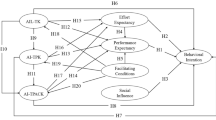
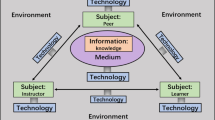
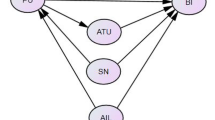
Abstract
This research investigated 1,552 university students to explore the correlation between their learning effectiveness of artificial intelligence (AI) technology application and its influencing factors. The aim is to provide a reference for school planning and application of AI in information and communications technology (ICT) teaching. The results show that ICT self-efficacy (ICT-SE) has a significant direct effect, and human-computer interaction experience (HCIE) has a significant indirect effect on lLearning effectiveness of AI-based technology applications (LE-AITA). The impact model of university student ICT-SE and HCIE on LE-AITA exhibits a good fit. The recommendation is that Taiwan education improve the AI learning environment, provide a suitable platform for the use and development of educational technology, and create a seamless teaching and learning experience. We discuss influencing factors and provide suggestions for the development of AI education.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, K., Qadir, J., Al-Fuqaha, A., Iqbal, W., El-Hassan, A., Benhaddou, D., & Ayyash, M. (2020). Artificial intelligence in education: A panoramic review. IEEE Access, 8, 75264-75278. https://doi.org/10.35542/osf.io/zvu2n
Ahn, J., & Clegg, T. (2017). Human-Computer Interaction and Education: Designing for Technology-Enhanced Learning Experiences. In The Wiley Handbook of Human Computer Interaction Set (Vol. 2, pp. 821-830). Wiley-Blackwell. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118976005.ch38
Ajzen, I. (2020). The theory of planned behavior: Frequently asked questions. Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies, 2(4). https://doi.org/10.1002/hbe2.195
Alahakoon, C. N. K., & Somaratne, S. (2020). Measuring the levels of sources of ICT self-efficacy among the humanities and social sciences undergraduates in Sri Lanka. Journal of the University Librarians Association of Sri Lanka, 23(2), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.4038/jula.v23i2.8006
Alawamleh, M., Al-Twait, L. M., & Al-Saht, G. R. (2020). The effect of online learning on communication between instructors and students during Covid-19 pandemic. Asian Education and Development Studies. https://doi.org/10.1108/AEDS-06-2020-0131
Al-Rahmi, A.M., Al-Rahmi, W.M., Alturki, U., Aldraiweesh, A., Almutairy, S., Al-Adwan, A.S. (2021). Exploring the factors affecting mobile learning for sustainability in higher education. Sustainability, 13(14), Article 7893. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13147893
Al-Said, N., & Al-Said, K. M. (2020). Assessment of acceptance and user experience of human-computer interaction with a computer interface. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, 14(11), 107–125.
Ardito, G. & Betül, C. (2021). The development of autonomous student learning networks: Patterns of interactions in an open world learning environment for teachers exploring teaching with and through computer science. Sustainability, 13(16). Article: 8696. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13168696
Ardito, L., Coccia, M., & Petruzzelli, A.M. (2021). Technological exaptation and crisis management: Evidence from COVID-19 outbreaks. R & D Management 51(2). https://doi.org/10.1111/radm.12455.
Asthana, P., & Hazela, B. (2020). Applications of machine learning in improving learning environment. Multimedia Big Data Computing for Iot Applications, 163, 417–433.
Balakrishnan, J., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2021). Role of cognitive absorption in building user trust and experience. Psychology & Marketing, 38(4), 643–668. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21462
Bagozzi, R. P., & Yi, Y. (1988). On the evaluation of structural equation models. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 16(1), 74–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02723327
Bentler, P. M., & Bonett, D. G. (1980). Significance tests and goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychological Bulletin, 88(3), 588–606.
Chang, Y., Lee, S., Wong, S. F., & Jeong, S. P. (2021). AI-powered learning application use and gratification: an integrative model. Information Technology & People. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITP-09-2020-0632
Chaudhry, M. A., & Kazim, E. (2021). Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIEd): A high-level academic and industry note 2021. AI and Ethics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43681-021-00074-z
Che, Y., Sivaparthipan, C. B., & Daniel, J. A. (2021). Human–computer interaction on IoT-based college physical education. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05895-y
Chen, H. R., Lin, W. S., & Lin Koong, H. C. (2021). Is it possible for young students to learn the AI-STEAM application with experiential learning? Sustainability, 13(19), 11114. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131911114
Chen, X., Xie, H., Zor, D., & Hwang, G. (2020). Application and theory gaps during the rise of Artificial Intelligence in Education. Computers & Education: Artificial Intelligence, 1, 100002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2020.100002
Criollo, C. S., Abad-Vásquez, D., Martic-Nieto, M., Velásquez-G, F. A., Pérez-Medina, J.-L., & Luján-Mora, S. (2021). Towards a new learning experience through a mobile spplication with augmented reality in engineering education. Applied Sciences, 11(11), 4921. https://doi.org/10.3390/app1111492
Choi, Y.J. & Park, J.W. (2020). Investigating factors influencing the behavioral intention of online duty-free shop users. Sustainability, 12(17). Artice l7108. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177108
Cox, A. M. (2021). Exploring the impact of Artificial Intelligence and robots on higher education through literature-based design fictions. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 18(3). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-020-00237-8
Davis, F. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly, 13, 319–340. https://doi.org/10.2307/249008
Ehrenbrink, P., & Möller, S. (2018). Development of a reactance scale for human–computer interaction. Quality and User Experience, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41233-018-0016-y
Epoch Times (2021). Taiwan's AI development is expected to catch up with the United States within three years (台AI發展 3年內有望追近美國). Retrieved December 30, 2021, form https://www.epochtimes.com/b5/21/3/24/n12832844.htm
Future City (2021). Rushing to catch up and cultivating AI talents to make Taiwan more competitive in the AI generation 急起直追培育AI人才 讓台灣在AI世代更具競爭力. Retrieved December 30, 2021, form https://futurecity.cw.com.tw/article/1209
Fahimirad, M., & Kotamjani, S. S. (2018). A review on application of Artificial Intelligence in teaching and learning in educational contexts. International Journal of Learning and Development, 8(4). https://doi.org/10.5296/ijld.v8i4.14057
González-Calatayud, V., Prendes-Espinosa, P., & Roig-Vila, R. (2021). Artificial intelligence for student assessment: A systematic review. Applied Sciences, 11, 5467.
Gopal, R., Singh, V., & Aggarwal, A. (2021). Impact of online classes on the satisfaction and performance of students during the pandemic period of COVID 19. Education and Information Technologies, 26, 6923–6947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10523-1
Guan, C., Mou, J., & Jiang, Z. (2020). Artificial intelligence innovation in education: A twenty-year data-driven historical analysis. International Journal of Innovation Studies, 4, 134–147.
Guillén-Gámez, F. D., Martínez, S. J. R., & Camacho, X. G. O. (2020). Diagnosis of the attitudes towards ICT of education students according to gender and educational modality. Apertura, 12(1), 56–71. https://doi.org/10.32870/Ap.v12n1.1786
Gravett, S., & Kroon, R. (2021). Learning to become a teacher: Student teachers’ experiences and perceptions of a one-year initial teacher education programme. Educational Studies, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/03055698.2021.1935216
Hatlevik, O. E., Throndsen, I., Loi, M., & Guðmundsdóttir, G. B. (2018). Students' ICT self-efficacy and computer and information literacy: Determinants and relationships. Computer & Education, 118, 107–119.
Hair Jr., J. F., Anderson, R. E., Tatham, R. L., & Black, W. C. (1998). Multivariate Data Analysis (5th ed.). Prentice Hall.
Hornbæk, K., & Hertzum, M. (2017). Technology acceptance and user experience: A review of the experiential component in HCI. ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction, 24, Article 33. https://doi.org/10.1145/3127358
Hu, L., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6(1), 1–55.
Jarvenpaa, S. L., Tractinsky, N., & Vitale, M. (2000). Consumer trust in an internet store. Information Technology and Management, 1(1/2), 45–71.
Junyi Educational Learning Platform (均一教育平台) (2021). Taipei cool cloud class (Junyi Academy). Retrieved December 12, 2021, from https://www.junyiacademy.org/partner/cooc
Kaplan, A. M., & Haenlein, M. (2016). Higher education and the digital revolution: About MOOC, SPOCs, social media, and the cookie monster. Business Horizons, 59, 441–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2016.03.008
Krejcie, R. V., & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 30, 607–610.
Liu, J., & Wang, S. (2020). The change of teachers’ role in teaching under the environment of “Artificial Intelligence +”. 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Education (ICAIE), 98–102. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAIE50891.2020.00030
Lopatovska, I. (2019). Overview of the intelligent personal assistants. Ukrainian Journal on Library and Information Science. https://doi.org/10.31866/2616-7654.3.2019.169669
Loeng, S. (2020). Self-directed learning: A core concept in adult education. Education Research International, 2020(4/5), 3816132. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3816132
Luckin, R., Holmes, W., Griffiths, M., & Forcier, L. B. (2016). Intelligence unleashed: An argument for AI in education. UCL Knowledge Lab: London, UK. http://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1475756/
Martin, A. M. (2021). Instructor qualities and student success in higher education online courses. Journal of Digital Learning in Teacher Education, 37(1), 65–80.
Maqableh, M., & Jaradat, M. (2021). Exploring the determinants of students’ academic performance at university level: The mediating role of internet usage continuance intention. Education and Information Technologies, 26, 4003–4025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10453-y
Ministry of Education (2021). In material network (因材網). Retrieved December 12, 2021, form https://adl.edu.tw/HomePage/home/
Mlambo, S., Rambe, P., & Schlebusch, L. (2020). Effects of Gauteng province’s educators’ ICT self-efficacy on their pedagogical use of ICTS in classrooms. Heliyon, 4(6), e03730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03730
Mozer, M. C., Wiseheart, M., & Novikoff, T. P. (2019). Artificial intelligence to support human instruction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116(10). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1900370116
MUhie, Y. A., & Woldie, A. B. (2020). Integration of artificial intelligence technologies in teaching and learning in higher education. Science and Technology, 10(1), 1–7.
Musharraf, S., Bauman, S., Anis-ul-Haque, M., & Malik, J. A. (2018). Development and validation of ICT self-efficacy scale: Exploring the relationship with cyberbullying and victimization. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(12), 2867.
Nayanajith, D. A. G., & Damunupola, K. A. (2021). Impact of perceived behavioral control on e-learning adoption. Interdisciplinary Research in Education, 5(1-2), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3126/ire.v5i1-2.34728
Nazari, N., Shabbir, M. S., & Setiawan, R. (2021). Application of artificial intelligence powered digital writing assistant in higher education: randomized controlled trial. Heliyon, 7(5), e07014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07014
Netherlands Innovation Network in Taiwan (2020). Artificial Intelligence: an overview of policies and developments in Taiwan. Taipei: The Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Policy. https://www.rvo.nl/sites/default/files/2020/04/AI-Developments-in-Taiwan.pdf
Oberländer, M., Beionicke, A., & Bipp, T. (2020). Digital competencies: A review of the literature and applications in the workplace. Computer & Education, 146, 103752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103752
Oudeyer, P.Y. (2019). Developmental autonomous learning: AI, cognitive sciences and educational technology. The 19th ACM International conference on intelligent virtual agents. Paris France. https://doi.org/10.1145/3308532.3337710
Owoc, M.L., Sawicka, A., & Weichbroth, P. (2021). Artificial intelligence technologies in education: Benefits, challenges and strategies of implementation, ArXiv, abs/2102.09365. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85001-2_4
Pan, X. (2020). Technology acceptance, technological self-efficacy, and attitude toward technology-based self-directed learning: Learning motivation as a mediator. Frontier in Psychology, (11), 564294. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.564294
Paul, J., & Jefferson, F. (2019). A comparative analysis of student performance in an online vs. face-to-face environmental science course from 2009 to 2016. Frontiers Computer Science, 1(7). https://doi.org/10.3389/fcomp.2019.00007
Pei, L., & Wu, H. (2019). Does online learning work better than offline learning in undergraduate medical education? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medical Education Online, 24(1), 1666538.
Pillai, K. R., Upadhyaya, P., Prakash, A. V., Ramaprasad, B. S., Mukesh, H. V., & Pai, Y. (2021). End-user satisfaction of technology-enabled assessment in higher education: A coping theory perspective. Education and Information Technologies, 26, 3677–3698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10401-2
Podgorsek, S., Kacjan, B., & Starcic, A. I. (2019). The foreign language teacher’s role in ICT-supported instruction. Journal of Contemporary Educational Studies, 70(36), 174–190.
Rahoo, L. A., Hasnain, P., Ahmed, T., Khan, M. A., & Asghar, A. (2021). Measuring the awareness and acceptance level innovative learning strategies of higher secondary school teachers of Sindh, Pakistan. Journal of Contemporary Issues in Business and Government, 27(2), 6781–6788.
Rajabalee, Y. B., & Santally, M. I. (2020). Learner satisfaction, engagement and performances in an online module: Implications for institutional e-learning policy. Education and Information Technologies, 26, 2623–2656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-020-10375-1
Rapanta, C., Botturi, L., Goodyear, P., & Koole, M. (2020). Online university teaching during and after the Covid-19 crisis: Refocusing teacher presence and learning activity. Postdigital Science and Education, 2, 923–945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42438-020-00155-y
Reljić, V., Milenković, I., Dudić, S., Šulc, J., & Bajči, B. (2021). Augmented reality applications in Industry 4.0 environment. Applied Sciences, 11(12), 5592. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125592
Rohatgi, A., Scherer, R., & Hatlevik, O. E. (2016). The role of ICT self-efficacy for students' ICT use and their achievement in a computer and information literacy test. Computer & Education, 102, 103–116.
Schiff, D. (2021). Out of the laboratory and into the classroom: the future of artificial intelligence in education. AI & Society, 36, 331–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-020-01033-8
Scott, S., & Bruce, R. (1994). Determinants of innovative behavior: A path model of individual innovation in the workplace. The Academy of Management Journal, 37(3), 580–607. https://doi.org/10.2307/256701
Sahin, D. & Yilmaz, R. M. (2020). The effect of augmented reality technology on middle school students’ achievements and attitudes towards science education. Computer & Education, 144. Article 103710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103710
Şendurur, P., & Yılıdrım, S. (2019). Teachers’ computer self-efficacy scale: Development and validation. Kastamonu Education Journal, 27(2), 433–441. https://doi.org/10.24106/kefdergi.2497
Seo, K., Tang, J., Roll, I., Fels, A., & Yoon, D. (2021). The impact of artificial intelligence on learner–instructor interaction in online learning. Internation Journal of Education Technology in Higher Education, 18(54). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-021-00292-9
Sezer, B. & Yuilmaz, R. (2019). Learning management system acceptance scale (LMSAS): A validity and reliability study. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 35(3), 15–30. https://ajet.org.au/index.php/AJET/article/view/3959
Shehzadi, S., Nisar, Q. A., Hussain, M. S., Basheer, M. F., Hameed, W. U., & Chaudhry, N. I. (2020). The role of digital learning toward students' satisfaction and university brand image at educational institutes of Pakistan: a post-effect of COVID-19. Asian Education and Development Studies, 10(2), 276–294.
Siswa, T. A. Y. (2020). The effectiveness of artificial intelligence on education: learning during the pandemic and in the future. International Journal of Engineering & Computer Science, 3(1), 24–30. https://doi.org/10.31295/ijecs.v3n1.195
Stojsic, I., Ivkov-Dzigurski, A., Maricic, O., Stanisavljevic, J., Jovanov, J. M., & Visnic, T. (2020). Students' attitudes toward the application of mobile augmented reality in higher education. Journal for General Social Issues, 29(4), 535–554. https://doi.org/10.5559/di.29.4.02
Taiwan Bureau of Industry (2021). Taiwan AI new generation talent training program (AI人才培育計畫). Retrieved December 29, 2021, form http://140.92.87.33/zh-tw/info
Taiwan Executive Yuan (2021). Digital economy (數位經濟). Retrieved December 30, 2021, form https://www.ey.gov.tw/achievement/5B6F7E717F7BADCE
Taiwan Industrial Technology Research Institute (2021). Artificial intelligence co-creation platform. Retrieved December 2, 2021, form https://www.itri.org.tw/english/Artificial-intelligence-co-creation-platform?CRWP=1070633546353516140
Taiwan Ministry of Education Statistics (2021a). Number of students in colleges and universities-search by subject category (大專院校學生數). Retrieved December 2, 2021, form https://eds.moe.gov.tw/edust/webMain.aspx?sys=100&funid=eduout&funid2=B030300&cycle=4&outkind=1&outmode=8&defmk=1&outkind=1&fldlst=11111111111&codlst0=1111111111111111111111111111111&codlst1=1&dfknd=1212
Taiwan’s Ministry of Education Statistics (2021b). Number of students by colleges and universities (大專院校學生數). Retrieved December 2, 2021, form https://depart.moe.edu.tw/ed4500/News_Content.aspx?n=5A930C32CC6C3818&sms=91B3AAE8C6388B96&s=596D9D77281BE257
Taiwan News (2021). Three industries in Taiwan to face talent shortages before 2023: Talent needed for AI, offshore wind energy, IC design over next three years. https://www.taiwannews.com.tw/en/news/4196350
Tang, L. P., & Austin, M. J. (2009). Students’ perceptions of teaching technologies, application of technologies, and academic performance. Computers & Education, 53(4), 1241–1255.
Tezer, M., & Soykan, F. (2017). Acceptance scale of tablet computers by secondary education students: Validity and reliability study. Journal of Universal Computer Science, 23(12), 1132–1146.
Tuomi, I. (2018). The impact of artificial intelligence on learning, teaching, and education: Policies for the future. European Union: Luxembourg. https://doi.org/10.2760/12297
Tussyadiah, I., & Miller, G. (2019). Perceived impacts of artificial intelligence and responses to positive behaviour change intervention. Information and Communication Technologies in Tourism, 28, 359–370.
Tsai, C. C., Cheng, Y. M., Tsai, Y. S., & Lou, S. J. (2021). Impacts of AIOT implementation course on the learning outcomes of senior high school students. Education Sciences, 11(2), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11020082
van Schaik, P., & Ling, J. (2005). Five psychometric scales for online measurement of the quality of human-computer interaction in web sites. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 18(3), 309–322.
Wang, L. Y. K., Lew, S. L., Lau, S. H., & Leow, M. C. (2019). Usability factors predicting continuance of intention to use cloud e-learning application., Heliyon, 5(6), e01788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01788
Wang, Y., Liu, C., & Tu, Y. F. (2021). Factors affecting the adoption of AI-based applications in higher education: An analysis of teachers' perspectives using structural equation modeling. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 24(3), 116–129.
Wang, Y. P., & Zheng, G. (2021). Application of artificial intelligence in college dance teaching and its performance analysis. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning, 15(16), 178. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v15i16.15939
Wang, Y. Y., Wang, Y. S. (2019). Development and validation of an artificial intelligence anxiety scale: an initial application in predicting motivated learning behavior. Journal of Interactive Learning Environments. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2019.1674887
Xu, W., Dainoff, M.J., Ge, L., & Gao, Z. (2021). From human-computer interaction to human-AI interaction: New challenges and opportunities for enabling human-centered AI. ArXiv, abs/2105.05424.
Yang, B., Wei, L., & Pu, Z. (2020). Measuring and improving user experience through artificial intelligence-aided design. Frontiers in Psychology, 11, 595374. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.595374
Yang, Y. (2021). The talent training mode of international service design using a human–computer interaction intelligent service robot from the perspective of cognitive psychology. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 600218. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.600218
Yen, S. C., Lo, Y., Lee, A., & Enriquez, J. (2018). Learning online, offline, and in-between: Comparing student academic outcomes and course satisfaction in face-to-face, online, and blended teaching modalities. Education and Information Technologies, 23(5), 2141–2153.
Yu, T. K. (2007). A comparative study of the learning effectiveness of the technological media learning environment. Journal of Educational Psychology, 39, 69–90. http://epbulletin.epc.ntnu.edu.tw/upload/journal/prog/8ca09628_20171213.pdf
Yusop, F. D., Habibi, A., & Razak, R. A. (2021). Factors affecting Indonesian preservice teachers' use of ICT during teaching practices through theory of planned behavior. SAGE Open, 11(2). https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440211027572
Yunusa, A. A., & Umar, I. N. (2021). A scoping review of critical predictive factors (CPFs) of satisfaction and perceived learning outcomes in E-learning environments. Education and Information Technologies, 26(1), 1223–1270.
Zanzotto, F. M. (2019). Viewpoint: Human-in-the-loop Artificial Intelligence. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 64, 243–252.
Zawacki-Richter, O., Marín, V. I., Bond, M., & Gouverneur, F. (2019). Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education – where are the educators? International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 16, 39. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-0171-0
Zhou, P., Wu, X., Xu, H., & Wang, G. (2021). The college students' oral English education strategy using human-computer interaction simulation system from the perspective of educational psychology. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 723981. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.723981
Acknowledgements
This paper was written while the authors were supported by a grant from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (MOST 109-2511-H-224-002-MY3)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Each author listed above has made substantial contributions (data collection, data analysis and interpretation, draft, major revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be released) to the conception, design of the study, manuscript or substantively revised it. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chou, CM., Shen, TC., Shen, TC. et al. Influencing factors on students’ learning effectiveness of AI-based technology application: Mediation variable of the human-computer interaction experience. Educ Inf Technol 27, 8723–8750 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10866-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10866-9