Abstract
Background
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a frequent complication of severe acute pancreatitis (SAP). Ferroptosis is involved in a range of diseases. However, the role of ferroptosis in SAP-induced AKI has yet to be elucidated.
Aims
We aimed to investigate whether ferroptosis is induced in the kidney after SAP and whether inhibition of ferroptosis ameliorates AKI in a rat model of SAP.
Methods
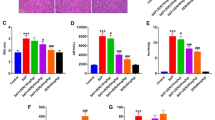
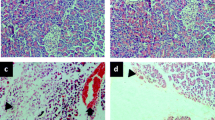
Sodium taurocholate (5%) was retrogradely perfused into the biliopancreatic duct to establish a model of SAP with AKI in rats. The levels of serum amylase, lipase, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6, creatinine (Cr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in rats were measured. We also determined the biochemical and morphological changes associated with ferroptosis in renal tissue, including iron accumulation, lipid peroxidation assays, and mitochondrial shrinkage. H&E staining was used to assess pancreatic and renal histological changes. Western blot analysis, RT-PCR, and immunofluorescence staining were performed to analyze the expression of ferroptosis-related proteins and genes.
Results
SAP-induced AKI was followed by iron accumulation, increased lipid peroxidation, and upregulation of ferroptosis-related proteins and genes. Twenty-four hours after SAP, TEM confirmed the presence of typical shrunken mitochondria. Furthermore, treatment with liproxstatin-1 lowered the levels of serum amylase, TNF-α, IL-6, Cr and BUN, decreased kidney lipid peroxidation and alleviated pancreatic and renal histopathology injury in SAP rats.
Conclusion
Our findings are the first to demonstrate the involvement of ferroptosis in SAP-associated renal damage and present ferroptosis as a therapeutic target for effective treatment of SAP-induced AKI.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forsmark CE, Vege SS, Wilcox CM. Acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1972–1981.
Frossard JL, Steer ML, Pastor CM. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 2008;371:143–152.
Singh VK, Wu BU, Bollen TL, et al. Early systemic inflammatory response syndrome is associated with severe acute pancreatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:1247–1251.
Zhou JJ, Li Y, Tang Y, et al. Effect of acute kidney injury on mortality and hospital stay in patient with severe acute pancreatitis. Nephrology (Carlton). 2015;20:485–491.
Kumar R, Pahwa N, Jain N. Acute kidney injury in severe acute pancreatitis: an experience from a tertiary care center. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2015;26:56–60.
Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P. Acute renal failure—definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care. 2004;8:R204–R212.
Herrera GME, Seller PG, de La Rubia D, et al. Acute renal failure profile and prognostic value in severe acute pancreatitis. Med Clin (Barc). 2000;115:721–725.
Pupelis G. Renal failure in acute pancreatitis. Timing of dialysis and surgery. Prz. Lek.. 2000;57:29–31.
Li H, Qian ZX, Liu ZL, Liu XL, Han XT, Kang H. Risk factors and outcome of acute renal failure in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. J Crit Care. 2010;25:225–229.
Schönfeld P, Wieckowski MR, Lebiedzińska M, Wojtczak L. Mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and oxidative stress: lack of reverse electron transfer-associated production of reactive oxygen species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1797:929–938.
Bonventre JV, Yang L. Cellular pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:4210–4221.
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149:1060–1072.
Lachaier E, Louandre C, Godin C, et al. Sorafenib induces ferroptosis in human cancer cell lines originating from different solid tumors. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:6417–6422.
Li Q, Han XN, Lan X, et al. Inhibition of neuronal ferroptosis protects hemorrhagic brain. JCI Insight. 2017;2:e90777.
Tuo QZ, Lei P, Jackman KA, et al. Tau-mediated iron export prevents ferroptotic damage after ischemic stroke. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22:1520–1530.
Martin-Sanchez D, Ruiz-Andres O, Poveda J, et al. Ferroptosis, but not necroptosis, is important in nephrotoxic folic acid-induced AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:218–229.
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir H, et al. Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 2017;171:273–285.
Masaldan S, Bush AI, Devos D, Rolland AS, Moreau C. Striking while the iron is hot: iron metabolism and ferroptosis in neurodegeneration. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;133:221–233.
Imai H, Matsuoka M, Kumagai T, Sakamoto T, Koumura T. Lipid peroxidation-dependent cell death regulated by GPx4 and ferroptosis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;403:143–170.
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156:317–331.
Doll S, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. 2017;13:91–98.
Kagan VE, Mao G, Qu F, et al. Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 2017;13:81–90.
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, et al. Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23:369–379.
Sheng X, Shan C, Liu J, Yang J, Sun B, Chen D. Theoretical insights into the mechanism of ferroptosis suppression via inactivation of a lipid peroxide radical by liproxstatin-1. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017;19:13153–13159.
Guerrero-Hue M, García-Caballero C, Palomino-Antolín A, et al. Curcumin reduces renal damage associated with rhabdomyolysis by decreasing ferroptosis-mediated cell death. FASEB J. 2019;33:8961–8975.
Huang L, Jiang Y, Sun Z, Gao Z, Wang J, Zhang D. Autophagy strengthens intestinal mucosal barrier by attenuating oxidative stress in severe acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2018;63:910–919. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-4962-2.
Friedmann Angeli JP, Schneider M, Proneth B, et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16:1180–1191.
Li Y, Feng D, Wang Z, et al. Ischemia-induced ACSL4 activation contributes to ferroptosis-mediated tissue injury in intestinal ischemia/reperfusion. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26:2284–2299.
Zhao X, Zhang Y, Li J, et al. Tissue pharmacology of Da-Cheng-Qi decoction in experimental acute pancreatitis in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:283175.
Zhang YM, Ren HY, Zhao XL, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of Da-Cheng-Qi decoction in the liver of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:1367–1374.
Gibson-Corley KN, Olivier AK, Meyerholz DK. Principles for valid histopathologic scoring in research. Vet Pathol. 2013;50:1007–1015.
Cao JY, Dixon SJ. Mechanisms of ferroptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73:2195–2209.
Seibt TM, Proneth B, Conrad M. Role of GPX4 in ferroptosis and its pharmacological implication. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;133:144–152.
Cardoso BR, Hare DJ, Bush AI, Roberts BR. Glutathione peroxidase 4: a new player in neurodegeneration? Mol Psychiatry.. 2017;22:328–335.
Maiorino M, Conrad M, Ursini F. GPx4, lipid peroxidation, and cell death: discoveries, rediscoveries, and open issues. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018;29:61–74.
Makhija R, Kingsnorth AN. Cytokine storm in acute pancreatitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2002;9:401–410.
Ge N, Xia Q, Yang ZH, Ding QF, Zeng Z. Vascular endothelial injury and apoptosis in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterol Res Pract.. 2015;2015:235017.
Angeli JPF, Shah R, Pratt DA, Conrad M. Ferroptosis inhibition: mechanisms and opportunities. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2017;38:489–498.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant Nos. 81270448 and 81470890.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, D., Li, C., Jiang, P. et al. Inhibition of Ferroptosis Attenuates Acute Kidney Injury in Rats with Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 66, 483–492 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06225-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06225-2