Abstract
Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) is an entity that has been recognized since 1961. Prior to the discovery of elevated serum IgG4 as a useful biomarker for its diagnosis, Dr. Yoshida in 1995 first described the entity of AIP, which in retrospect closely resembles the current concept of type 1 AIP. Since the discovery of IgG4 as a biomarker (the IgG4-era), a novel concept of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) has been accepted as being comprised of two subtypes of AIP: type 1 defined as the pancreatic manifestation of IgG4-RD, and type 2 characterized by granulocytic epithelial lesions. The characteristic features of type 1 AIP are increased serum IgG4 levels, lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis (abundant infiltration of IgG4+ plasmocytes and lymphocytes, storiform fibrosis, and obliterative phlebitis), extrapancreatic manifestations of IgG4-RD (e.g., sclerosing cholangitis, sclerosing sialadenitis, retroperitoneal fibrosis), and steroid responsiveness. These entities can be differentiated from mimickers by a combination of serum IgG4 level, imaging features, and histopathological findings. The current first-line therapy is corticosteroids, or rituximab in high-risk patients with steroid intolerance. Although relapse rates are high, treatment of relapsed disease remains experimental.

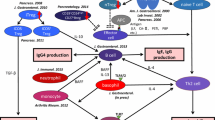
Reproduced from Ref. [1] with permission

Reproduced from Ref. [1] with permission

Reproduced from Ref. [1] with permission

Reproduced from Ref. [1] with permission

Reproduced from Ref. [26] with permission
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIP:
-
Autoimmune pancreatitis
- ANA:
-
Anti-nuclear antibody
- CDC:
-
Comprehensive diagnostic criteria
- ERCP:
-
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
- GEL:
-
Granulocytic epithelial lesion
- ICDC:
-
International consensus of diagnostic criteria
- IDCP:
-
Idiopathic duct-centric pancreatitis
- IgG4-RD:
-
IgG4-related disease
- JPS:
-
Japan Pancreas Society
- LPSP:
-
Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis
- MD:
-
Mikulicz disease
- MIF:
-
Multifocal idiopathic fibrosclerosis
- MOLPS:
-
Multi-organ lymphoproliferative disease
- MPD:
-
Main pancreatic duct
- OOI:
-
Other organ involvement
- PSC:
-
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- RF:
-
Rheumatoid factor
- SIPS:
-
IgG4-systemic plasmacytic syndrome
- SjS:
-
Sjögren’s syndrome
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- UNL:
-
Upper normal limit
References
Yoshida K, Toki F, Takeuchi T, Watanabe S, Shiratori K, Hayashi N. Chronic pancreatitis caused by an autoimmune abnormality. Proposal of the concept of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40:1561–1568. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02285209.
Shimosegawa T, Chari ST, Frulloni L, et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: guidelines of the International Association of Pancreatology. Pancreas. 2011;40:352–358.
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22:1–14.
Sarles H, Sarles JC, Muratore R, Guien C. Chronic inflammatory sclerosis of the pancreas—an autonomous pancreatic disease? Am J Dig Dis. 1961;6:688–698.
Comings DE, Skubi KB, Van Eyes J, Motulsky AG. Familial multifocal fibrosclerosis. Ann Intern Med. 1967;66:884–892.
Nakano S, Takeda I, Kitamura K, et al. Vanishing tumor of the abdomen in patient with Sjogren’s syndrome. Dig Dis. 1978;23:75–79.
Kawaguchi K, Koike M, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A, Tabata I, Fujita N. Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis with cholangitis: a variant of primary sclerosing cholangitis extensively involving pancreas. Hum Pathol. 1991;22:387–395.
Toki F, Kozu T, Oi I, et al. An unusual type of chronic pancreatitis showing “diffuse irregular narrowing of the entire main pancreatic duct” on ERCP—a report of four cases. Endoscopy. 1992;24:640. (abstract).
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. New Engl J Med. 1995;344:732–738.
Hamano H, Kawa S, Ochi Y, et al. Hydronephrosis associated with retroperitoneal fibrosis and sclerosing pancreatitis. Lancet. 2002;359:1403–1404.
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:982–984.
Kamisawa T, Okamoto A. Autoimmune pancreatitis: proposal of IgG4-related sclerosing disease. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41:613–625.
Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Ohara M, et al. A new conceptualization for Mikulicz’s disease as an IgG4-related plasmacytic disease. Mod Rheumatol. 2006;16:335–340.
Masaki Y, Dong L, Kurose N, et al. Proposal for a new clinical entity, IgG4-positive multi-organ lymphoproliferative syndrome: analysis of 64 cases of IgG4-related disorders. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:1310–1315.
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22:21–30.
Stone JH, Khosroshahi A, Deshpande V, et al. Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:3061–3067.
Notohara K, Burgart LJ, Yadav D, et al. Idiopathic chronic pancreatitis with periductal lymphoplasmacytic infiltration: clinicopathologic features of 35 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003;27:1119–1127.
Zamboni G, Luttges J, Capelli P, et al. Histopathological features of diagnostic and clinical relevance in autoimmune pancreatitis: a study on 53 resection specimens and 9 biopsy specimens. Virchows Arch. 2004;445:552–563.
Sah RP, Chari ST, Pannala R, et al. Differences in clinical profile and relapse rate of type 1 versus type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:140–148.
Okazaki K, Uchida K, Koyabu M, et al. Recent advances in the concept and diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related disease. J Gastroenterol. 2011;46:277–288.
Members of the Criteria Committee for Autoimmune Pancreatitis of the Japan Pancreas Society. Diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis by the Japan Pancreas Society [in Japanese]. J Jpn Pancreas Soc. 2002;17:585–587.
Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, et al. Clinical diagnostic criteria of autoimmune pancreatitis: revised proposal. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41:626–631.
Shimosegawa T, Working Group Members of the Japan Pancreas Society; Research Committee for Intractable Pancreatic Disease by the Ministry of Labor, Health and Welfare of Japan. The amendment of the Clinical Diagnostic Criteria in Japan (JPS2011) in response to the proposal of the International Consensus of Diagnostic Criteria (ICDC) for autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2012;41:1341–1342.
Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, et al. Amendment of the Japanese Consensus Guidelines for Autoimmune Pancreatitis, 2013 I. Concept and diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2014;49:567–588.
Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Levy MJ, et al. Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis: the Mayo Clinic experience. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:1010–1016.
Kim KP, Kim MH, Kim JC, et al. Diagnostic criteria for autoimmune chronic pancreatitis revisited. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:2487–2496.
Otsuki M, Chung JB, Okazaki K, et al. Asian diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: consensus of the Japan–Korea symposium on autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2008;43:403–408.
Frulloni L, Scattolini C, Falconi M, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis: differences between the focal and diffuse forms in 87 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:2288–2294.
Schneider A, Löhr JM. Autoimmune pancreatitis [in German]. Internist (Berl). 2009;50:318–330.
Masaki Y, Sugai S, Umehara H. IgG4-related diseases including Mikulicz’s disease and sclerosing pancreatitis: diagnostic insights. J Rheumatol. 2010;37:1380–1385.
Ohara H, Okazaki K, Tsubouchi H, et al. Clinical diagnostic criteria of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis 2012. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2012;19:536–542.
Kawano M, Saeki T, Nakashima H, et al. Proposal for diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2010;15:615–626.
Okazaki K, Umehara H. Are classification criteria for IgG4-RD now possible? The concept of IgG4-related disease and proposal of comprehensive diagnostic criteria in Japan. Int J Rheumatol. 2012;2012:357071.
Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:1181–1192.
Okazaki K, Chari ST, Frulloni L, et al. International consensus for the treatment of autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2017;17:1–6.
Hart PA, Topazian MD, Witzig TE, et al. Treatment of relapsing autoimmune pancreatitis with immunomodulators and rituximab: the Mayo Clinic experience. Gut. 2013;62:1607–1615.
Bi Y, Hart PA, Law R, et al. Obstructive jaundice in autoimmune pancreatitis can be safely treated with corticosteroids alone without biliary stenting. Pancreatology. 2016;16:391–396.
Masamune A, Nishimori I, Kikuta K, et al. Randomised controlled trial of long-term maintenance corticosteroid therapy in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2017;66:487–494.
Kamisawa T, Shimosegawa T, Okazaki K, et al. Standard steroid therapy for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2009;58:1504–1507.
Nishimori I, Tamakoshi A, Otsuki M. Prevalence of autoimmune pancreatitis in Japan from a nationwide survey. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:6–8.
Ito T, Nishimori I, Inoue N, et al. Treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis: consensus on the treatment for patients with autoimmune pancreatitis in Japan. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:50–58.
Muraki T, Hamano H, Ochi Y, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis and complement activation system. Pancreas. 2006;32:16–21.
Kamisawa T, Okazaki K, Kawa S, et al. Amendment of the Japanese Consensus Guidelines for Autoimmune Pancreatitis, 2013 III. Treatment and prognosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2014;49:961–970.
Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, et al. Second international symposium on IgG4-related disease. International consensus guidance statement on the management and treatment of IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:688–699.
Shirakashi M, Yoshifuji H, Kodama Y, et al. Factors in glucocorticoid regimens associated with treatment response and relapses of IgG4-related disease: a multicentre study. Sci Rep. 2018;8:10262. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28405-x.
Park DH, Kim MH, Oh HB, et al. Substitution of aspartic acid at position 57 of the DQb1 affects relapse of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:440–446.
Kamisawa T, Okazaki K, Kawa S, et al. Amendment of the Japanese Consensus Guidelines for Autoimmune Pancreatitis, 2013 III. Treatment and prognosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2014;49:961–970.
Ko SB, Mizuno N, Yatabe Y, et al. Corticosteroids correct aberrant CFTR localization in the duct and regenerate acinar cells in autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:1988–1996.
Takuma K, Kamisawa T, Tabata T, Inaba Y, Egawa N, Igarashi Y. Short-term and long-term outcomes of autoimmune pancreatitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;23:146–152.
Uchida K, Yazumi S, Nishio A, et al. Long-term outcome of autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44:726–732.
Frulloni L, Scattolini C, Falconi M, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis: differences between the focal and diffuse forms in 87 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:2288–2294.
Maruyama M, Arakura N, Ozaki Y, et al. Type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis can transform into chronic pancreatitis: a long-term follow-up study of 73 Japanese patients. Int J Rheumatol. 2013;272595.
Maruyama M, Watanabe T, Kanai K, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis can develop into chronic pancreatitis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014;9:77.
Ikeura T, Miyoshi H, Uchida K, et al. Relationship between autoimmune pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer: a single-center experience. Pancreatology. 2014;14:373–379.
Hirano K, Tada M, Sasahira N, et al. Incidence of malignancies in patients with IgG4-related disease. Intern Med. 2014;53:171–176.
Shiokawa M, Kodama Y, Yoshimura K, et al. Risk of cancer in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:610–617.
Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Tabeya T, et al. Risk of malignancies in IgG4-related disease. Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22:414–418.
Kamisawa T, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A, et al. Frequent and significant K-ras mutation in the pancreas, the bile duct, and the gallbladder in autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2009;38:890–895.
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Culture and Science of Japan (23591017), and a Grant-in-Aid for “Research for Intractable Disease” Program from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author has nothing to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okazaki, K. Autoimmune Pancreatitis and IgG4-Related Disease: The Storiform Discovery to Treatment. Dig Dis Sci 64, 2385–2394 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-05746-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-05746-9