Abstract
Background
Non-invasive monitoring of inflammatory bowel disease is an unmet clinical need as patients in clinical remission may have residual mucosal inflammation preceding clinical relapse.
Aims
We aimed to assess the value of fecal calprotectin and standardized clinical activity scoring to monitor disease activity in ulcerative colitis under medical treatment.
Methods
Forty-one patients with ulcerative colitis were included in a prospective observational study. Medical treatment was guided by clinical judgement of treating physicians. Fecal calprotectin and the clinical activity index (CAI) were measured blinded to treating physicians every 2 months until the end of follow-up. Twenty-six patients received colonoscopy for clinical reason.
Results
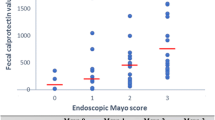
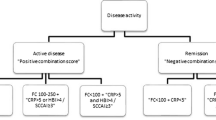
As defined by the CAI, patients were in clinical remission (63.4 %), having mild (26.8 %) or moderate (11.2 %) disease activity. Of those in clinical remission (CAI ≤ 4), 86.4 % showed residual endoscopic activity (Mayo Score ≥1). Calprotectin levels were higher in endoscopically active disease (779.0 vs 331.5 μg/g, P = 0.034) and calprotectin testing identified more patients with endoscopic disease activity (86.4 %) than the CAI (45.5 %, P = 0.034). Medical treatment was escalated in 90.2 % during the study. Values of the CAI and calprotectin correlated with therapy escalation (OR 3.94 and 3.22, respectively). Only for calprotectin, changes between two measurements were related to intensified medical treatment (OR 1.39).
Conclusion
Fecal calprotectin was similarly useful to the CAI to monitor disease activity of ulcerative colitis during medical treatment but identified endoscopic disease activity far more reliably. Changes of calprotectin values between measurements might indicate clinical relapse earlier than the CAI.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vatn MH. Natural history and complications of IBD. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2009;11:481–487.
Vilela EG, Torres HO, Martins FP. Evaluation of inflammatory activity in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:872–881.
Sostegni R, Daperno M, Scaglione N, Lavagna A, Rocca R, Pera A. Review article: Crohn’s disease: monitoring disease activity. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;17:11–17.
Saverymuttu SH. Clinical remission in Crohn’s disease—assessment using faecal 111In granulocyte excretion. Digestion. 1986;33:74–79.
Dignass A, Lindsay JO, Sturm A, et al. Second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis part 2: current management. J Crohns Colitis. 2012;6:991–1030.
Dignass A, Van Assche G, Lindsay JO, et al. The second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease: current management. J Crohns Colitis. 2010;4:28–62.
Tibble JA, Sigthorsson G, Foster R, Forgacs I, Bjarnason I. Use of surrogate markers of inflammation and Rome criteria to distinguish organic from nonorganic intestinal disease. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:450–460.
Langhorst J, Elsenbruch S, Koelzer J, Rueffer A, Michalsen A, Dobos GJ. Noninvasive markers in the assessment of intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases: performance of fecal lactoferrin, calprotectin, and PMN-elastase, CRP, and clinical indices. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:162–169.
van Rheenen PF, Van de Vijver E, Fidler V. Faecal calprotectin for screening of patients with suspected inflammatory bowel disease: diagnostic meta-analysis. BMJ. 2010;341:c3369.
Foell D, Frosch M, Sorg C, Roth J. Phagocyte-specific calcium-binding S100 proteins as clinical laboratory markers of inflammation. Clin Chim Acta. 2004;344:37–51.
Roseth AG, Schmidt PN, Fagerhol MK. Correlation between faecal excretion of indium-111-labelled granulocytes and calprotectin, a granulocyte marker protein, in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1999;34:50–54.
Schoepfer AM, Beglinger C, Straumann A, Trummler M, Renzulli P, Seibold F. Ulcerative colitis: correlation of the Rachmilewitz endoscopic activity index with fecal calprotectin, clinical activity, C-reactive protein, and blood leukocytes. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009;15:1851–1858.
Ricanek P, Brackmann S, Perminow G, et al. Evaluation of disease activity in IBD at the time of diagnosis by the use of clinical, biochemical, and fecal markers. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011;46:1081–1091.
D’Haens G, Ferrante M, Vermeire S, et al. Fecal calprotectin is a surrogate marker for endoscopic lesions in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012;18:2218–2224.
Schoepfer AM, Beglinger C, Straumann A, et al. Fecal calprotectin more accurately reflects endoscopic activity of ulcerative colitis than the Lichtiger Index, C-reactive protein, platelets, hemoglobin, and blood leukocytes. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013;19:332–341.
Tibble JA, Sigthorsson G, Bridger S, Fagerhol MK, Bjarnason I. Surrogate markers of intestinal inflammation are predictive of relapse in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2000;119:15–22.
Costa F, Mumolo MG, Ceccarelli L, et al. Calprotectin is a stronger predictive marker of relapse in ulcerative colitis than in Crohn’s disease. Gut. 2005;54:364–368.
Gisbert JP, Bermejo F, Perez-Calle JL, et al. Fecal calprotectin and lactoferrin for the prediction of inflammatory bowel disease relapse. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009;15:1190–1198.
D’Incà R, Dal Pont E, Di Leo V, et al. Can calprotectin predict relapse risk in inflammatory bowel disease? Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:2007–2014.
Sipponen T, Kolho KL. Faecal calprotectin in children with clinically quiescent inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:872–877.
De Vos M, Dewit O, D’Haens G, et al. Fast and sharp decrease in calprotectin predicts remission by infliximab in anti-TNF naive patients with ulcerative colitis. J Crohns Colitis. 2012;6:557–562.
Gerasimidis K, Nikolaou CK, Edwards CA, McGrogan P. Serial fecal calprotectin changes in children with Crohn’s disease on treatment with exclusive enteral nutrition: associations with disease activity, treatment response, and prediction of a clinical relapse. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011;45:234–239.
Sipponen T, Savilahti E, Karkkainen P, et al. Fecal calprotectin, lactoferrin, and endoscopic disease activity in monitoring anti-TNF-alpha therapy for Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14:1392–1398.
Wagner M, Peterson CGB, Ridefelt P, Sangfelt P, Carlson M. Fecal markers of inflammation used as surrogate markers for treatment outcome in relapsing inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:5584–5589; discussion 5588.
Silverberg MS, Satsangi J, Ahmad T, et al. Toward an integrated clinical, molecular and serological classification of inflammatory bowel disease: report of a working party of the 2005 Montreal World Congress of Gastroenterology. Can J Gastroenterol. 2005;19:5–36.
Schroeder KW, Tremaine WJ, Ilstrup DM. Coated oral 5-aminosalicylic acid therapy for mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis. A randomized study. N Engl J Med. 1987;317:1625–1629.
Rachmilewitz D. Coated mesalazine (5-aminosalicylic acid) versus sulphasalazine in the treatment of active ulcerative colitis: a randomised trial. BMJ. 1989;298:82–86.
Manz M, Burri E, Rothen C, et al. Value of fecal calprotectin in the evaluation of patients with abdominal discomfort: an observational study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012;12:5.
Burri E, Beglinger C. Faecal calprotectin—a useful tool in the management of inflammatory bowel disease. Swiss Med Wkly. 2012;142:w13557.
Modigliani R. Endoscopic management of inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994;89:S53–S65.
Garcia-Sanchez V, Iglesias-Flores E, Gonzalez R, et al. Does fecal calprotectin predict relapse in patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis? J Crohns Colitis. 2010;4:144–152.
Mao R, Xiao YL, Gao X, et al. Fecal calprotectin in predicting relapse of inflammatory bowel diseases: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012;18:1894–1899.
Vos MD, Louis EJ, Jahnsen J, et al. Consecutive fecal calprotectin measurements to predict relapse in patients with ulcerative colitis receiving infliximab maintenance therapy. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013;19:2111–2117.
Sipponen T, Bjorkesten CG, Farkkila M, Nuutinen H, Savilahti E, Kolho KL. Faecal calprotectin and lactoferrin are reliable surrogate markers of endoscopic response during Crohn’s disease treatment. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:325–331.
Acknowledgments
Viollier AG (Basel, Switzerland) performed all measurements of FC. Researchers were independent of funding. We are indebted to the patients who participated in the study for their most valuable efforts.
Conflict of interest
All authors report no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burri, E., Beglinger, C., von Felten, S. et al. Fecal Calprotectin and the Clinical Activity Index Are Both Useful to Monitor Medical Treatment in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Dig Dis Sci 60, 485–491 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3383-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3383-0