Abstract
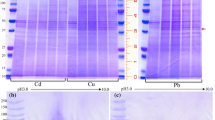
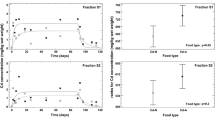
One of multiple functions of metalloproteins is to provide detoxification to excess metal levels in organisms. Here we address the induction and persistence of a range of low to high molecular weight copper- and zinc binding proteins in the collembolan species Tetrodontophora bielanensis exposed to copper- and zinc-enriched food, followed by a period of recovery from metal exposure, in absence and presence of food. After 10 days of feeding copper and zinc contaminated yeast, specimens were either moved to ample of leaf litter material from their woodland stand of origin or starved (no food offered). The molecular weight distribution of metal binding proteins was determined by native polyacryl gel electrophoresis. One gel was stained with Comassie brilliant blue and a duplicate gel dried and scanned for the amount of copper and zinc by particle-induced X-ray emission. Specimens exposed to copper and recovered from it with ample of food had copper bound to two groups of rather low molecular weight proteins (40–50 kDa) and two of intermediate size (70–80 kDa). Most zinc in specimens from the woodland stand was bound to two large proteins of about 104 and 106 kDa. The same proteins were holding some zinc in metal-exposed specimens, but most zinc was found in proteins <40 kDa in size. Specimens recovered from metal exposure in presence of ample of food had the same distribution pattern of zinc binding proteins, whereas starved specimens had zinc as well as copper mainly bound to two proteins of 8 and 10 kDa in size. Thus, the induction and distribution of copper- and zinc-binding proteins depend on exposure conditions, and the presence of low molecular weight binding proteins, characteristic of metallothioneins, was mainly limited to starving conditions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiard J-C, Amiard-Triquet C, Barka S, Pellerin J, Rainbow PS (2006) Metallothioneins in aquatic invertebrates: their role in metal detoxification and their use as biomarkers. Aquat Toxicol 76:160–202
Babczyńska A, Wilczek G, Wilczek P, Szulińska E, Witas I (2011a) Metallothioneins and energy budget indices in cadmium and copper exposed spiders Agelena labyrinthica in relation to their developmental stage, gender and origin. Comp Biochem Physiol C 154:161–171
Babczyńska A, Wilczek G, Szulińska E, Franiel I (2011b) Quantitative immunodetection of meallothioneins in relation to metals concentration in spiders from variously polluted areas. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1498–1503
Baudrimont M, Lemaire-Gony S, Ribeyre F, Metivaud J, Boudou A (1997) Seasonal variations of metallothionein concentrations in the Asiatic clam (Corbicula fluminea). Comp Biochem Physiol C 118:361–367
Bengtsson G, Gunnarsson T (1984) A micromethod for the determination of metal ions in biological tissues by furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Microchem J 29:282–287
Bengtsson G, Ek H, Rundgren S (1992) Evolutionary response of earthworms to long-term metal exposure. Oikos 63:289–297
Bertini I, Sigel A, Sigel H (2001) Handbook of metalloproteins. Marcel Dekker, New York
Binet MRB, Ma R, McLeod CW, Poole RK (2003) Detection and characterization of zinc- and cadmium-binding proteins in Escherichia coli by gel electrophoresis and laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 318:30–38
Bremner I, Davies NT (1975) The induction of metallothionein in rat liver by zinc injection and restriction of food intake. Biochem J 149:733–738
Capdevila M, Atrian S (2011) Metallothionein protein evolution: a miniassay. J Biol Inorg Chem 16:977–989
Dallinger R, Wieser W (1984) Molecular fractionation of Zn, Cu, Cd and Pb in the midgut gland of Helix Pomatia L. Comp Biochem Physiol C 79:125–129
Dallinger R, Berger B, Hunziger P, Kägi JHR (1997) Metallothionein in snail Cd and Cu metabolism. Nature 388:237–238
Dallinger R, Lagg B, Egg M, Schipflinger R, Chabicovsky M (2004) Cd accumulation and Cd-Metallothionein as a biomarker in Cepaea hortensis (Helcidae, Pulmonata) from laboratory exposure and metal-polluted habitats. Ecotoxicology 13:757–772
Degtyarenko K (2000) Bioinorganic motifs: towards functional classification of metalloproteins. Bioinformatics 16:851–864
den Besten PJ, Herwig HJ, Zandee DI, Voogt PA (1990) Cadmium accumulation and metallothionein-like proteins in the sea star Asterias rubens. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19:858–862
Engel DW, Brouwer M, Mercaldo-Allen R (2001) Effects of molting and environmental factors on trace metal body-burdens and hemocyanin concentrations in the American lobster, Homarus americanus. Mar Environ Res 52:257–269
Finger JM, Smith JD (1987) Molecular association of Cu, Zn, Cd and 210Po in the digestive gland of the squid Nototodarus gouldi. Mar Biol 95:87–91
Hashemi S, Kunwar PS, Blust R, De Boeck G (2008) Differential metallothionen induction patterns in fed and starved carp (Cyprinus carpio) during waterborne copper exposure. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:2154–2158
Hensbergen PJ, Donker MH, van Velzen MJM, Roelofs D, van der Schors RC, Hunziker PE, van Straalen NM (1999) Primary structure of a cadmium-induced metallothionein from the insect Orchesella cincta (Collembola). Eur J Biochem 259:197–203
Hensbergen PJ, Donker MH, Hunziger PE, van der Schors RC, van Straalen NM (2001) Two metal-binding peptides from the insect Orchesella cincta (Collembola) as a result of metallothionein cleavage. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 31:1105–1114
Holwerda DA (1991) Cadmium kinetics in freshwater clams. V. Cadmium-copper interaction in metal accumulation by Anodonta cygnea and characterization of the metal-binding protein. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 21:432–437
Irving H, Williams RJP (1948) Order of stability of metal complexes. Nature 162:746–747
Janssen H, Dallinger R (1991) Diversification of cadmium-binding proteins due to different levels of contamination in Arion lusitanicus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 20:132–137
Jiménez I, Gotteland M, Zarzuelo A, Uauy R, Speisky H (1997) Loss of the metal binding properties of metallothionein induced by hydrogen peroxide and free radicals. Toxicology 120:37–46
Kägi JHR (1991) Overview of metallothionein. Methods Enzymol 205:613–626
Nejmeddine A, Sautiere P, Dhainaut-Courtois N, Baert J-L (1992) Isolation and characterization of a Cd-binding protein from Allolobophora caliginosa (Annelida, Oligochaeta): distinction from metallothioneins. Comp Biochem Physiol Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 101:601–605
Nielsen JL, Abildtrup A, Christensen J, Watson P, Cox A, McLeod CW (1998) Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry in combination with gel electrophoresis: a new strategy for speciation of metal binding serum proteins. Spectrochim Acta Part B 53:339–345
Nordberg GF, Fowler BA, Nordberg M, Friberg LT (2007) Handbook on the toxicology of metals. Academic Press, Amsterdam Boston
O’Halloran TV, Culotta VC (2000) Metallochaperones, an intracellular shuttle service for metal ions. J Biol Chem 275:25057–25060
Palacios Ò, Atrian S, Capdevila M (2011) Zn- and Cu-thioneins: a functional classification for metallothioneins? J Biol Inorg Chem 16:991–1009
Roegener J, Lutter P, Reinhardt R, Blüggel M, Meyer HE, Anselmetti D (2003) Ultrasensitive detection of unstained proteins in acrylamide gels by native UV fluorescence. Anal Chem 75:157–159
Rogival D, van Campenhout K, Goenaga Infante H, Hearn R, Scheirs J, Blust R (2007) Induction and metal speciation of metallothionein in wood mice (Apodemus sylvaticus) along a metal pollution gradient. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:506–514
Sato M, Bremner I (1993) Oxygen free radicals and metallothionein. Free Radic Biol Med 14:325–337
Serafim MA, Company RM, Bebianno MJ, Langston WJ (2002) Effect of temperature and size on metallothionein synthesis in the gill of Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to cadmium. Mar Environ Res 54:361–365
Stürzenbaum SR, Winters C, Galay M, Morgan AJ, Kille P (2001) Metal ion trafficking in earthworms. Identification of a cadmium-specific metallothionein. J Biol Chem 276:34013–34018
Susnea I, Bernevic B, Wicke M, Ma L, Liu S, Schellander K, Przybylski M (2013) Application of MALDI-TOF-mass spectrometry to proteome analysis using stain-free gel electrophoresis. In: Cai Z, Liu S (eds) Applications of MALDI-TOF spectroscopy, Topics in current chemistry 331. Springer, Berlin, pp 37–54
Sutherland DEK, Stillman MJ (2011) The „magic numbers“of metallothionein. Metallomics 3:444–463
Tainer JA, Roberts VA, Getzoff ED (1991) Metal-binding sites in proteins. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2:582–591
Ulrich W, Fiera C (2010) Environmental correlates of body size distributions of European springtails (Hexapoda: Collembola). Glob Ecol Biogeogr 19:905–915
Weiss W, Weiland F, Görg A (2009) Protein detection and quantitation technologies for gel-based proteome analysis. Proteomics Methods Mol Biol 564:59–82
Yamamura M, Mori T, Suzuki KT (1981) Metallothionein induced in the earthworm. Experentia 37:1187–1189
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Heike Reise, Senckenberg Museum for Natural Science Görlitz, for providing T. bielanensis. The study was financed by the European Environmental Research Organization (EERO), The German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD, Bonn), and the Swedish Institute (SI, Stockholm). Thanks are also due to Sten Rundgren, Lund University, and to Kåseberga-Fisk AB, Löderup, for motivational support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bengtsson, G., Pallon, J., Nilsson, C. et al. PIXE-electrophoresis shows starving collembolan reallocates protein-bound metals. Ecotoxicology 25, 115–120 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1573-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1573-y