Abstract
Background
Bilateral endoscopic biliary stenting remains technically challenging, which limits its wider clinical application.
Aims
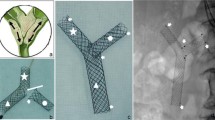
We have developed a novel long (10–12 cm) and slimmer (6 mm) self-expanded metal stent. The aim of this study was to evaluate the feasibility, efficacy, and safety of the new metal stent for palliative treatment of malignant hilar biliary strictures (MHBS).
Methods
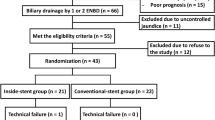
This retrospective study of prospectively collected data included 45 patients with unresectable malignant hilar biliary strictures of Bismuth type II or higher. A pair of long slimmer metal stents were sequentially placed into the intrahepatic duct using the stent-by-stent mode. The success rate and short- and long-term clinical outcomes were observed.
Results
The technical success rate was 100%, with a mean procedure time of 43.7 ± 11.5 min. The clinical success was achieved in 44 patients (97.8%). Early adverse events included mild acute pancreatitis (n = 2) and cholangitis (n = 3). Later cholangitis occurred in 14 of the 45 patients due to stent occlusions. The median stent patency was 260 days (95% CI 228.3–291.7). Stent malfunctions occurred in 23 of the 45 patients, and 15 of them received bilateral endoscopic plastic stents placements. The technical success for the re-intervention was 100% with the mean procedure time of 24.3 ± 4.5 min. The median overall survival of the whole group was 229 days (95% CI 171.2–286.8).
Conclusions
The long slimmer metal stent for bilateral endoscopic stent-by-stent placement proved to be safe, feasible, and effective for MHBS and facilitates endoscopic re-intervention as well.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Everhart JE, Ruhl CE. Burden of digestive diseases in the United States Part III: Liver, biliary, and pancreas. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:1134–1144
Law R, Baron TH. Bilateral metal stents for hilar biliary obstruction using a 6Fr delivery system: outcomes following bilateral and side-by-side stent deployment. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58:2667–2672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-013-2671-4.
Smith AC, Dowsett JF, Russell RC, Hatfield AR, Cotton PB. Randomised trial of endoscopic stenting versus surgical bypass in malignant low bileduct obstruction. Lancet. 1994;344:1655–1660
Speer AG, Cotton PB, Russell RC et al. Randomised trial of endoscopic versus percutaneous stent insertion in malignant obstructive jaundice. Lancet. 1987;2:57–62
Mukai T, Yasuda I, Nakashima M et al. Metallic stents are more efficacious than plastic stents in unresectable malignant hilar biliary strictures: a randomized controlled trial. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2013;20:214–222
Kawamoto H, Tsutsumi K, Harada R et al. Endoscopic deployment of multiple JOSTENT SelfX is effective and safe in treatment of malignant hilar biliary strictures. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:401–408
Chennat J, Waxman I. Initial performance profile of a new 6F self-expanding metal stent for palliation of malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:632–636
Naitoh I, Nakazawa T, Ban T et al. 8-mm versus 10-mm diameter self-expandable metallic stent in bilateral endoscopic stent-in-stent deployment for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2015;22:396–401
Fukasawa M, Takano S, Shindo H, Takahashi E, Sato T, Enomoto N. Endoscopic biliary stenting for unresectable malignant hilar obstruction. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2017;10:485–490
Hookey LC, Le Moine O, Deviere J. Use of a temporary plastic stent to facilitate the placement of multiple self-expanding metal stents in malignant biliary hilar strictures. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;62:605–609
Chahal P, Baron TH. Expandable metal stents for endoscopic bilateral stent-within-stent placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;71:195–199
Lee JH, Kang DH, Kim JY et al. Endoscopic bilateral metal stent placement for advanced hilar cholangiocarcinoma: a pilot study of a newly designed Y stent. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;66:364–369
Park do H, Lee SS, Moon JH, et al Newly designed stent for endoscopic bilateral stent-in-stent placement of metallic stents in patients with malignant hilar biliary strictures: multicenter prospective feasibility study (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69:1357–1360.
Kim JY, Kang DH, Kim HW et al. Usefulness of slimmer and open-cell-design stents for endoscopic bilateral stenting and endoscopic revision in patients with hilar cholangiocarcinoma (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70:1109–1115
Bismuth H, Castaing D, Traynor O. Resection or palliation: priority of surgery in the treatment of hilar cancer. World J Surg. 1988;12:39–47
Vienne A, Hobeika E, Gouya H et al. Prediction of drainage effectiveness during endoscopic stenting of malignant hilar strictures: the role of liver volume assessment. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:728–735
Lee TH, Moon JH, Choi JH et al. Prospective comparison of endoscopic bilateral stent-in-stent versus stent-by-stent deployment for inoperable advanced malignant hilar biliary stricture. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;90:222–230
Cotton PB, Lehman G, Vennes J et al. Endoscopic sphincterotomy complications and their management: an attempt at consensus. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991;37:383–393
Isayama H, Hamada T, Yasuda I et al. TOKYO criteria 2014 for transpapillary biliary stenting. Dig Endosc. 2015;27:259–264
Sawas T, Al Halabi S, Parsi MA, Vargo JJ. Self-expandable metal stents versus plastic stents for malignant biliary obstruction: a meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82:e257
Lee TH, Kim TH, Moon JH et al. Bilateral versus unilateral placement of metal stents for inoperable high-grade malignant hilar biliary strictures: a multicenter, prospective, randomized study (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86:817–827
Xia MX, Cai XB, Pan YL et al. Optimal stent placement strategy for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: a large multicenter parallel study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91:1117–1128
Gamanagatti S, Singh T, Sharma R, Srivastava DN, Dash NR, Garg PK. Unilobar versus bilobar biliary drainage: effect on quality of life and bilirubin level reduction. Indian J Palliat Care. 2016;22:50–62
Lee CH, Kim SH, Kim IH et al. Endoscopic stenting in bile duct cancer increases liver volume. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;80:447–455
Hwang JC, Kim JH, Lim SG, Kim SS, Yoo BM, Cho SW. Y-shaped endoscopic bilateral metal stent placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: prospective long-term study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011;46:326–332
Lee TH, Park DH, Lee SS et al. Technical feasibility and revision efficacy of the sequential deployment of endoscopic bilateral side-by-side metal stents for malignant hilar biliary strictures: a multicenter prospective study. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58:547–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2346-6.
Zhang WH, Ding PP, Liu L, et al. CO(2) or air cholangiography reduces the risk of post-ERCP cholangitis in patients with Bismuth type IV hilar biliary obstruction. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020;20:189.
Zhang R, Zhao L, Liu Z et al. Effect of CO2 cholangiography on post-ERCP cholangitis in patients with unresectable malignant hilar obstruction - a prospective, randomized controlled study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2013;48:758–763
Sud R, Puri R, Choudhary NS, Mehta A, Jain PK. Air cholangiogram is not inferior to dye cholangiogram for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: a randomized study of efficacy and safety. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2014;33:537–542
Loew BJ, Howell DA, Sanders MK et al. Comparative performance of uncoated, self-expanding metal biliary stents of different designs in 2 diameters: final results of an international multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70:445–453
Dowdy GS Jr, Waldron GW, Brown WG. Surgical anatomy of the pancreatobiliary ductal system. Obs Arch Surg. 1962;84:229–246
Shah RJ, Howell DA, Desilets DJ et al. Multicenter randomized trial of the spiral Z-stent compared with the Wallstent for malignant biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;57:830–836
Peynircioglu B, Cho KJ, Cwikiel W. Portal hypertension and obstructive jaundice after hepatic interventions: report of two unusual complications. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007;18:567–571
Lee TH, Moon JH, Kim JH et al. Primary and revision efficacy of cross-wired metallic stents for endoscopic bilateral stent-in-stent placement in malignant hilar biliary strictures. Endoscopy. 2013;45:106–113
Kogure H, Isayama H, Nakai Y et al. High single-session success rate of endoscopic bilateral stent-in-stent placement with modified large cell Niti-S stents for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Endosc. 2014;26:93–99
Heo JY, Lee HS, Son JH, Lee SH, Bang S. Clinical outcomes of bilateral stent-in-stent placement using self-expandable metallic stent for high-grade malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Yonsei Med J. 2018;59:827–833
Cheng JL, Bruno MJ, Bergman JJ, Rauws EA, Tytgat GN, Huibregtse K. Endoscopic palliation of patients with biliary obstruction caused by nonresectable hilar cholangiocarcinoma: efficacy of self-expandable metallic Wallstents. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56:33–39
Kawakubo K, Kawakami H, Kuwatani M et al. Single-step simultaneous side-by-side placement of a self-expandable metallic stent with a 6-Fr delivery system for unresectable malignant hilar biliary obstruction: a feasibility study. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2015;22:151–155
Yamaguchi Y, Morozumi K, Yamato T et al. New guide wire technique for stent placement through an occluded self-expandable metal stent: The hairpin technique. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;20:595–598
Acknowledgment
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this type of study formal consent is not required. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Dj., Xing, L., Ye, X. et al. Long Slimmer Metal Stent Is Feasible and Effective for Endoscopic Dual Stent-by-Stent Placement in Malignant Hilar Biliary Stricture. Dig Dis Sci 67, 1073–1082 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-06906-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-06906-6