Abstract
Background
Cyclophilin A (CyPA) is an immunomodulatory protein, high expression of which correlates with poor outcome of patients with inflammatory diseases. However, its role in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has not been studied.
Aim
This study analyzes the correlation between cyclophilin A, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9, and tissue inhibitor of MMP (TIMP)/MMP-9 complexes in the inflamed and non-inflamed colon mucosa of UC and CD patients.
Methods
Serum and biopsy specimens from inflamed and non-inflamed colonic mucosa of 38 patients with IBD (19 with UC and 19 with CD) and 16 controls were included in our study. We measured serum and tissue level of CyPA, and tissue level of TNF-α, MMP-9, TIMP-1/MMP-9, and TIMP-2/MMP-9 using ELISA method.
Results
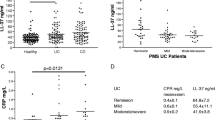
Our results indicated that serum, but not tissue CyPA is increased in UC, rather than in CD patients, compared to the control. The increase correlated with higher tissue concentration of MMP-9 and TNF-α, especially in the UC group. Moreover, we observed significantly higher level of TIMP-1/MMP-9 in UC and CD group, which overlapped with the change in MMP-9. There was no change in TIMP-2/MMP-9 in the analyzed groups.
Conclusion
The current study suggests that serum CyPA may be an independent additional marker of IBD, especially of UC. Higher CyPA level may be followed by increased MMP-9 in those patients. However, further studies are necessary to verify the role of CyPA in IBD development.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matricon J, Barnich N, Ardid D. Immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Self Nonself. 2010;1:299–309.
Rioux JD, Xavier RJ, Taylor KD, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for Crohn disease and implicates autophagy in disease pathogenesis. Nat Genet. 2007;39:596–604.
Suzuki J, Jin ZG, Meoli DF, et al. Cyclophilin A is secreted by a vesicular pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 2006;98:811–817.
Nigro P, Pompilio G, Capogrossi MC. Cyclophilin A: a key player for human disease. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e888.
Wang L, Wang CH, Jia JF, et al. Contribution of cyclophilin A to the regulation of inflammatory processes in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Immunol. 2010;30:24–33.
Li Y, Guo H, Dong D, et al. Expression and prognostic relevance of cyclophilin A and matrix metalloproteinase 9 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:207.
Gao Q, Meijer MJ, Kubben FJ, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 in intestinal tissue of patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Dig Liver Dis. 2005;37:584–592.
Santana A, Medina C, Paz-Cabrera MC, et al. Attenuation of dextran sodium sulphate induced colitis in matrix metalloproteinase-9 deficient mice. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:6464–6472.
La Pietra V, Marinelli L, Cosconati S, et al. Identification of novel molecular scaffolds for the design of MMP-13 inhibitors: a first round of lead optimization. Eur J Med Chem. 2012;47:143–152.
Meijer MJ, Mieremet-Ooms MA, van der Zon AM, et al. Increased mucosal matrix metalloproteinase-1, -2, -3 and -9 activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and the relation with Crohn’s disease phenotype. Dig Liver Dis. 2007;39:733–739.
Cadman E, Bostwick JR, Eichberg J. Determination of protein by a modified Lowry procedure in the presence of some commonly used detergents. Anal Biochem. 1979;96:21–23.
Yuan W, Ge H, He B. Pro-inflammatory activities induced by CyPA–EMMPRIN interaction in monocytes. Atherosclerosis. 2010;213:415–421.
Heinzmann D, Bangert A, Muller AM, et al. The novel extracellular cyclophilin A (CyPA)—inhibitor MM284 reduces myocardial inflammation and remodeling in a mouse model of troponin I—Induced Myocarditis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0124606.
Lakatos G, Hritz I, Varga MZ, et al. The impact of matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in inflammatory bowel diseases. Dig Dis. 2012;30:289–295.
O’Sullivan S, Gilmer JF, Medina C. Matrix metalloproteinases in inflammatory bowel disease: an update. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:964131.
Yurchenko V, Constant S, Eisenmesser E, Bukrinsky M. Cyclophilin–CD147 interactions: a new target for anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010;160:305–317.
Song T, Yang M, Chen J, et al. Prognosis of sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture in mice improved by anti-Clonorchis Sinensis cyclopholin a antibodies. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:502.
Dear JW, Leelahavanichkul A, Aponte A, et al. Liver proteomics for therapeutic drug discovery: inhibition of the cyclophilin receptor CD147 attenuates sepsis-induced acute renal failure. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:2319–2328.
Zhu X, Song Z, Zhang S, et al. CD147: a novel modulator of inflammatory and immune disorders. Curr Med Chem. 2014;21:2138–2145.
Saksena S, Theegala S, Bansal N, et al. Mechanisms underlying modulation of monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1) by somatostatin in human intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009;297:G878–G885.
Jin ZG, Lungu AO, Xie L, et al. Cyclophilin A is a proinflammatory cytokine that activates endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:1186–1191.
Bahmed K, Henry C, Holliday M, et al. Extracellular cyclophilin-A stimulates ERK1/2 phosphorylation in a cell-dependent manner but broadly stimulates nuclear factor kappa B. Cancer Cell Int. 2012;12:19.
Xie Z, Qu Y, Leng Y, et al. Human colon carcinogenesis is associated with increased interleukin-17-driven inflammatory responses. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:1679–1689.
Qian Z, Zhao X, Jiang M, et al. Downregulation of cyclophilin A by siRNA diminishes non-small cell lung cancer cell growth and metastasis via the regulation of matrix metallopeptidase 9. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:442.
Manicone AM, McGuire JK. Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008;19:34–41.
Jakubowska K, Pryczynicz A, Januszewska J, et al. Expressions of matrix metalloproteinases 2, 7, and 9 in carcinogenesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Dis Markers. 2016;2016:9895721.
Mao JW, He XM, Tang HY, Wang YD. Protective role of metalloproteinase inhibitor (AE-941) on ulcerative colitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:7063–7069.
Medina C, Santana A, Paz-Cabrera MC, et al. Increased activity and expression of gelatinases in ischemic colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2006;51:2393–2399.
Matusiewicz M, Neubauer K, Mierzchala-Pasierb M, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9: its interplay with angiogenic factors in inflammatory bowel diseases. Dis Markers. 2014;2014:643645.
Yang Y, Lu N, Zhou J, et al. Cyclophilin A up-regulates MMP-9 expression and adhesion of monocytes/macrophages via CD147 signalling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47:1299–1310.
Iordanskaia T, Malesevic M, Fischer G, et al. Targeting extracellular cyclophilins ameliorates disease progression in experimental biliary atresia. Mol Med. 2015;21:657–664.
Xu Q, Cao X, Pan J, et al. Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) remodels the extracellular matrix through enhancing matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and inhibiting tissue inhibitors of MMPs expression in HPV-positive cervical cancer cells. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2015;36:539–545.
Calabro SR, Maczurek AE, Morgan AJ, et al. Hepatocyte produced matrix metalloproteinases are regulated by CD147 in liver fibrogenesis. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e90571.
Attia M, Huet E, Gossard C, et al. Early events of overused supraspinatus tendons involve matrix metalloproteinases and EMMPRIN/CD147 in the absence of inflammation. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41:908–917.
Acknowledgments
Supported by the grants from the Medical University of Lodz (#503/1-156-04/503-01 to JF). Aleksandra Piechota-Polanczyk is currently working at the Department of Medical Biotechnology, Faculty of Biochemistry, Biophysics and Biotechnology, Jagiellonian University, Krakow, Poland. Faculty of Biochemistry, Biophysics and Biotechnology of Jagiellonian University is a partner of the Leading National Research Center (KNOW) supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piechota-Polanczyk, A., Włodarczyk, M., Sobolewska-Włodarczyk, A. et al. Serum Cyclophilin A Correlates with Increased Tissue MMP-9 in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis, but Not with Crohn’s Disease. Dig Dis Sci 62, 1511–1517 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4568-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4568-0