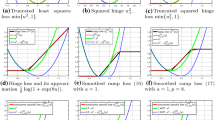
Abstract
Support vector machine is an important and fundamental technique in machine learning. In this paper, we apply a semismooth Newton method to solve two typical SVM models: the L2-loss SVC model and the \(\epsilon \)-L2-loss SVR model. The semismooth Newton method is widely used in optimization community. A common belief on the semismooth Newton method is its fast convergence rate as well as high computational complexity. Our contribution in this paper is that by exploring the sparse structure of the models, we significantly reduce the computational complexity, meanwhile keeping the quadratic convergence rate. Extensive numerical experiments demonstrate the outstanding performance of the semismooth Newton method, especially for problems with huge size of sample data (for news20.binary problem with 19,996 features and 1,355,191 samples, it only takes 3 s). In particular, for the \(\epsilon \)-L2-loss SVR model, the semismooth Newton method significantly outperforms the leading solvers including DCD and TRON.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We realized this work when we drafted our paper.
We use the software LIBNIEAR version 2.11 downloaded from https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/ cjlin/liblinear/
References
Al-Mubaid, H., Umair, S.A.: A new text categorization technique using distributional clustering and learning logic. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 18(9), 1156–1165 (2006)
Barzilai, J., Borwein, J.M.: Two-point step size gradient methods. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 8(1), 141–148 (1988)
Basak, D., Pal, S., Patranabis, D.C.: Support vector regression. Neural Inf. Process.-Lett. Rev. 11(10), 203–224 (2007)
Boser, B.E., Guyon, I., Vapnik, V.: A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. In: Proceeding COLT ’92 Proceedings of the Fifth Annual Workshop on Computational Learning Theory, pp. 144–152. ACM, Pittsburgh (1992)
Bottou, L., Curtis, F.E., Nocedal, J.: Optimization methods for large-scale machine learning. SIAM Rev. 60(2), 223–311 (2018)
Chang, K.W., Hsieh, C.J., Lin, C.J.: Coordinate descent method for large-scale L2-loss linear support vector machines. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9(3), 1369–1398 (2008)
Chen, Z., Qi, L.: A semismooth Newton method for tensor eigenvalue complementarity problem. Comput. Optim. Appl. 65(1), 109–126 (2016)
Clarke, F.H.: Optimization and Nonsmooth Analysis. Wiley, Hoboken (1983)
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.: Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20(3), 273–297 (1995)
Cruz, J.Y.B., Ferreira, O.P., Prudente, L.F.: On the global convergence of the inexact semi-smooth Newton method for absolute value equation. Comput. Optim. Appl. 65(1), 1–16 (2016)
Facchinei, F., Kanzow, C., Karl, S., et al.: The semismooth Newton method for the solution of quasi-variational inequalities. Comput. Optim. Appl. 62(1), 85–109 (2015)
Fan, R.E., Chang, K.W., Hsieh, C.J., et al.: LIBLINEAR: a library for large linear classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9(9), 1871–1874 (2008)
Friedman, J., Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R.: The Elements of Statistical Learning. Springer Series in Statistics, New York (2001)
Gu, W., Chen, W.P., Ko, C.H., et al.: Two smooth support vector machines for \(\epsilon \)-insensitive regression. Comput. Optim. Appl. 70, 1–29 (2018)
Hestenes, M.R., Stiefel, E.: Methods of conjugate gradients for solving linear systems. J. Res. Nat. Bur. Stand. 49(6), 409–436 (1952)
Ho, C.H., Lin, C.J.: Large-scale linear support vector regression. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 13(Nov), 3323–3348 (2012)
Hsia, C.Y., Zhu, Y., Lin, C.J.: A study on trust region update rules in Newton methods for large-scale linear classification. In: Workshop and Conference Proceedings, pp. 1–16 (2017)
Hsieh, C.J., Chang, K.W., Lin, C.J., et al.: A dual coordinate descent method for large-scale linear SVM. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 408–415. ACM (2008)
Johnson, R., Zhang, T.: Accelerating stochastic gradient descent using predictive variance reduction. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 26, 315–323 (2013)
Keerthi, S.S., DeCoste, D.: A modified finite Newton method for fast solution of large scale linear SVMs. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 6(Mar), 341–361 (2005)
Labusch, K., Barth, E., Martinetz, E.: Simple method for high-performance digit recognition based on sparse coding. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 19(11), 1985–1989 (2008)
Lee, Y.J., Mangasarian, O.L.: SSVM: a smooth support vector machine for classification. Comput. Optim. Appl. 20(1), 5–22 (2001)
Li, Q.N., Qi, H.D.: A sequential semismooth Newton method for the nearest low-rank correlation matrix problem. SIAM J. Optim. 21(4), 1641–1666 (2011)
Li, X.D., Sun, D.F., Toh, K.C.: A highly efficient semismooth Newton augmented Lagrangian method for solving Lasso problems. SIAM J. Optim. 28(1), 433–458 (2018)
Lin, C.J., Weng, R.C., Keerthi, S.S.: Trust region newton methods for large-scale logistic regression. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 561–568. ACM (2007)
Luo, Z.Y., Sun, D.F., Toh, K.C., et al.: Solving the OSCAR and SLOPE models using a semismooth Newton-based augmented Lagrangian method (2018). arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.10740
Mangasarian, O.L.: A finite newton method for classification. Optim. Methods Softw. 17(5), 913–929 (2002)
Mifflin, R.: Semismooth and semiconvex functions in constrained optimization. SIAM J. Control Optim. 15(6), 959–972 (1977)
Qi, H.D.: A semismooth Newton method for the nearest Euclidean distance matrix problem. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 34(34), 67–93 (2013)
Qi, H.D., Shen, J., Xiu, N.H.: A sequential majorization method for approximating weighted time series of finite rank. Stat. Interface (2017)
Qi, H.D., Sun, D.F.: A quadratically convergent newton method for computing the nearest correlation matrix. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 28(2), 360–385 (2006)
Qi, L.: C-differentiability, C-differential operators and generalized Newton methods. Applied Mathematics Report AMR96/5, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia (1996)
Qi, L., Sun, J.: A nonsmooth version of Newton’s method. Math. Program. 58(1–3), 353–367 (1993)
Robbins, H., Monro, S.: A stochastic approximation method. Ann. Math. Stat. 22, 400–407 (1951)
Rockafellar, R.T., Wets, R.J.B.: Variational analysis. In: Sobolev and BV Spaces, MPS-SIAM Series on Optimization, vol. 30, pp. 324–326 (1998)
Tan, C., Ma, S., Dai, Y.H., et al,: Barzilai-Borwein step size for stochastic gradient descent. In: The 13th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Curran Associates Inc., pp. 685–693 (2016)
Vapnik, V.: The nature of statistical learning. Springer, New York (1995)
Vapnik, V., Golowich, S.E., Smola, A.J.: Support vector method for function approximation, regression estimation and signal processing. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 9, 281–287 (1970)
Vapnik, V.N., Kotz, S.: Estimation of Dependences Based on Empirical Data. Springer-Verlag, New York (1982)
Wu, K., Yap, K.H.: Fuzzy SVM for content-based image retrieval: a pseudo-label support vector machine framework. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 1(2), 10–16 (2006)
Yuan, Y.B., Huang, T.Z.: A polynomial smooth support vector machine for classification. In: International Conference on Advanced Data Mining and Applications. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 157–164 (2005)
Yuan, Y.C., Sun, D.F., Toh, K.C.: An efficient semismooth Newton based algorithm for convex clustering (2018). arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.07091
Zhang, L., Zhou, W.: On the sparseness of 1-norm support vector machines. Neural Netw. 23(3), 373–385 (2010)
Zhao, X.Y.: A Semismooth Newton-CG Augmented Lagrangian Method for Large Scale Linear and Convex Quadratic SDPS. Ph D (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This author’s research was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No.11671036).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, J., Li, Q. A semismooth Newton method for support vector classification and regression. Comput Optim Appl 73, 477–508 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-019-00075-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-019-00075-z