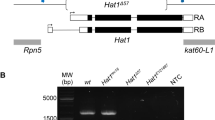
Abstract
Methylation of H3K9 histone residue is a marker of gene silencing in eukaryotes. Three enzymes responsible for adding this modification — G9a, SetDB1/Egg, and Su(var)3-9 — are known in Drosophila. To understand how simultaneous mutations of SetDB1 and Su(var)3-9 may affect the fly development, appropriate combinations were obtained. Double mutants egg; Su(var)3-9 displayed pronounced embryonic lethality, slower larval growth and died before or during metamorphosis. Analysis of transcription in larval salivary glands and wing imaginal disks indicated that the effect of double mutation is tissue-specific. In salivary gland chromosomes, affected genes display low H3K9me2 enrichment and are rarely bound by SetDB1 or Su(var)3-9. We suppose that each of these enzymes directly or indirectly controls its own set of gene targets in different organs, and double mutation results in an imbalanced developmental program. This also indicates that SetDB1 and Su(var)3-9 may affect transcription via H3K9-independent mechanisms. Unexpectedly, in double and triple mutants, amount of di- and tri-methylated H3K9 is drastically reduced, but not completely absent. We hypothesize that this residual methylation implies the existence of additional H3K9-specific methyltransferase in Drosophila.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
RNA-seq data have been deposited in the GEO under accession number GSE223579.
References
Andersen EC, Horvitz HR (2007) Two C. elegans histone methyltransferases repress lin-3 EGF transcription to inhibit vulval development. Development 134:2991–2999
Bharadwaj R, Peter CJ, Jiang Y, Roussos P, Vogel-Ciernia A, Shen EY, Mitchell AC, Mao W, Whittle C, Dincer A et al (2014) Conserved higher-order chromatin regulates NMDA receptor gene expression and cognition. Neuron 84:997–1008
Black JC, Van Rechem C, Whetstine JR (2012) Histone lysine methylation dynamics: establishment, regulation, and biological impact. Mol Cell 48:491–507
Brower-Toland B, Riddle NC, Jiang H, Huisinga KL, Elgin SCR (2009) Multiple SET methyltransferases are required to maintain normal heterochromatin domains in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 181:1303–1319
Cakouros D, Daish TJ, Kumar S (2004) Ecdysone receptor directly binds the promoter of the Drosophila caspase dronc, regulating its expression in specific tissues. J Cell Biol 165:631–640
Calpena E, Palau F, Espinós C, Galindo MI (2015) Evolutionary history of the Smyd gene family in metazoans: a framework to identify the orthologs of human Smyd genes in Drosophila and other animal species. PLoS ONE 10:e0134106
Clough E, Moon W, Wang S, Smith K, Hazelrigg T (2007) Histone methylation is required for oogenesis in Drosophila. Development 134:157–165
Clough E, Tedeschi T, Hazelrigg T (2014) Epigenetic regulation of oogenesis and germ stem cell maintenance by the Drosophila histone methyltransferase Eggless/dSetDB1. Dev Biol 388:181–191
Czermin B, Melfi R, McCabe D, Seitz V, Imhof A, Pirrotta V (2002) Drosophila enhancer of Zeste/ESC complexes have a histone H3 methyltransferase activity that marks chromosomal Polycomb sites. Cell 111:185–196
De Gregorio E, Spellman PT, Tzou P, Rubin GM, Lemaitre B (2002) The Toll and Imd pathways are the major regulators of the immune response in Drosophila. EMBO J 21:2568–2579
Delaney CE, Methot SP, Kalck V, Seebacher J, Hess D, Gasser SM, Padeken J (2022) SETDB1-like MET-2 promotes transcriptional silencing and development independently of its H3K9me-associated catalytic activity. Nat Struct Mol Biol 29:85–96
Ebert A, Schotta G, Lein S, Kubicek S, Krauss V, Jenuwein T, Reuter G (2004) Su(var) genes regulate the balance between euchromatin and heterochromatin in Drosophila. Genes Dev 18:2973–2983
Eissenberg JC, Elgin SCR (2014) HP1a: a structural chromosomal protein regulating transcription. Trends Genet 30:103–110
Fei Q, Shang K, Zhang J, Chuai S, Kong D, Zhou T, Fu S, Liang Y, Li C, Chen Z et al (2015b) Histone methyltransferase SETDB1 regulates liver cancer cell growth through methylation of p53. Nat Commun 6:8651
Fei Q, Yang X, Jiang H, Wang Q, Yu Y, Yu Y, Yi W, Zhou S, Chen T, Lu C et al (2015a) SETDB1 modulates PRC2 activity at developmental genes independently of H3K9 trimethylation in mouse ES cells. Genome Res 25:1325–1335
Figueiredo MLA, Philip P, Stenberg P, Larsson J (2012) HP1a recruitment to promoters is independent of H3K9 methylation in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Genet 8:e1003061
Guittard E, Blais C, Maria A, Parvy J-P, Pasricha S, Lumb C, Lafont R, Daborn PJ, Dauphin-Villemant C (2011) CYP18A1, a key enzyme of Drosophila steroid hormone inactivation, is essential for metamorphosis. Dev Biol 349:35–45
Hearn MG, Hedrick A, Grigliatti TA, Wakimoto BT (1991) The effect of modifiers of position-effect variegation on the variegation of heterochromatic genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 128:785–797
Jeong H-H, Yalamanchili HK, Guo C, Shulman JM, Liu Z (2018) An ultra-fast and scalable quantification pipeline for transposable elements from next generation sequencing data. Pac Symp Biocomput 23:168–179
Jiang C, Lamblin AF, Steller H, Thummel CS (2000) A steroid-triggered transcriptional hierarchy controls salivary gland cell death during Drosophila metamorphosis. Mol Cell 5:445–455
Jiang Y, Loh Y-HE, Rajarajan P, Hirayama T, Liao W, Kassim BS, Javidfar B, Hartley BJ, Kleofas L, Park RB et al (2017) The methyltransferase SETDB1 regulates a large neuron-specific topological chromatin domain. Nat Genet 49:1239–1250
Kalashnikova DA, Maksimov DA, Romanov SE, Laktionov PP, Koryakov DE (2021) SetDB1 and Su(var)3-9 play non-overlapping roles in somatic cell chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Sci 134:jcs253096
Kato Y, Kato M, Tachibana M, Shinkai Y, Yamaguchi M (2008) Characterization of Drosophila G9a in vivo and identification of genetic interactants. Genes Cells 13:703–722
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2015) HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods 12:357–360
Koryakov DE, Walther M, Ebert A, Lein S, Zhimulev IF, Reuter G (2011) The SUUR protein is involved in binding of SU(VAR)3-9 and methylation of H3K9 and H3K27 in chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosome Res 19:235–249
Kouzarides T (2007) Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 128:693–705
Kramer JM, Kochinke K, Oortveld MAW, Marks H, Kramer D, de Jong EK, Asztalos Z, Westwood JT, Stunnenberg HG, Sokolowski MB et al (2011) Epigenetic regulation of learning and memory by Drosophila EHMT/G9a. PLoS Biol 9:e1000569
Lanouette S, Mongeon V, Figeys D, Couture J-F (2014) The functional diversity of protein lysine methylation. Mol Syst Biol 10:724
Lee K-S, Yoon J, Park JS, Kang Y-K (2010) Drosophila G9a is implicated in germ cell development. Insect Mol Biol 19:131–139
Liao Y, Smyth GK, Shi W (2014) featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 30:923–930
Ligoxygakis P, Pelte N, Ji C, Leclerc V, Duvic B, Belvin M, Jiang H, Hoffmann JA, Reichhart J-M (2002) A serpin mutant links Toll activation to melanization in the host defence of Drosophila. EMBO J 21:6330–6337
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15:550
Maksimov DA, Koryakov DE (2019) Binding of SU(VAR)3-9 partially depends on SETDB1 in the chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Cells 8:1030
Maksimov DA, Laktionov PP, Posukh OV, Belyakin SN, Koryakov DE (2018) Genome-wide analysis of SU(VAR)3-9 distribution in chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 127:85–102
Marcel M (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J 17(1):10–12. https://doi.org/10.14806/ej.17.1.200
Mazina MY, Ziganshin RH, Magnitov MD, Golovnin AK, Vorobyeva NE (2020) Proximity-dependent biotin labelling reveals CP190 as an EcR/Usp molecular partner. Sci Rep 10:4793
Merkling SH, Bronkhorst AW, Kramer JM, Overheul GJ, Schenck A, Van Rij RP (2015) The epigenetic regulator G9a mediates tolerance to RNA virus infection in Drosophila. PLoS Pathog 11:e1004692
Methot SP, Padeken J, Brancati G, Zeller P, Delaney CE, Gaidatzis D, Kohler H, van Oudenaarden A, Großhans H, Gasser SM (2021) H3K9me selectively blocks transcription factor activity and ensures differentiated tissue integrity. Nat Cell Biol 23:1163–1175
Minakhina S, Steward R (2006) Melanotic mutants in Drosophila: pathways and phenotypes. Genetics 174:253–263
Mis J, Ner SS, Grigliatti TA (2006) Identification of three histone methyltransferases in Drosophila: dG9a is a suppressor of PEV and is required for gene silencing. Mol Genet Genomics 275:513–526
Montavon T, Shukeir N, Erikson G, Engist B, Onishi-Seebacher M, Ryan D, Musa Y, Mittler G, Graff Meyer A, Genoud C, Jenuwein T (2021) Complete loss of H3K9 methylation dissolves mouse heterochromatin organization. Nat Commun 12:4359
Müller J, Hart CM, Francis NJ, Vargas ML, Sengupta A, Wild B, Miller EL, O’Connor MB, Kingston RE, Simon JA (2002) Histone methyltransferase activity of a Drosophila Polycomb group repressor complex. Cell 111:197–208
Nakayama J, Rice JC, Strahl BD, Allis CD, Grewal SI (2001) Role of histone H3 lysine 9 methylation in epigenetic control of heterochromatin assembly. Science 292:110–113
Nunes С, Sucena É, Koyama T (2021) Endocrine regulation of immunity in insects. FEBS J 288:3928–3947
O’Carroll D, Scherthan H, Peters AHFM, Opravil S, Haynes AR, Laible G, Rea S, Schmid M, Lebersorger A, Jerratsch M et al (2000) Isolation and characterization of Suv39h2, a second histone H3 methyltransferase gene that displays testis-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol 20:9423–9433
Ohhara Y, Kato Y, Kamiyama T, Yamakawa-Kobayashi K (2022) Su(var)2-10- and Su(var)205-dependent upregulation of the heterochromatic gene neverland is required for developmental transition in Drosophila. Genetics 222:iyac137
Ou Q, King-Jones K (2013) What goes up must come down: transcription factors have their say in making ecdysone pulses. Curr Top Dev Biol 103:35–71
Paddibhatla I, Gautam DK, Mishra RK (2019) SETDB1 modulates the differentiation of both the crystal cells and the lamellocytes in Drosophila. Dev Biol 456:74–85
Padeken J, Methot SP, Gasser SM (2022) Establishment of H3K9-methylated heterochromatin and its functions in tissue differentiation and maintenance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 23:623–640
Peng JC, Karpen GH (2009) Heterochromatic genome stability requires regulators of histone H3 K9 methylation. PLoS Genet 5:e1000435
Pengelly AR, Copur Ö, Jäckle H, Herzig A, Müller J (2013) A histone mutant reproduces the phenotype caused by loss of histone-modifying factor Polycomb. Science 339:698–699
Penke TJR, McKay DJ, Strahl BD, Matera AG, Duronio RJ (2016) Direct interrogation of the role of H3K9 in metazoan heterochromatin function. Genes Dev 30:1866–1880
Penke TJR, McKay DJ, Strahl BD, Matera AG, Duronio RJ (2018) Functional redundancy of variant and canonical histone H3 lysine 9 modification in Drosophila. Genetics 208:229–244
Peters AHFM, O’Carroll D, Scherthan H, Mechtler K, Sauer S, Schöfer C, Weipoltshammer K, Pagani M, Lachner M, Kohlmaier A et al (2001) Loss of the Suv39h histone methyltransferases impairs mammalian heterochromatin and genome stability. Cell 107:323–337
Pinheiro I, Margueron R, Shukeir N, Eisold M, Fritzsch C, Richter FM, Mittler G, Genoud C, Goyama S, Kurokawa M et al (2012) Prdm3 and Prdm16 are H3K9me1 methyltransferases required for mammalian heterochromatin integrity. Cell 150:948–960
Pongor LS, Gross JM, Alvarez RV, Murai J, Jang S-M, Zhang H, Redon C, Fu H, Huang S-Y, Thakur B et al (2020) BAMscale: quantification of next-generation sequencing peaks and generation of scaled coverage tracks. Epigenetics Chromatin 13:21
Rewitz KF, Yamanaka N, O’Connor MB (2010) Steroid hormone inactivation is required during the juvenile-adult transition in Drosophila. Dev Cell 19:895–902
Riahi H, Fenckova M, Goruk KJ, Schenck A, Kramer JM (2021) The epigenetic regulator G9a attenuates stress-induced resistance and metabolic transcriptional programs across different stressors and species. BMC Biol 19:112
Rus F, Flatt T, Tong M, Aggarwal K, Okuda K, Kleino A, Yates E, Tatar M, Silverman N (2013) Ecdysone triggered PGRP-LC expression controls Drosophila innate immunity. EMBO J 32:1626–1638
Sankar A, Mohammad F, Sundaramurthy AK, Wang H, Lerdrup M, Tatar T, Helin K (2022) Histone editing elucidates the functional roles of H3K27 methylation and acetylation in mammals. Nat Genet 54:754–760
Schmidt RL, Trejo TR, Plummer TB, Platt JL, Tang AH (2008) Infection-induced proteolysis of PGRP-LC controls the IMD activation and melanization cascades in Drosophila. FASEB J 22:918–929
Schotta G, Ebert A, Krauss V, Fischer A, Hoffmann J, Rea S, Jenuwein T, Dorn R, Reuter G (2002) Central role of Drosophila SU(VAR)3-9 in histone H3-K9 methylation and heterochromatic gene silencing. EMBO J 21:1121–1131
Seum C, Bontron S, Reo E, Delattre M, Spierer P (2007b) Drosophila G9a is a nonessential gene. Genetics 177:1955–1957
Seum C, Reo E, Peng H, Rauscher FJ III, Spierer P, Bontron S (2007a) Drosophila SETDB1 is required for chromosome 4 silencing. PLoS Genet 3:e76
Shimaji K, Konishi T, Tanaka S, Yoshida H, Kato Y, Ohkawa Y, Sato T, Suyama M, Kimura H, Yamaguchi M (2015) Genomewide identification of target genes of histone methyltransferase dG9a during Drosophila embryogenesis. Genes Cells 20:902–914
Sienski G, Batki J, Senti K-A, Dönertas D, Tirian L, Meixner K, Brennecke J (2015) Silencio/CG9754 connects the piwi-piRNA complex to the cellular heterochromatin machinery. Genes Dev 29:2258–2271
Stabell M, Bjørkmo M, Aalen RB, Lambertsson A (2006b) The Drosophila SET domain encoding gene dEset is essential for proper development. Hereditas 143:177–188
Stabell M, Eskeland R, Bjørkmo M, Larsson J, Aalen RB, Imhof A, Lambertsson A (2006a) The Drosophila G9a gene encodes a multi-catalytic histone methyltransferase required for normal development. Nucleic Acids Res 34:4609–4621
Stephens M (2017) False discovery rates: a new deal. Biostatistics 18:275–294
Tachibana M, Sugimoto K, Nozaki M, Ueda J, Ohta T, Ohki M, Fukuda M, Takeda N, Niida H, Kato H et al (2002) G9a histone methyltransferase plays a dominant role in euchromatic histone H3 lysine 9 methylation and is essential for early embryogenesis. Genes Dev 16:1779–1791
Takehana A, Katsuyama T, Yano T, Oshima Y, Takada H, Aigaki T, Kurata S (2002) Overexpression of a pattern-recognition receptor, peptidoglycan-recognition protein-LE, activates imd/relish-mediated antibacterial defense and the prophenoloxidase cascade in Drosophila larvae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13705–13710
Towbin BD, González-Aguilera C, Sack R, Gaidatzis D, Kalck V, Meister P, Askjaer P, Gasser SM (2012) Step-wise methylation of histone H3K9 positions heterochromatin at the nuclear periphery. Cell 150:934–947
Tschiersch B, Hofmann A, Krauss V, Dorn R, Korge G, Reuter G (1994) The protein encoded by the Drosophila position-effect variegation suppressor gene Su(var)3-9 combines domains of antagonistic regulators of homeotic gene complexes. EMBO J 13:3822–3831
Tsurumi A, Dutta P, Shang R, Yan S-J, Li WX (2013) Drosophila Kdm4 demethylases in histone H3 lysine 9 demethylation and ecdysteroid signaling. Sci Rep 3:2894
Tzeng T-Y, Lee C-H, Chan L-W, Shen C-KJ (2007) Epigenetic regulation of the Drosophila chromosome 4 by the histone H3K9 methyltransferase dSETDB1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:12691–12696
Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, Sivertsson Å, Kampf C, Sjöstedt E, Asplund A et al (2015) Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 347:1260419
Ushijima Y, Inoue YH, Konishi T, Kitazawa D, Yoshida H, Shimaji K, Kimura H, Yamaguchi M (2012) Roles of histone H3K9 methyltransferases during Drosophila spermatogenesis. Chromosome Res 20:319–331
Uyehara CM, Leatham-Jensena M, McKay DJ (2022) Opportunistic binding of EcR to open chromatin drives tissue-specific developmental responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 119:e2208935119
Uyehara CM, McKay DJ (2019) Direct and widespread role for the nuclear receptor EcR in mediating the response to ecdysone in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:9893–9902
Wakimoto BT, Hearn MG (1990) The effects of chromosome rearrangements on the expression of heterochromatic genes in chromosome 2L of D. melanogaster. Genetics 125:141–154
Warrier T, El Farran C, Zeng Y, Ho BSQ, Bao Q, Zheng ZH, Bi X, Ng HH, Ong DST, Chu JJH et al (2022) SETDB1 acts as a topological accessory to Cohesin via an H3K9me3-independent, genomic shunt for regulating cell fates. Nucleic Acids Res 50:7326–7349
Watson KL, Johnson TK, Denell RE (1991) Lethal(1) aberrant immune response mutations leading to melanotic tumor formation in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Genet 12:173–187
Wood AM, Van Bortle K, Ramos E, Takenaka N, Rohrbaugh M, Jones BC, Jones KC, Corces VG (2011) Regulation of chromatin organization and inducible gene expression by a Drosophila insulator. Mol Cell 44:29–38
Wu T, Hu E, Xu S, Chen M, Guo P, Dai Z, Feng T, Zhou L, Tang W, Zhan L et al (2021) clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation (NY) 2:100141
Xu L, Jiang H (2020) Writing and reading histone H3 lysine 9 methylation in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 11:452
Yoon J, Lee K-S, Park JS, Yu K, Paik S-G, Kang Y-K (2008) dSETDB1 and SU(VAR)3-9 sequentially function during germline-stem cell differentiation in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE 3:e2234
Yuan J, Chang S-Y, Yin S-G, Liu Z-Y, Cheng X, Liu X-J, Jiang Q, Gao G, Lin D-Y, Kang X-L et al (2020) Two conserved epigenetic regulators prevent healthy ageing. Nature 579:118–122
Zakharova VV, Magnitov MD, Del Maestro L, Ulianov SV, Glentis A, Uyanik B, Williart A, Karpukhina A, Demidov O, Joliot V et al (2022) SETDB1 fuels the lung cancer phenotype by modulating epigenome, 3D genome organization and chromatin mechanical properties. Nucleic Acids Res 50:4389–4413
Zeller P, Padeken J, van Schendel R, Kalck V, Tijsterman M, Gasser SM (2016) Histone H3K9 methylation is dispensable for Caenorhabditis elegans development but suppresses RNA:DNA hybrid-associated repeat instability. Nat Genet 48:1385–1395
Zhang X, Wen H, Shi X (2012) Lysine methylation: beyond histones. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 44:14–27
Zhang Z, Palli SR (2009) Identification of a cis-regulatory element required for 20-hydroxyecdysone enhancement of antimicrobial peptide gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Mol Biol 18:595–605
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation #23-24-00114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Barbara Mellone
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Romanov, S.E., Shloma, V.V., Maksimov, D.A. et al. SetDB1 and Su(var)3-9 are essential for late stages of larval development of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosome Res 31, 35 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-023-09743-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-023-09743-7