (eds) Handbook of Ecological Modelling and Informatics. WIT Press, Boston, MA, pp 255–281
Ecotox database, USEPA. www.epa.gov/ecotox. Accessed 25 May 2016
Fukuda S, Kang IJ, Moroishi J, Nakamura A (2010) The application of entropy for detecting behavioral responses in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) exposed to different toxicants. Environ Toxicol 25:446–455. doi:10.1002/tox.20589
Garaventa F, Gambardella C, Di Fino A, Pittore M, Faimali M (2010) Swimming speed alteration of Artemia sp. and Brachionus plicatilis as a sub-lethal behavioural end-point for ecotoxicological surveys. Ecotoxicology 19:512–519. doi:10.1007/s10646-010-0461-8
Gonzalez-Pleiter M et al. (2013) Toxicity of five antibiotics and their mixtures towards photosynthetic aquatic organisms: implications for environmental risk assessment. Water Res 47:2050–2064. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.01.020
ISO (1996) Water quality — Determination of the acute lethal toxicity of substances to a freshwater fish [Brachydanio rerio Hamilton-Buchanan (Teleostei, Cyprinidae)] -- Part 3: Flow-through method. ISO 7346-3. http://www.iso.org/iso/home/store/catalogue_tc/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=14030. Accessed 8 Feb 2015
Jin YF, Shi WL, Ren G, Han L (2010) Effects of combined toxicity of LAS and Cd2+ on Cd accumulation and antioxidant enzyme activities in Carassius aquratus (in Chinese). J Zhejiang Univ 36:230–236
JSET (2006) Eco-Tox Statics software, the Japanese Society of Environmental Toxicology. http://www.intio.or.jp/jset/ecotox.htm. Accessed 10 Sept 2015
Le TT, Peijnenburg WJ (2013) Modeling toxicity of mixtures of perfluorooctanoic acid and triazoles (triadimefon and paclobutrazol) to the benthic cladoceran Chydorus sphaericus. Environ Sci Technol 47:6621–6629. doi:10.1021/es4001104
Lee S, Jung D, Kho Y, Ji K, Kim P, Ahn B, Choi K (2015) Ecotoxicological assessment of cimetidine and determination of its potential for endocrine disruption using three test organisms: Daphnia magna, Moina macrocopa, and Danio rerio. Chemosphere 135:208–216
Luo H, Li X, Fang T, Liu P, Zhang C, Xie H, Sun E (2015) The toxicity of binary mixture of Cu (II) ion and phenols on Tetrahymena thermophila. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:412–417. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.12.027
Mattsson K, Ekvall MT, Hansson LA, Linse S, Malmendal A, Cedervall T (2014) Altered behavior, physiology and metabolism in fish exposed to polystyrene nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 49:553–561. doi:10.1021/es5053655
Naddy RB, Cohen AS, Stubblefield WA (2015) The interactive toxicity of cadmium, copper, and zinc to Ceriodaphnia dubia and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ Toxicol Chem 34:809–815. doi:10.1002/etc.2870
Needleman HL (1995) Behavioral toxicology. Environ Health Perspect 103:77–79
OECD (2004) OECD Guideline for the Testing of chemicals, Daphina sp. Acute immobilisation test. http://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/essai-n-202-daphnia-sp-essai-d-immobilisation-immediate_9789264069954-fr. Accessed 26 Oct 2015
Oleszczuk P, Josko I, Skwarek E (2015) Surfactants decrease the toxicity of ZnO, TiO2 and Ni nanoparticles to Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology 24:1923–1932. doi:10.1007/s10646-015-1529-2
Pareschi MC, Ferretti ME, Zeni C, Caligiuri AS, Vignocchi B, Biondi C (1997) Effect of exposure to linear alkylbenzene sulphonateon cAMP levels in Ictalurus sp. Olfactory and gustatory tissues. Comp Biochem Physiol 116:11–16
Pourahmad J, O’Brien PJ (2000) A comparisson of cytotoxic mechanisms for Cu2+ and Cd2+. Toxicology 143:173–263
Poynton HC et al. (2007) Daphnia magna ecotoxicogenomics provides mechanistic insights into metal toxicity. Environ Sci Technol 41:1044–1050
Qi SZ, Wang C, Chen XF, Qin ZH, Li XF, Wang CJ (2013) ) Toxicity assessments with Daphnia magna of Guadipyr, a new neonicotinoid insecticide and studies of its effect on acetylcholinesterase (AChE), glutathione S-transferase (GST), catalase (CAT) and chitobiase activities. Ecotox Environ Safe 98:339–344
Ramazani RB, Krishnan HR, Bergeson SE, Atkinson NS (2007) Computer automated movement detection for the analysis of behavior. J Neurosci Methods 162:171–179. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.01.005
Sanchis J, Olmos M, Vincent P, Farre M, Barcelo D (2016) New insights on the influence of organic co-contaminants on the aquatic toxicology of carbon nanomaterials. Environ Sci Technol 50:961–969
SEPA (1987a) Water quality-determination of anionic surfactants – Methylene blue spectrophotometric method. GB/T 7494-1987. http://www.queshao.com/docs/43942/. Accessed 8 Feb 2015
SEPA (1987b) Water quality-determination of copper,zinc,lead and cadmium—Atomic absorption spectrometry. GB/T 7475-1987. http://www.doc88.com/p-5176184679255.html. Accessed 7 Feb 2015
SEPA (1996) Integrated wastewater discharge standard. GB8978-1996. http://www.safe001.com/2003wen/guobiao2/g139.htm. Accessed 27 Oct 2015
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal-ions. Free Radic Biol Med 18:321–336
Tollefsen KE, Petersen K, Rowland SJ (2012) Toxicity of synthetic naphthenic acids and mixtures of these to fish liver cells. Environ Sci Technol 46:5143–5150. doi:10.1021/es204124w
Tong F, Zhao Y, Gu X, Gu C, Lee CC (2015) Joint toxicity of tetracycline with copper(II) and cadmium(II) to Vibrio fischeri: effect of complexation reaction. Ecotoxicology 24:346–355. doi:10.1007/s10646-014-1383-7
Wang J, Pan ZJ, Zhang XD, Wen FY, Ma T, Jiang YF, Sun W (2006) Investigation on sonocatalytic degradation of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS) in the presence of ordinary anatase TiO2. Res Environ Sci 3:81–87
Wang L, Ye W, Zhou S, Lin K, Zhao M, Liu W (2009) Acute and chronic toxicity of organophosphate monocrotophos to Daphnia magna. J Environ Sci Health B 44:38–43. doi:10.1080/03601230802519611
Watanabe H et al. (2015) Chronic toxicity of an environmentally relevant mixture of pharmaceuticals to three aquatic organisms (alga, daphnid, and fish). Environ Toxicol Chem. doi:10.1002/etc.3285
Wu MY, Li KB (2002) Advances in research on treatment of surfactant pollution. Chinese J Nat 24:138–141 (in Chinese)
Wu Y, Zheng H, Chen J, Zhuo S, Wang L, Li Y, Zhu C (2007) Spectrophotometric method for the direct determination of anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl benzenesulfonate (SDBS) using a hydrophobic near‐infrared (NIR) cationic cyanine dye without solvent extraction. Anal Lett 37:711–723. doi:10.1081/al-120029747
Wu B, Zhao DY, Jia HY, Zhang Y, Zhang XX, Cheng SP (2009) Preliminary risk assessment of trace metal pollution in surface water from Yangtze River in Nanjing Section, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82:405–409
Wu JF, Yu ZM, Song XX, Wang Y (2006) Response of integrated biomarkers of fish (Lateolabrax japonicus) exposed to benzo[a]pyrene and sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate. Ecotox Environ Safe 65:230–236
Zeng XM (2008) Toxic effects of complex pollution of copper-surfactant and zinc-surfactant on Carassius Auratus Var. Pengze (in Chinese). Environ Sci Manage 33:37–39
Zeng XX et al. (2015) Spatial distribution, health risk assessment and statistical source identification of the trace elements in surface water from the Xiangjiang River, China. Environ Sci Pollut R 22:9400–9412
Zhang H, Yu J, Zhou SW (2014) Spatial distribution of As, Cr, Pb, Cd, Cu, and Zn in the water and sediment of a river impacted by gold mining. Mine Water Environ 33:206–216
Zhang Y, Ma J, Zhou S, Ma F (2015) Concentration-dependent toxicity effect of SDBS on swimming behavior of freshwater fishes. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40:77–85. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2015.05.005
Zhou S et al. (2015) Reduction in toxicity of coking wastewater to aquatic organisms by vertical tubular biological reactor. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 115:217–222. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.02.017
Zou XM, Lin ZF, Deng ZQ, Yin DQ, Zhang YL (2012) The joint effects of sulfonamides and their potentiator on Photobacterium phosphoreum: differences between the acute and chronic mixture toxicity mechanisms. Chemosphere 86:30–35
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, 21477014; NSFC-JST, 21261140334) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities. Thanks also go to Seiko Electric Co. Ltd. (Japan) for friendly provision of the lab-mode 3D-biosensor. Sincere thanks also are given to the anonymous reviewers who provided constructive suggestion and comments to us.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Ma, J., Shi, L. et al. Joint toxicity of cadmium and SDBS on Daphnia magna and Danio rerio . Ecotoxicology 25, 1703–1711 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1701-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1701-3