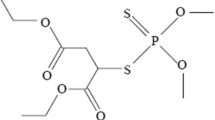
Abstract
The insecticide imidacloprid was evaluated under laboratory conditions in the adult male Italian wall lizards (Podarcis sicula) to assess its potential toxicity. By an acute oral test, LD50 was 503.76 mg/kg. Changes in spermatogenesis, plasma sex hormone levels and androgen and oestrogen receptor mRNAs were analysed by subchronic test and simulated environmental exposure. 15-days subchronic test, in which lizards were orally dosed on alternate days at 0, 10, 50, 100 mg/kg bw, showed a dose-dependent changes of testicular architecture and an increase of apoptotic processes. In a 30-days simulated environmental exposure spermatogenesis was arrested at secondary spermatocyte level and only few primary spermatocytes were TUNEL-positive. In all experimental groups imidacloprid was able to decrease both the level of sex hormones and the steroid receptor mRNAs. The results demonstrate that imidacloprid affects reproduction function of male lizards therefore precautions must be taken to minimize the harmful effects of this compound.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Donia MB, Goldstein LB, Bullman S, Tu T, Khan WA, Dechkovskaia AM, Abdel-Rahman AA (2008) Imidacloprid induces neurobehavioral deficits and increases expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein in the motor cortex and hippocampus in offspring rats following in utero exposure. J Toxicol Environ Health A 71(2):119–130
Amaral MJ, Carretero MA, Bicho RC, Soares AM, Mann RM (2012a) The use of a lacertid lizard as a model for reptile ecotoxicology studies–part 1 field demographics and morphology. Chemosphere 87(7):757–764
Amaral MJ, Bicho RC, Carretero MA, Sanchez-Hernandez JC, Faustino AM, Soares AM, Mann RM (2012b) The use of a lacertid lizard as a model for reptile ecotoxicology studies: part 2–biomarkers of exposure and toxicity among pesticide exposed lizards. Chemosphere 87(7):765–774
Andò S, Panno ML, Ciarcia G, Imbrogno E, Buffone M, Beraldi E, Scisci D, Angelini F, Botte V (1990) Plasma sex hormone concentration during the reproductive cycle in the male lizard Podarcis s sicula. J Reprod Fertil 90:353–360
Angelini F, Botte V (1992) Spermatogenesis in reptiles, dynamic and regulatory aspect. In: Dallai R (ed) Sex origin and evolution. Mucchi Selected Symposia and Monographs UZI, Modena, pp 211–230
Bal R, Naziroğlu M, Türk G, Yilmaz Ö, Kuloğlu T, Etem E, Baydas G (2012a) Insecticide imidacloprid induces morphological and DNA damage through oxidative toxicity on the reproductive organs of developing male rats. Cell Biochem Funct 30(6):492–499
Bal R, Türk G, Tuzcu M, Yilmaz O, Kuloglu T, Gundogdu R, Gür S, Agca A, Ulas M, Cambay Z, Tuzcu Z, Gencoglu H, Guvenc M, Ozsahin AD, Kocaman N, Aslan A, Etem E (2012b) Assessment of imidacloprid toxicity on reproductive organ system of adult male rats. J Environ Sci Health B 47(5):434–444
Balani T, Agrawal S, Thaker AM (2011) Hematological and biochemical changes due to short-term oral administration of imidacloprid. Toxicol Int 18:2–4
Bicho RC, Amaral MJ, Faustino AM, Power DM, Rêma A, Carretero MA, Soares AM, Mann RM (2013) Thyroid disruption in the lizard Podarcis bocagei exposed to a mixture of herbicides: a field study. Ecotoxicol 22(1):156–165
Bretveld R, Brouwers M, Ebisch I, Roeleveld N (2007) Influence of pesticides on male fertility. Scand J Work Environ Health 33(1):13–28
Bro E, Decors A, Millot F, Soyez D, Moinet M, Berny P, Mastain O (2010) Intoxications des perdrix grises en nature. Nouveau bilan de la surveillance « SAGIR». Faune Sauvage 289:26–32
Capula M, Aloise G (2011) Extreme feeding behaviours in the Italian wall lizard, Podarcis siculus. Acta Herpet 6(1):11–14
Cardone A (2012) Testicular toxicity of methyl thiophanate in the Italian wall lizard (Podarcis sicula): morphological and molecular evaluation. Ecotoxicol 21:512–523
Cardone A, Angelini F, Varriale B (1998) Autoregulation of estrogen and androgen receptor mRNAs and down regulation of androgen receptor mRNA by estrogen in primary cultures of lizard testis cells. Gen Comp Endocrinol 110:227–236
Cardone A, Comitato R, Bellini L, Angelini F (2002) Effects of the aromatase inhibitor fadrozole on plasma sex steroid secretion and spermatogenesis, and epididymis morphology in the lizard, Podarcis sicula. Mol Reprod Dev 63:63–70
Carreau S, Bouraima-Lelong H, Delalande C (2012) Estrogen, a female hormone involved in spermatogenesis. Adv Med Sc. 57(1):31–36
Carretero MA (2004) From set menu to a la carte. Linking issues in trophic ecology of Mediterranean lacertids. Ital J Zool 2:121–133
Chao SL, Casida JE (1997) Interaction of imidacloprid metabolites and analogues with the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor of mouse brain in relation to toxicity. Pest Biochem Physiol 58:77–88
De Falco M, Sciarrillo R, Capaldo A, Russo T, Gay F, Valiante S, Varano L, Laforgia V (2007) The effects of the fungicide methyl thiophanate on adrenal gland morphophysiology of the lizard, Podarcis sicula. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 53:241–248
de Snoo GR, Scheidegger NMI, de Jong FMW (1999) Vertebrate wildlife incidents with pesticides: a European survey. Pestic Sci 55:47–54
Frigato E, Vallone D, Bertolucci C, Foulkes NS (2006) Isolation and characterization of melanopsin and pinopsin expression within photoreceptive sites of reptiles. Naturwissenschaften 93(8):379–385
Gibbons JW, Scott DE, Ryan TJ, Buhlman KA, Tubervulle TD, Metts BS, Greene JL, Mills T, Leiden Y, Poppy S, Winne CT (2000) The global decline of reptiles, déjà vu amphibians. Bioscience 50:653–666
Holdcraft RW, Braun RE (2004) Hormonal regulation of spermatogenesis. Int J Androl 27(6):335–342
Hopkins WA (2000) Reptile ecotoxicology: challenges and opportunities on the last frontier in vertebrate ecotoxicology. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2391–2393
Kapoor U, Srivastava MK, Srivastava LP (2011) Toxicological impact of technical imidacloprid on ovarian morphology hormones and antioxidant enzymes in female rats. Food Chem Toxicol 49:3086–3089
Latli B, D’Amour K, Casida JE (1999) Novel and potent 6-chloro-3-pyridinyl ligands for the α4β2 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Med Chem 42:2227–2234
Maclean JA II, Wilkinson MF (2005) Gene regulation in spermatogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol 71:131–197
Mathur PP, Huang L, Kashou A, Vaithinathan S, Agarwal A (2011) Environmental toxicants and testicular apoptosis. Open Reprod Sc. J 3:114–124
Matsuda K, Buckingham SD, Kleier D, Rauh JJ, Grauso M, Sattelle DB (2001) Neonicotinoids: insecticides acting on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22(11):573–580
Matthews J, Zacharewski T (2000) Differential binding affinities of PCBs, HO-PCBs, and aroclors with recombinant human, rainbow trout (Onchorhynkiss mykiss), and green anole (Anolis carolinensis) estrogen receptors, using a semi-high throughput competitive binding assay. Toxicol Sci 53(2):326–339
McFarland CA, Quinn MJ Jr, Boyce J, Bazar MA, Talent LG, Johnson MS (2009) Toxic effects of oral hexahydro-1,3,5-triazine in the western fence lizard (Sceloporus occidentalis). Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1043–1050
McFarland CA, Quinn MJ Jr, Boyce J, LaFiandra EM, Bazar MA, Talent LG, Johnson MS (2011) Toxic effects of oral 2-amino-4,6- dinitrotoluene in the western fence lizard (Sceloporus occidentalis). Environ Pollut 159:466–473
Mencke N, Jeschke P (2002) Therapy and prevention of parasitic insects in veterinary medicine using imidacloprid. Curr Top Med Chem 2:701–715
Najafi GR, Razi M, Hoshyar A, Shahmohamadloo S, Feyzi S (2010) The effect of chronic exposure with imidacloprid insecticide on fertility in mature male rats. Inter J Steril Fertil 4:9–16
Pauli BD, Money S, Sparling DW (2010) Ecotoxicology of pesticides in reptiles. In: Sparling DW, Linder G, Bishop CA, Krest S (eds) Ecotoxicology of amphibians and reptiles, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 203–224
Rich CN, Talent LG (2009) Soil ingestion may be an important route for the uptake of contaminants by some reptiles. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:311–315
Rosen G, O’Bryant E, Matthews J, Zacharewski T, Wade J (2002) Distribution of androgen receptor mRNA expression and immunoreactivity in the brain of the green anole lizard. J Neuroendocrinol 14(1):19–28
Rouchaud J, Gustin F, Wauters A (1994) Soil biodegradation and leaf transfer of insecticide imidacloprid applied in seed dressing in sugar beet crops. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 53:344–350
Saradha PP, Mathur B (2006) Effect of environmental contaminants on male reproduction. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 21:34–41
Schirmer SU, Eckhardt I, Lau H, Klein J, DeGraaf YC, Lips KS, Pineau C, Gibbins IL, Kummer W, Meinhardt A, Haberberger RV (2011) The cholinergic system in rat testis is of non-neuronal origin. Reproduction 142(1):157–166
Siddiqui A, Choudhary M, Goriya HV, Bhavsar SK, Thaker AM (2007) Evaluation of immunotoxic effect of short-term administration of quinalphos and imidacloprid in white leghorn cockerels. Toxicol Int 14:15–19
Sparling DW, Linder G, Bishop CA, Krest SK (2010) Recent advancements in amphibian and reptile ecotoxicology. In: Sparling DW, Linder G, Bishop CA, Krest S (eds) Ecotoxicology of amphibians and reptiles, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 1–14
Sumida K, Ooe N, Saito K, Kaneko H (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of reptilian estrogen receptor cDNAs. Mol Cell Endocrinol 183(1–2):33–39
Tabb MM, Blumberg B (2006) New modes of action for endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Mol Endocrinol 20(3):475–482
Todd BD, Wilson JD, Gibbons JW (2010) The global status of reptiles and causes of their decline. In: Sparling DW, Linder G, Bishop CA, Krest S (eds) Ecotoxicology of amphibians and reptiles, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 69–104
Tomizawa M (2004) Neonicotinoids and derivatives: effects in mammalian cells and mice. J Pestic Sci 29(3):177–183
Tomizawa M, Casida JE (2000) Imidacloprid, thiacloprid, and their imine derivatives up-regulate the α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in M10 cells. Toxicol App Pharmacol 169:114–120
Tomizawa M, Casida JE (2005) Neonicotinoid insecticide toxicology: mechanisms of selective action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 45:247–268
Tomlin C (2009) The pesticide manual: a world compendium, 15th edn. British Crop Protection Council, London
TSK (Trimmed Spearman-Karber) program, (1991) Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory, US Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, OH 45268, USA
Weir SM, Suski JG, Salice CJ (2010) Ecological risk of anthropogenic pollutants to reptiles: evaluating assumptions of sensitivity and exposure. Environ Pollut 158:3596–3606
Yeh IJ, Lin TJ, Hwang DY (2010) Acute multiple organ failure with imidacloprid and alcohol ingestion. Am J Emerg Med 28(255):e1–e3
Young LJ, Godwin J, Grammer M, Gahr M, Crews D (1995) Reptilian sex steroid receptors: amplification, sequence and expression analysis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 55(2):261–269
Acknowledgments
The author wish to thank Mr. Mark Walters for linguistic revision. This work was supported by intramural funds of Biology Department to A.C.
Conflict of interest
The author declare they have no competing interests, be it financial, personal or professional.
Ethical standards
All animals were captured with the authorization of 06/01/2000 No. SCN/2D/2000/9213 of the Italian Ministry of the Environment. The experiments were carried out in compliance with the ethical provisions enforced by the European Union and authorized by the National Committee of the Italian Ministry of Health on in vivo experimentation ( Dept. for Veterinary Public Health, Nutrition and Food Safety). All efforts were made to avoid animal suffering and to minimize the number of specimens used. The animals were maintained in accordance with the institutional guidelines for care and use of laboratory animals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to the memory of Giuseppe Falcone, an unforgettable friend who died prematurely, in recognition of his devotion to the pursuit of perfection in photography and digital art-work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cardone, A. Imidacloprid induces morphological and molecular damages on testis of lizard (Podarcis sicula). Ecotoxicology 24, 94–105 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1361-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1361-0