Summary
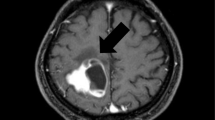
Primary acinar soft part sarcoma of the lung (ASPS) is a rare malignancy with unique cellular structure and clinical and genetic characteristics. Most patients do not exhibit clear clinical symptoms, with only a few developing respiratory symptoms. The typical histological characteristics are acinoid or organ-like structures. Immunofluorescence in situ hybridization suggests a rearrangement of the transcription factor E3 gene. Patients respond poorly to chemotherapy and are, thus, primarily treated with surgery and targeted therapy. We report herein a unique case of primary alveolar soft part sarcoma of the lung. The patient was a 24-year-old man with metastases to multiple organs, such as the brain, lungs, pancreas, and liver. The craniocerebral lesions attained partial remission after whole-brain radiotherapy and targeted combined immunotherapy, and other distant metastases completely disappeared after targeted combined immunotherapy (anlotinib and camrelizumab), indicating significant treatment efficacy. Anlotinib is an oral multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that exerts its anti-tumor effects by acting on various kinases. Camrelizumab is a humanized immunoglobulin G4 monoclonal antibody that can target PD-1 to block the interaction between PD-L1 and programmed death ligand 2, ultimately causing an anti-tumor effect. This is the first report of successful use of anlotinib combined with camrelizumab in the treatment of advanced primary ASPS. The treatment benefit provides preliminary evidence that targeted therapy, combined with immunotherapy, may be a safe and effective approach to treat primary pulmonary ASPS patients, thus warranting further investigation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christopherson WM, Foote FW, Stewart FW (1952) Alveolar soft part sarcomas; structurally characteristic tumors of uncertain histogenesis. Cancer 5(1):100–111
Soheilifar MH, Taheri RA, Zolfaghari Emameh R et al (2018) Molecular landscape in alveolar soft part sarcoma:implications for molecular targeted therapy. Biomed Pharmacother 103:889–896
Mitton B, Federman N (2012) Alveolar soft part sarcomas: molecular pathogenesis and implications for novel targeted therapies. Sarcoma 2012:428789
Paoluzzi L, Maki RG (2019) Diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of alveolar soft part sarcoma: a review. JAMA Oncol 5(2):254–260
Trabelsi A, Ben Abdelkrim S, Taher Yacoubi M et al (2009) Sarcome alvéolaire primitif du poumon. Rev Mal Respir 26(3):329–332
Zhao M, Rao Q, Wu C, Zhao Z, He X, Ru G (2015) Alveolar soft part sarcoma of lung: report of a unique case with emphasis on diagnostic utility of molecular genetic analysis for TFE3 gene rearrangement and immunohistochemistry for TFE3 antigen expression. Diagn Pathol 10:160
Tsutsumi Y, Deng YL (1991) Alveolar soft part sarcoma of the pulmonary vein. Acta Pathol Jpn 41(10):771–777
Kim YD, Lee CH, Lee MK et al (2007) Primary alveolar soft part sarcoma of the lung. J Korean Med Sci 22(2):369–372
Wang H, Jacobson A, Harmon DC et al (2016) Prognostic factors in alveolar soft part sarcoma: a SEER analysis. J Surg Oncol 113(5):581–586
Jagodzińska-Mucha P, Świtaj T, Kozak K et al (2017) Long-term results of therapy with sunitinib in metastatic alveolar soft part sarcoma. Tumori 103(3):231–235
Orbach D, Brennan B, Casanova M et al (2013) Paediatric and adolescent alveolar soft part sarcoma:a joint series from European cooperative groups. Pediatr Blood Cancer 60(11):1826–1832
Meng N, Zhang X, Liao A et al (2014) Management of recurrent alveolar soft-part sarcoma of the tongue after external beam radiotherapy with iodine-125 seed brachytherapy. Head Neck 36(12):E125–E128
Sparber-Sauer M, Seitz G, Von Kalle T et al (2018) Alveolar soft-part sarcoma: primary metastatic disease and metastatic relapse occurring during long-term follow-up. Pediatr Blood Cancer 65(12):e27405
Falkensternge RF, Kimmich M, Wohlleber M et al (2013) Lung metastasis of primary alveolar soft-part sarcoma occurring 20 years after initial treatment. Case Rep Oncol Med 2013(1):690520
Brennan B, Zanetti I, Orbach D et al (2018) Alveolar soft part sarcoma in children and adolescents: the European Paediatric Soft Tissue Sarcoma study group prospective trial (EpSSG NRSTS 2005). Pediatr Blood Cancer 65:4
Flores RJ, Harrison DJ, Federman NC, Furman WL, Huh WW, Broaddus EG, Okcu MF, Venkatramani R (2018) Alveolar soft part sarcoma in children and young adults: a report of 69 cases. Pediatr Blood Cancer 65(5):e26953
Chi Y, Fang Z, Hong X et al (2018) Safety and efficacy of anlotinib, a multikinase angiogenesis inhibitor, in patients with refractory metastatic soft tissue sarcoma. Clin Cancer Res 24(21):5233–5238
Chi Y, Yao Y, Wang S et al (2018) Anlotinib for metastasis soft tissue sarcoma: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled and multi-centered clinical trial. J Clin Oncol 36:11503
Randrup HC, Grimm D, Bauer J et al (2017) Effects and side effects of using sorafenib and sunitinib in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Inter J Mol Sci 18(2):4611–4625
Li T, Wang L, Wang H et al (2016) A retrospective analysis of 14 consecutive Chinese patients with unresectable or metastatic alveolar soft part sarcoma treated with sunitinib. Investig New Drugs 34(6):1–6
Cranmer LD, Loggers ET, Pollack SM (2016) Pazopanib in the management of advanced soft tissue sarcomas. Ther Clin Risk Manag 12:941–955
Minocha M, Khurana V, Mitra AK (2012) Determination of pazopanib (GW-786034) in mouse plasma and brain tissue by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS-MS). J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 901:85–92
Kim M, Kim TM, Keam B et al (2019) A phaseIItrial of pazopanib in patients with metastatic alveolar soft part sarcoma. Oncologist 24(1):20–e29
Stacchiotti S, Mir O, Le Cesne A et al (2018) Activity of pazopanib and trabectedin in advanced alveolar soft part sarcoma. Oncologist 23(1):62–70
Judson I, Morden JP, Kilburn L et al (2019) Cediranib in patients with alveolar soft part sarcoma (CASPS): a double blind, placebo controlled, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 20(7):1023–1034. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30215-3
Glod J, Cohen JW, Widemann BC et al (2018) Cediranib phaseIIstudy in children with metastatic alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS). J Clin Oncol 36(15_suppl):10540
Zhou Y, Tang F, Wang Y et al (2017) Advanced alveolar soft part sarcoma responds to apatinib. Oncotarget 8(30):50314–50322
Schöffski P, Wozniak A, Kasper B et al (2018) Activity and safety of crizotinib in patients with alveolar soft part sarcoma with rearrangement of TFE3:European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC)phaseIItrial90101 ‘CREATE’. Ann Oncol 29(3):758–765
Conley AP, Trinh VA, Zobniw CM et al (2017) Positive tumor response to combined checkpoint inhibitors in a patient with refractory alveolar soft part sarcoma. J Global Oncol 4:1–6
Mo HN, Huang J, Xu JC, Chen X, Wu D, Qu D, Wang X, Lan B, Wang X, Xu J, Zhang H, Chi Y, Yang Q, Xu B (2018) Safety, anti-tumour activity, and pharmacokinetics of fixed-dose SHR-1210, an anti-PD-1 antibody in advanced solid tumours: a dose-escalation, phase 1 study. Br J Cancer 119(5):538–545
Guzik K, Tomala M, Muszak D et al (2019) Development of the inhibitors that target the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction-a brief look at progress on small molecules, peptides and macrocycles. Molecules 24(11):E2071
Nie J, Wang C, Liu Y, Yang Q, Mei Q, Dong L, Li X, Liu J, Ku W, Zhang Y, Chen M, An X, Shi L, Brock MV, Bai J, Han W (2019) Addition of low-dose decitabine to anti-PD-1 antibody camrelizumab in relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 37(17):1479–1489
Song Y, Wu J, Chen X, Lin T, Cao J, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Jin J, Huang H, Hu J, Luo J, Zhang L, Xue H, Zhang Q, Wang W, Chen C, Feng J, Zhu J (2019) A single- arm, multicenter, phase II study of camrelizumab in relapsed or refractory classical hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 25(24):7363–7369
Markham A, Keam SJ (2019) Camrelizumab: first global approval. Drugs 79(12):1355–1361
Xu Z, Zhang Y, Yu YH (2021 Jan) Successful treatment of advanced alveolar soft part sarcoma with camrelizumab combined with apatinib: a case report. Ann Palliat Med 10(1):785–792
Lu X, Wei G, Jie X et al (2019) Apatinib plus camrelizumab (SHR1210) for unresectable high-grade osteosarcoma (APFAO) progressing after chemotherapy: a prospective, open label, phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 37(15 Suppl):11013
Pang Q, Li X, Zhang W (2018) Safety and effect of radiation therapy combined with anti- PD- 1 antibody SHR- 1210 as firstline treatment on patients with intolerable concurrent chemoradiotherapy esophageal cancer: a phase 1b clinical trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 102(3):E39
Jing H, Binghe X, Hongnan M et al (2018) Safety, activity, and biomarkers of SHR-1210, an anti- PD-1 antibody, for patients with advanced esophageal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 24(6):1206–1304
Shen L, Peng Z, Zhang YQ (2019) Camrelizumab combined with capecitabine and oxaliplatin followed by camrelizumab and apatinib as first-line therapy for advanced or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: updated results from a multicenter, open label phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 37(15):4031–4031
Qin SK, Ren ZG, Meng ZQ et al (2018) A randomized multicentered phase II study to evaluate SHR-1210 (PD-1 antibody) in subjects with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who failed or intolerable to prior systemic treatment. Ann Oncol 29:719–720
Xu J, Zhang Y, Jia R, Yue C, Chang L, Liu R, Zhang G, Zhao C, Zhang Y, Chen C, Wang Y, Yi X, Hu Z, Zou J, Wang Q (2019) Anti-PD-1 antibody SHR-1210 combined with apatinib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, gastric, or esophagogastric junction cancer: an open- label, dose escalation and expansion study. Clin Cancer Res 25(2):515–523
Zhou C, Gao G, Wu F (2018) A phase Ib study of SHR-1210 plus Apatinib for heavily previously treated advanced nonsquamous non- small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients [abstract no. e21017]. J Clin Oncol 36(15):e21017
Kwong DLW (2018) Camrelizumab for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a new hope? Lancet Oncol 19(10):1266–1267
Postow MA, Sidlow R, Hellmann MD (2018) Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. N Engl J Med 378(2):158–168
Wilky BA, Trucco MM, Subhawong TK et al (2019) Axitinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced sarcomas including alveolar soft part sarcoma: a single centre, single arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 20(6):837–848
Lewin J, Davidson S, Anderson ND et al (2018) Response to immune checkpoint inhibition in two patients with alveolar softpart sarcoma. Cancer Immunol Res 6(9):1001–1007
Yang S, Yang J, Han X et al (2018) Effect of JS001, a monoclonal antibody targeting programed death-1(PD-1), on responses and disease control in patients with advanced or refractory alveolar soft part sarcoma:results from a phase 1 trial. J Clin Oncol 36(15_suppl):11572
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the patient for his participation in this study and for the patients’ agreement to the publication of the report.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hui Su and Qingcui Song drafted the manuscript and the collation of the case. Xuezhen Ma critically revised the paper. Chao Yu participated in the collection and sorting of images and the format editing of the article. All authors contributed toward data analysis, drafting and revising the paper and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The case report comply with the current laws of the country in which he was performed.
Informed consent
We obtained informed consent from the patient in this case report.
Consent for publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Hui Su declares no conflict of interest, Chao Yu declares no conflict of interest, Xuezhen Ma declares no conflict of interest, Qingcui Song declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, H., Yu, C., Ma, X. et al. Combined immunotherapy and targeted treatment for primary alveolar soft part sarcoma of the lung: case report and literature review. Invest New Drugs 39, 1411–1418 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-021-01105-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-021-01105-6