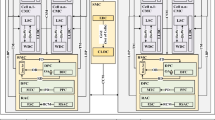
Abstract
Fog paradigms minimize response times for delay-sensitive applications by bringing computation and storage closer to the edge of the network, thus reducing the need for data transmission to centralized cloud servers. However, one key challenge of fog computing is the constrained network resources in comparison with the cloud core. This yields a bottleneck when the delay-sensitive applications demand intensive computation and processing resources. Here migrating tasks to the cloud can be prohibited due to the delay bounds impelled by offered services. Therefore, running delay-sensitive and computation-intensive applications at the fog nodes compels efficient resource management solutions to avoid saturation and congestion. Along this, this paper presents a novel dynamic redistribution mechanism that alleviates heavily-loaded (HL) fog nodes from excess load and instead migrates it to nearby lightly-loaded (LL) nodes. The method implements a hybrid model that combines the saliencies of coarse-grained and fine-grained techniques, i.e., adaptive selection based on the load status at the proximity nodes and traffic volume. Results demonstrate that the proposed method results in minimal migration iterations at low failure rates, along with reduced migration delay and cost, as compared to standalone fine-grained and coarse-grained methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Bonomi, F., Milito, R., Zhu, J., Addepalli, S.: Fog computing and its role in the internet of things. In: 1\(^{\rm st}\) Edition MCC Workshop Mobile Cloud Computing, Helsinki, Finland (2012)
Chiosi., M., et al.: Network functions virtualisation: an introduction, benefits, enablers, challenges & call for action. ETSI White Paper (2012)
Ningning, S., Chao, G., Xingshuo, A., Qiang, Z.: Fog computing dynamic load balancing mechanism based on graph repartitioning. China Commun. 13(3), 156–164 (2016)
Puthal, D., Ranjan, R., Nanda, A., Nanda, P., Jayaraman, P., Zomaya, A.: Secure authentication and load balancing of distributed edge datacenters. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 124, 60–69 (2019)
Wan, J., et al.: Fog computing for energy-aware load balancing and scheduling in smart factory. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 14(10), 4548–4556 (2018)
Cai, P., Fuqian, Y., Wang, J., Wu, X., Yang, Y., Luo, X.: JOTE: joint offloading of tasks and energy in fog-enabled IoT networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(4), 3067–3082 (2020)
Yang, Y., et al.: MEETS: maximal energy efficient task scheduling in homogeneous fog networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 5(5), 4076–4087 (2018)
Yang, J., Ling, L., Liu, H.: A hierarchical load balancing strategy considering communication delay overhead for large-distributed computing systems. Math. Probl. Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5641831
Jin, Q., Rongheng, L., Zou, H., Yang, F.: A distributed fog computing architecture supporting multiple migrating mode. In: IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Cloud Computing (CSCloud)/IEEE International Conference on Edge Computing and Scalable Cloud (EdgeCom), Shanghai, China (2018)
Fan, Q., Ansari, N.: Towards workload balancing in fog computing empowered IoT. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 7(1), 253–262 (2018)
Pereira, E., et al.: Increasing the efficiency of fog nodes through of priority-based load balancing. In: IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications, Rennes, France (2020)
Yan, J., et al.: Task offloading algorithms for novel load balancing in homogeneous fog network. In: IEEE 24th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design, Dalian, China (2021)
Maswood, M., et al.: A novel strategy to achieve bandwidth cost reduction and load balancing in a cooperative three-layer fog-cloud computing environment. IEEE Access 8, 113737–113750 (2020)
Wang, S., Zhao, T., Pang, S.: Task scheduling algorithm based on improved firework algorithm in fog computing. IEEE Access 8, 32385–32394 (2020)
Al-Khafajiy, M., et al.: IoT-fog optimal workload via fog offloading. In: IEEE/ACM International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing Companion, Zurich, Switzerland (2018)
Jasim, M., Siasi, N., Ghani, N.: Efficient load migration scheme for fog networks. In: IEEE Annual Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA (2022)
Siasi, N., Jasim, M., Ghani, N.: Service function chain mapping in fog networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 25(1), 99–102 (2021)
Jasim, M., Siasi, N., Almalag, M., Honary, V., Aldalbahi, A.: Asynchronous coarse-grained load migration scheme for IoT applications in fog networks. In: IEEE Global Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things (GCAIoT), Dubai, UAE (2021)
OpenFog Consortium Architecture Working Group: OpenFog reference architecture for fog computing. OPFRA001 20817, 162 (2017)
Siasi, N., Jasim, M.: Migration of VNF instances for service continuity. Wiley Internet Technol. Lett. 6, e422 (2023)
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.S. (investigation, writing, algorithms, software, revision), M.J. (conceptualization, methodology, algorithms, writing, validation).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jasim, M., Siasi, N. Hybrid-grained migration method for load redistribution in heavily-loaded fog nodes. Cluster Comput (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-023-04255-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-023-04255-9