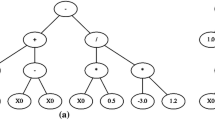
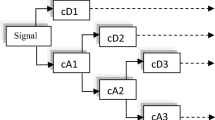
Abstract
Financial time series prediction is considered as a challenging task. The task becomes difficult due to inherent nonlinear and non-stationary characteristics of financial time series. This article proposes a combination of wavelet and Postfix-GP, a postfix notation based genetic programming system, for financial time series prediction. The discrete wavelet transform approach is used to smoothen the time series by separating the fluctuations from the trend of the series. Postx-GP is then employed to evolve models for the smoothen series. The out-of-sample prediction capability of evolved solutions is tested on two stocks price and two stock indexes series. The results are compared with those obtained using ECJ, a Java based evolutionary framework. The nonparametric statistical tests are applied to evaluate the significance of the obtained results.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abarbanel, H. D., Brown, R., Sidorowich, J. J., & Tsimring, L. S. (1993). The analysis of observed chaotic data in physical systems. Reviews of modern physics, 65(4), 1331.
Abarbanel, H. D., & Gollub, J. P. (1996). Analysis of observed chaotic data. Physics Today, 49, 86.
Ahalpara, D., & Parikh, J. (2008). Genetic programming based approach for modeling time series data of real systems. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 19(01), 63–91.
Atsalakis, G. S., & Valavanis, K. P. (2009). Forecasting stock market short-term trends using a neuro-fuzzy based methodology. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(7), 10 696–10 707.
Beran, J., Shumeyko, Y., et al. (2012). On asymptotically optimal wavelet estimation of trend functions under long-range dependence. Bernoulli, 18(1), 137–176.
Brabazon, A., O’Neill, M., & Dempsey, I. (2008). An introduction to evolutionary computation in finance. Computational Intelligence Magazine, IEEE, 3(4), 42–55.
Chang, P.-C., & Fan, C.-Y. (2008). A hybrid system integrating a wavelet and tsk fuzzy rules for stock price forecasting. Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C: Applications and Reviews, IEEE Transactions on, 38(6), 802–815.
Chatfield, C. (2003). The analysis of time series: An introduction. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Cheng, H. (2004). Self-similar, chaos and fractal matlab toolbox. http://www.cs.ucf.edu/~haocheng/code.htm.
Dabhi, V., & Chaudhary, S. (2013). Semantic sub-tree crossover operator for postfix genetic programming. In J. C. Bansal, P. K. Singh, K. Deep, M. Pant, & A. K. Nagar (Eds.), Proceedings of seventh international conference on bio-inspired computing: Theories and applications (BIC-TA 2012) (Vol. 201, pp. 391–402). Advances in intelligent systems and computing. Springer.
Dabhi, V., & Vij, S. (2011). Empirical modeling using symbolic regression via postfix genetic programming. In Image Information Processing (ICIIP), 2011 International Conference on (pp. 1–6).
Daubechies, I. (1992). Ten lectures on wavelets. Philadelphia: SIAM.
Ferreira, C. (2001). Gene expression programming: A new adaptive algorithm for solving problems. Complex Systems, 13(2), 87–129.
García, S., Molina, D., Lozano, M., & Herrera, F. (2009). A study on the use of non-parametric tests for analyzing the evolutionary algorithms’ behaviour: A case study on the cec’2005 special session on real parameter optimization. Journal of Heuristics, 15(6), 617–644.
Grosan, C., & Abraham, A. (2006). Stock market modeling using genetic programming ensembles. Genetic systems programming (pp. 131–146). Berlin: Springer.
Gustafson, S., Burke, E., & Krasnogor, N. (2005). On improving genetic programming for symbolic regression. In Evolutionary computation, 2005. The 2005 IEEE congress on (Vol. 1, pp. 912–919). IEEE.
Hansen, J. V., & Nelson, R. D. (1997). Neural networks and traditional time series methods: A synergistic combination in state economic forecasts. Neural Networks, IEEE Transactions on, 8(4), 863–873.
Holland, J. H. (1992). Adaptation in natural and artificial Systems: An introductory analysis with applications to biology, control and artificial intelligence. Cambridge, USA: MIT Press.
Hong Tan, B. (1995). Neural network model for stock forecasting, Ph.D. dissertation, Texas Tech University.
Hsieh, T.-J., Hsiao, H.-F., & Yeh, W.-C. (2011). Forecasting stock markets using wavelet transforms and recurrent neural networks: An integrated system based on artificial bee colony algorithm. Applied Soft Computing, 11(2), 2510–2525.
Huang, S.-C., & Wu, T.-K. (2010). Integrating recurrent SOM with wavelet-based kernel partial least square regressions for financial forecasting. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(8), 5698–5705.
Huang, S.-C. (2011). Forecasting stock indices with wavelet domain kernel partial least square regressions. Applied Soft Computing, 11(8), 5433–5443.
Iba, H., & Sasaki, T. (1999). Using genetic programming to predict financial data. In Evolutionary computation, 1999. CEC 99. Proceedings of the 1999 congress on (Vol. 1, pp. 244–251).
Kaboudan, M. A. (2000). Genetic programming prediction of stock prices. Computational Economics, 16(3), 207–236.
Kampouridis, M., & Tsang, E. (2010). Eddie for investment opportunities forecasting: Extending the search space of the gp. In Evolutionary computation (CEC). IEEE congress on, 2010 (pp. 1–8).
Kantz, H., & Schreiber, T. (1997). Nonlinear time series analysis. Cambridge nonlinear science series. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Kara, Y., Acar Boyacioglu, M., & Baykan, O. K. (2011). Predicting direction of stock price index movement using artificial neural networks and support vector machines: The sample of the istanbul stock exchange. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(5), 5311–5319.
Kazem, A., Sharifi, E., Hussain, F. K., Saberi, M., & Hussain, O. K. (2012). Support vector regression with chaos-based firefly algorithm for stock market price forecasting. Applied Soft Computing, 13, 947–958.
Keith, M. J., & Martin, M. C. (1994). Genetic programming in c++: Implementation issues. Advances in Genetic Programming, 1, 285–310.
Kennel, M., Brown, R., & Abarbanel, H. D. I. (1992). Determining embedding dimension for phase-space reconstruction using a geometrical construction. Physical Review A, 45, 3403–3411.
Kim, K.-J. (2003). Financial time series forecasting using support vector machines. Neurocomputing, 55(1), 307–319.
Koza, J. R. (1992). Genetic programming: On the programming of computers by means of natural selection. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Laumanns, M., Thiele, L., Zitzler, E., & Deb, K. (2002). Archiving with guaranteed convergence and diversity in multi-objective optimization. In Proceedings of the genetic and evolutionary computation conference (GECCO) (pp. 439–447), GECCO ’02. San Francisco, CA, USA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.
Li, J., & Taiwo, S. ( 2006). Enhancing financial decision making using multi-objective financial genetic programming. In Evolutionary computation, 2006. CEC 2006. IEEE congress on(pp. 2171–2178). IEEE.
Li, J., Shi, Z., & Li, X. (2006). Genetic programming with wavelet-based indicators for financial forecasting. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 28(3), 285–297.
Lopes, H. S., & Weinert, W. R. (2004). A gene expression programming system for time series modeling. In Proceedings of XXV Iberian Latin American congress on computational methods in engineering (CILAMCE), Recife (Brazil) (pp. 10–12).
Luke, S., Panait, L., Balan, G., & Et (2007). ECJ 16: A java-based evolutionary computation research system. http://cs.gmu.edu/~eclab/projects/ecj/. Accessed 13 Jan 2014.
Majhi, R., Panda, G., & Majhi, B. (2009). Efficient prediction of stock market indices using adaptive bacterial foraging optimization (abfo) and BFO based techniques. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(6), 10 097–10 104.
Mallat, S. (1999). A wavelet tour of signal processing. Academic Press.
Manimaran, P., Parikh, J., Panigrahi, P., Basu, S., Kishtawal, C., & Porecha, M. (2006). Modelling financial time series. Econophysics of stock and other markets (pp. 183–191). Milan: Springer.
Porecha, M., Panigrahi, P., Parikh, J., Kishtawal, C., & Basu, S. (2005). Forecasting non-stationary financial time series through genetic algorithm. arXiv:nlin/0507037v1.
Potvin, J.-Y., Soriano, P., & Vallée, M. (2004). Generating trading rules on the stock markets with genetic programming. Computers & Operations Research, 31(7), 1033–1047.
Saad, E. W., Prokhorov, D. V., & W, D. C, I. I. (1998). Comparative study of stock trend prediction using time delay, recurrent and probabilistic neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 9(6), 1456–1470.
Santini, M., & Tettamanzi, A. (2001). Genetic programming for financial time series prediction. In Proceedings of the 4th European Conference on Genetic Programming, ser. EuroGP ’01(pp. 361–370). London, UK: Springer.
Takens, F. (1980). Detecting strange attractors in turbulence. In D. A. Rand & L. S. Young (Eds.), Dynamical systems and turbulence (pp. 366–381). New York: Spinger.
Tan, T. Z., Quek, C., & Ng, G. S. (2005). Brain-inspired genetic complementary learning for stock market prediction. In Congress on evolutionary computation. IEEE (pp. 2653–2660).
Uy, N. Q., Hoai, N. X., & O’Neill, M. (2009). Semantic aware crossover for genetic programming: The case for real-valued function regression. Proceedings of the 12th European conference on genetic programming (pp. 292–302)., EuroGP ’09 Berlin: Springer.
Uy, N. Q., Hoai, N. X., O’Neill, M., Mckay, R. I., & Galván-López, E. (2011). Semantically-based crossover in genetic programming: Application to real-valued symbolic regression. Genetic Programming and Evolvable Machines, 12, 91–119.
Vapnik, V. (2000). The nature of statistical learning theory. New York: Springer.
Vasanthi, D., Subha, D., & Nambi, M. S. T. (2011). An empirical study on stock index trend prediction using markov chain analysis. Journal of Banking Financial Services and Insurance Research, 1, 72–91.
Wagner, N., Michalewicz, Z., Khouja, M., & McGregor, R. R. (2007). Time series forecasting for dynamic environments: the dyfor genetic program model. Evolutionary Computation, IEEE Transactions on, 11(4), 433–452.
Wang, W., & Ding, J. (2003). Wavelet network model and its application to the prediction of hydrology. Nature and Science, 1(1), 67–71.
Yeh, C.-Y., Huang, C.-W., & Lee, S.-J. (2011). A multiple-kernel support vector regression approach for stock market price forecasting. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(3), 2177–2186.
Zhang, G., & Hu, M. Y. (1998). Neural network forecasting of the british pound/us dollar exchange rate. Omega, 26(4), 495–506.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dabhi, V.K., Chaudhary, S. Financial Time Series Modeling and Prediction Using Postfix-GP. Comput Econ 47, 219–253 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10614-015-9482-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10614-015-9482-y