Abstract
Introduction
Current guidelines recommend endoscopic eradication therapy (EET) for Barrett’s esophagus (BE) with dysplasia and intramucosal adenocarcinoma using either radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or liquid nitrogen spray cryotherapy (LNSC). The aims of this multicenter study are to compare the rate and number of treatment sessions of RFA vs. LNSC to achieve CE-D and CE-IM and assess outcomes for those who switched therapy.
Methods
This is a retrospective cohort study of patients with BE undergoing EET. Demographics, baseline variables, endoscopy details, and histology information were abstracted.
Results
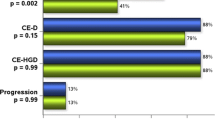
One hundred and sixty-two patients were included in this study with 100 patients in the RFA group and 62 patients in the LNSC group. The rate of CE-D and CE-IM did not differ between the RFA group and LNSC group (81% vs. 71.0%, p = 0.14) and (64% vs. 66%, p = 0.78), respectively. The number of sessions to achieve CE-D and CE-IM was higher with LNSC compared to RFA (4.2 vs. 3.2, p = 0.05) and (4.8 vs. 3.5, p = 0.04), respectively. The likelihood of developing recurrent dysplasia was higher among patients who did not achieve CE-IM (12%) compared to those who did achieve CE-IM (4%), p = 0.04. Similar findings were found in those who switched treatment modalities.
Discussion
EET is highly effective in eradication of Barrett’s associated dysplasia and neoplasia. Both RFA and LNSC achieved similar rates of CE-D and CE-IM although LNSC required more sessions. Also, achievement of CE-IM was associated with less recurrence rates of dysplasia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayeck TJ, Kong CY, Spechler SJ, Gazelle GS, Hur C. The prevalence of Barrett’s esophagus in the US: estimates from a simulation model confirmed by SEER data. Dis Esophagus. 2010;23:451–457.
Runge TM, Abrams JA, Shaheen NJ. Epidemiology of Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2015;44:203–231.
Spechler SJ. Barrett’s esophagus. Semin Gastrointest Dis. 1996;7:51–60.
Orloff M, Peterson C, He X et al. Germline mutations in msr1, ascc1, and cthrc1 in patients with Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. JAMA. 2011;306:410–419. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2011.1029.
Spechler SJ. Disputing dysplasia. Gastroenterology. 2001;120:1864–1868.
Haidry R, Lovat L, Sharma P. Radiofrequency ablation for Barrett’s dysplasia: past, present and the future? Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2015;17:13.
Ghorbani S, Tsai FC, Greenwald BD et al. Safety and efficacy of endoscopic spray cryotherapy for Barrett’s dysplasia: results of the National Cryospray Registry. Dis Esophagus. 2016;29:241–247.
Haidry R, Lovat L. Long-term durability of radiofrequency ablation for Barrett’s-related neoplasia. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2015;31:316–320.
Shaheen NJ, Greenwald BD, Peery AF et al. Safety and efficacy of endoscopic spray cryotherapy for Barrett’s esophagus with highgrade dysplasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;71:680–685.
Greenwald BD, Dumot JA, Horwhat JD et al. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of endoscopic low-pressure liquid nitrogen spray cryotherapy in the esophagus. Dis Esophagus. 2010;23:13–19.
Solomon SS, Kothari S, Smallfield GB et al. Liquid Nitrogen Spray Cryotherapy is Associated With Less Postprocedural Pain Than Radiofrequency Ablation in Barrett’s Esophagus: A Multicenter Prospective Study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2019;53:e84–e90.
Raju GS, Ahmed I, Xiao SY, Brining D, Bhutani MS, Pasricha PJ. Graded esophageal mucosal ablation with cryotherapy, and the protective effects of submucosal saline. Endoscopy. 2005;37:523–526. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-861312. (PMID: 15933923).
ASGE Technology Committee, Navaneethan U, Thosani N, et al. Radiofrequency ablation devices. VideoGIE. 2017;2(10):252–259. Published 2017 Sep 28. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vgie.2017.06.002.
ASGE Technology Committee, Parsi MA, Trindade AJ, et al. Cryotherapy in gastrointestinal endoscopy. VideoGIE. 2017;2(5):89–95. Published 2017 Feb 6. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vgie.2017.01.021.
Wani S, Muthusamy VR, Shaheen NJ et al. Development of quality indicators for endoscopic eradication therapies in Barrett’s esophagus: the TREAT-BE (Treatment with Resection and Endoscopic Ablation Techniques for Barrett’s Esophagus) Consortium. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86:1-17.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2017.03.010 ((Epub May 30 2017 PMID: 28576294)).
Phoa KN, van Vilsteren FG, Weusten BL et al. Radiofrequency ablation vs endoscopic surveillance for patients with Barrett esophagus and low-grade dysplasia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2014;311:1209–1217. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.2511. (PMID: 24668102).
Cotton PB, Eisen GM, Aabakken L, Baron TH, Hutter MM, Jacobson BC, Mergener K, Nemcek A Jr, Petersen BT, Petrini JL, Pike IM, Rabeneck L, Romagnuolo J, Vargo JJ. A lexicon for endoscopic adverse events: report of an ASGE workshop. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;71:446–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2009.10.027. (PMID: 20189503).
Spechler SJ, Sharma P, Souza RF et al. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement on the management of Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1084–1091.
Sawas T, Alsawas M, Bazerbachi F, Iyer PG, Wang KK, Murad MH, Katzka DA. Persistent intestinal metaplasia after endoscopic eradication therapy of neoplastic Barrett’s esophagus increases the risk of dysplasia recurrence: meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89:913-925.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2018.11.035. ((Epub Dec 7 2018 PMID: 30529044)).
Halsey KD, Chang JW, Waldt A et al. Recurrent disease following endoscopic ablation of Barrett’s high-grade dysplasia with spray cryotherapy. Endoscopy. 2011;43:844–848.
Cotton CC, Wolf WA, Pasricha S et al. Recurrent intestinal metaplasia after radiofrequency ablation for Barrett’s esophagus: endoscopic findings and anatomic location. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81:1362–1369.
Thota PN, Arora Z, Dumot JA et al. Cryotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation for Eradication of Barrett’s Esophagus with Dysplasia or Intramucosal Cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 2018;63:1311–1319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5009-4.
Standards of Practice Committee, Wani S, Qumseya B, Sultan S, Agrawal D, Chandrasekhara V, Harnke B, Kothari S, McCarter M, Shaukat A, Wang A, Yang J, Dewitt J. Endoscopic eradication therapy for patients with Barrett's esophagus-associated dysplasia and intramucosal cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018 Apr;87(4):907–931.e9. (Epub Feb 15 2018. PMID: 29397943). doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2017.10.011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MF, GS, and TS performed study design; MF and MP collected the data; GS, AZ, PM, and TS done endoscopy; MF and TS performed statistical analysis; MF, GS, and TS prepared the manuscript; MF, TS, MP, AZ, RL, PM, GS reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fasullo, M., Shah, T., Patel, M. et al. Outcomes of Radiofrequency Ablation Compared to Liquid Nitrogen Spray Cryotherapy for the Eradication of Dysplasia in Barrett’s Esophagus. Dig Dis Sci 67, 2320–2326 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-06991-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-06991-7