Summary
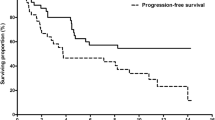
Background Conversion from sorafenib to regorafenib is primarily an evidence-based treatment strategy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of sequential therapy with sorafenib and regorafenib in patients with advanced HCC by analysis of outcomes in clinical practice with the aim to complement phase III findings. Methods The medical records of patients with advanced HCC receiving regorafenib were retrieved to collect data on sorafenib administration at seven Japanese institutions. Radiological responses and adverse events were evaluated using the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors version 1.1 and the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.0, respectively. Results Before March 2018, 44 patients were administered regorafenib for advanced HCC. The median sorafenib treatment duration was 8.4 months. The most common adverse events were similar to those reported by the RESORCE trial. The median overall survival (OS) was 17.3 months (95% confidence interval [CI] 11.4–22.9), and 17 of 37 patients (45.9%) discontinued regorafenib and received sequential systemic therapy after regorafenib. These patients had significantly longer OS than those who were treated by the best supportive care or sub-optimal therapy (not reached versus 8.7 months [95% CI 5.8–11.7]; P < 0.001). Conclusion The results based on Japanese clinical practices verified the tolerability of regorafenib in advanced HCC. Major regorafenib-associated adverse events were similar to those related to sorafenib. OS was significantly longer than expected, which might be associated with the sequential systemic therapies after regorafenib, mainly lenvatinib.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V et al (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359:378–390
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z et al (2009) Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:25–34
Kudo M, Matsui O, Izumi N et al (2014) JSH consensus-based clinical practice guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2014 update by the liver Cancer study Group of Japan. Liver Cancer 3:458–468
Omata M, Cheng AL, Kokudo N et al (2017) Asia-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: a 2017 update. Hepatol Int 11:317–370
European Association for the Study of the Liver (2018) EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 69:182–236
Heimbach JK, Kulik LM, Finn RS et al (2018) AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 67:358–380
Ogasawara S, Chiba T, Ooka Y et al (2014) Efficacy of sorafenib in intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients refractory to transarterial chemoembolization. Oncology 87:330–341
Arizumi T, Ueshima K, Minami T et al (2015) Effectiveness of Sorafenib in patients with Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) refractory and intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 4:253–262
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L et al (2004) BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 64:7099–7109
Wilhelm SM, Dumas J, Adnane L et al (2011) Regorafenib (BAY 73-4506): a new oral multikinase inhibitor of angiogenic, stromal and oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases with potent preclinical antitumor activity. Int J Cancer 129:245–255
Abou-Elkacem L, Arns S, Brix G et al (2013) Regorafenib inhibits growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis in a highly aggressive, orthotopic colon cancer model. Mol Cancer Ther 12:1322–1331
Johnson PJ, Qin S, Park JW et al (2013) Brivanib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with unresectable, advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: results from the randomized phase III BRISK-FL study. J Clin Oncol 31:3517–3524
Cainap C, Qin S, Huang WT et al (2015) Linifanib versus Sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 33:172–179
Llovet JM, Decaens T, Raoul JL et al (2013) Brivanib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma who were intolerant to sorafenib or for whom sorafenib failed: results from the randomized phase III BRISK-PS study. J Clin Oncol 31:3509–3516
Zhu AX, Park JO, Ryoo BY et al (2015) Ramucirumab versus placebo as second-line treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma following first-line therapy with sorafenib (REACH): a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 16:859–870
Zhu AX, Kudo M, Assenat E et al (2014) Effect of everolimus on survival in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma after failure of sorafenib: the EVOLVE-1 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 312:57–67
Kudo M, Moriguchi M, Numata K et al (2017) S-1 versus placebo in patients with sorafenib-refractory advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (S-CUBE): a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2:407–417
Bruix J, Qin S, Merle P et al (2017) Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 389:56–66
Nannini M, Nigro MC, Vincenzi B et al (2017) Personalization of regorafenib treatment in metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumours in real-life clinical practice. Ther Adv Med Oncol 9:731–739
Yamaguchi K, Komatsu Y, Satoh T, et al (2019) Large-scale, Prospective Observational Study of Regorafenib in Japanese Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in a Real-World Clinical Setting. Oncologist
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247
Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S et al (2018) Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 391:1163–1173
Ueshima K, Nishida N, Kudo M (2017) Sorafenib-Regorafenib sequential therapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-institute experience. Dig Dis 35:611–617
Finn RS, Merle P, Granito A et al (2018) Outcomes of sequential treatment with sorafenib followed by regorafenib for HCC: additional analyses from the phase III RESORCE trial. J Hepatol 69:353–358
Yoo C, Park JW, Kim YJ, et al (2018) Multicenter retrospective analysis of the safety and efficacy of regorafenib after progression on sorafenib in Korean patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Investig New Drugs
Hiraoka A, Kumada T, Kariyama K et al (2019) Clinical features of lenvatinib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in real-world conditions: multicenter analysis. Cancer Med 8:137–146
Abou-Alfa GK, Meyer T, Cheng AL et al (2018) Cabozantinib in patients with advanced and progressing hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 379:54–63
Zhu AX, Kang YK, Yen CJ et al (2019) Ramucirumab after sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and increased α-fetoprotein concentrations (REACH-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 20:282–296
Ogasawara S, Chiba T, Ooka Y et al (2018) Characteristics of patients with sorafenib-treated advanced hepatocellular carcinoma eligible for second-line treatment. Investig New Drugs 36:332–339
Uchikawa S, Kawaoka T, Aikata H et al (2018) Clinical outcomes of sorafenib treatment failure for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and candidates for regorafenib treatment in real-world practice. Hepatol Res 48:814–820
Terashima T, Yamashita T, Sunagozaka H et al (2018) Analysis of the liver functional reserve of patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing sorafenib treatment: prospects for regorafenib therapy. Hepatol Res 48:956–966
Acknowledgments
These authors would like to thank Enago (www.enago.jp) for the English language review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Sadahisa Ogasawara received grant support, advisory fee and honoraria from Bayer and Eisai. Naoya Kato received grant support, advisory fee and honoraria from Bayer and Eisai. The other authors who took part in this study indicated that they did not have anything to declare regarding funding or conflict of interest with respect to this study.
Research involving human participants
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent was not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 321 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogasawara, S., Ooka, Y., Itokawa, N. et al. Sequential therapy with sorafenib and regorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter retrospective study in Japan. Invest New Drugs 38, 172–180 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-019-00801-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-019-00801-8