Abstract
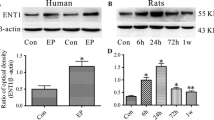
Aquaporin 4 (AQP4), a water-specific channel protein locating on the astrocyte membrane, has been found to be antagonist, agonist and undergone closely related to epilepsy. Our previous study showed that inhibition of an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) subunit NR2A can suppress epileptic seizures, suggesting that AQP4 is potentially involved in NR2A-mediated epilepsy treatment. In this study, we aimed to explore the relevance of AQP4 in NR2A-mediated seizures treatment in pentylenetetrazol (PTZ)-induced rat models. We performed electroencephalogram (EEG) recording and examined AQP4 expression at mRNA and protein levels, and the downstream molecules of AQP4 as well. It showed that AQP4 expression was increased after the induction of seizures. Lateral ventricle pretreatment of NR2A inhibitor could mitigate the PTZ-induced seizures severity and counterbalance the increase of AQP4 expression. In contrast, NR2A activator that resulted in seizures aggravation could further augment the seizure-related elevations of AQP4 expression. Pharmacological inhibition of AQP4 alone could also suppress the PTZ-induced seizure activities, with decreased expressions of NF-κB p65, interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in the brain. The results indicated that increased expression of AQP4 might be an important mechanism involved in NR2A of NMDAR-mediated treatment for epileptic seizures, enlightening a potentially new target for seizures treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borges K, Gearing M, McDermott DL, Smith AB, Almonte AG, Wainer BH, Dingledine R (2003) Neuronal and glial pathological changes during epileptogenesis in the mouse pilocarpine model. Exp Neurol 182(1):21–34
Burfeind KG, Murchison CF, Westaway SK, Simon MJ, Erten-Lyons D, Kaye JA, Quinn JF, Iliff JJ (2017) The effects of noncoding aquaporin-4 single-nucleotide polymorphisms on cognition and functional progression of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement (NY) 3(3):348–359
Cai M, Yu Z, Wang L, Song X, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Zhang W, Li W, Xiang J, Cai D (2016) Tongxinluo reduces brain edema and inhibits post-ischemic inflammation after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 181:136–145
Chen Q, He S, Hu XL, Yu J, Zhou Y, Zheng J, Zhang S, Zhang C, Duan WH, Xiong ZQ (2007) Differential roles of NR2A- and NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in activity-dependent brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene regulation and limbic epileptogenesis. J Neurosci 27(3):542–552
Chen L, Yu H, Zhou Y, Ma M, Wang L, Hu J, Lei S, Zhu X (2015) Effect of acetazolamide on the expression of aquaporin-4 in hippocampus of rats with PTZ-induced chronic epilepsy. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol (Med Sci) 05:510–514
Chen LH, Zhang HT, Xu RX, Li WD, Zhao H, Yang Y, Sun K (2018) Interaction of aquaporin 4 and N-methyl-d-aspartate NMDA receptor 1 in traumatic brain injury of rats. Iranian J Basic Med Sci 21(11):1148–1154
Choi J, Nordli DJ, Alden TD, DiPatri AJ, Laux L, Kelley K, Rosenow J, Schuele SU, Rajaram V, Koh S (2009) Cellular injury and neuroinflammation in children with chronic intractable epilepsy. J Neuroinflamm 6:38
Dai W, Yan J, Chen G, Hu G, Zhou X, Zeng X (2018) AQP4knockout alleviates the lipopolysaccharideinduced inflammatory response in astrocytes via SPHK1/MAPK/AKT signaling. Int J Mol Med 42(3):1716–1722
Das A, Wallace GT, Holmes C, McDowell ML, Smith JA, Marshall JD, Bonilha L, Edwards JC, Glazier SS, Ray SK, Banik NL (2012) Hippocampal tissue of patients with refractory temporal lobe epilepsy is associated with astrocyte activation, inflammation, and altered expression of channels and receptors. Neuroscience 220:237–246
Deng Z, Luo M, Zhao Y, Yu H, Xie L, Chen L, Zhu X, Hu J, Lei S (2014) Effect of GluN2A inhibitor on expression of P-glycoprotein in rats with status. Epilepticus. 2:168–172
Devinsky O, Vezzani A, O'Brien TJ, Jette N, Scheffer IE, de Curtis M, Perucca P (2018) Epilepsy. Nat Rev Dis Primers 4:18024
Duan L, Di Q (2017) Acetazolamide suppresses multi-drug resistance-related protein 1 and P-glycoprotein expression by inhibiting aquaporins expression in a mesial temporal epilepsy rat model. Med Sci Monit 23:5818–5825
Eyo UB, Peng J, Swiatkowski P, Mukherjee A, Bispo A, Wu LJ (2014) Neuronal hyperactivity recruits microglial processes via neuronal NMDA receptors and microglial P2Y12 receptors after status epilepticus. J Neurosci 34(32):10528–10540
Guo C, Wu T, Zhu H, Gao L (2019) Aquaporin 4 blockade attenuates acute lung injury through inhibition of Th17 cell proliferation in mice. Inflammation 42(4):1401–1412
Han X, Huang Q, Liu L, Sha X, Hu B, Liu H (2018) Changes in the expression of AQP4 and AQP9 in the hippocampus following eclampsia-like seizure. Int J Mol Sci 19(1):300
Hubbard JA, Szu JI, Binder DK (2017) The role of aquaporin-4 in synaptic plasticity, memory and disease. Brain Res Bull. 136:118–129
Ito H, Yamamoto N, Arima H, Hirate H, Morishima T, Umenishi F, Tada T, Asai K, Katsuya H, Sobue K (2006) Interleukin-1beta induces the expression of aquaporin-4 through a nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in rat astrocytes. J Neurochem 99(1):107–118
Kohr G (2006) NMDA receptor function: subunit composition versus spatial distribution. Cell Tissue Res 326(2):439–446
Kouis P, Mikroulis A, Psarropoulou C (2014) A single episode of juvenile status epilepticus reduces the threshold to adult seizures in a stimulus-specific way. Epilepsy Res 108(9):1564–1571
Lemke JR, Lal D, Reinthaler EM, Steiner I, Nothnagel M, Alber M, Geider K, Laube B, Schwake M, Finsterwalder K, Franke A, Schilhabel M, Jahn JA, Muhle H, Boor R, Van Paesschen W, Caraballo R, Fejerman N, Weckhuysen S, De Jonghe P, Larsen J, Moller RS, Hjalgrim H, Addis L, Tang S, Hughes E, Pal DK, Veri K, Vaher U, Talvik T, Dimova P, Guerrero LR, Serratosa JM, Linnankivi T, Lehesjoki AE, Ruf S, Wolff M, Buerki S, Wohlrab G, Kroell J, Datta AN, Fiedler B, Kurlemann G, Kluger G, Hahn A, Haberlandt DE, Kutzer C, Sperner J, Becker F, Weber YG, Feucht M, Steinbock H, Neophythou B, Ronen GM, Gruber-Sedlmayr U, Geldner J, Harvey RJ, Hoffmann P, Herms S, Altmuller J, Toliat MR, Thiele H, Nurnberg P, Wilhelm C, Stephani U, Helbig I, Lerche H, Zimprich F, Neubauer BA, Biskup S, von Spiczak S (2013) Mutations in GRIN2A cause idiopathic focal epilepsy with rolandic spikes. Nat Genet 45(9):1067–1072
Li X, Liu H, Yang Y (2017) Magnesium Sulfate attenuates brain edema by lowering AQP4 expression and inhibits glia-mediated neuroinflammation in a rodent model of eclampsia. Behavioural Brain Res. 364:403–412
Liu L, Wong TP, Pozza MF, Lingenhoehl K, Wang Y, Sheng M, Auberson YP, Wang YT (2004) Role of NMDA receptor subtypes in governing the direction of hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Science 304(5673):1021–1024
Luo T, Wu WH, Chen BS (2011) NMDA receptor signaling: death or survival? Front Biol (Beijing) 6(6):468–476
Medici V, Frassoni C, Tassi L, Spreafico R, Garbelli R (2011) Aquaporin 4 expression in control and epileptic human cerebral cortex. Brain Res 1367:330–339
Mei Z, Qiu J, Alcon S, Hashim J, Rotenberg A, Sun Y, Meehan WR, Mannix R (2018) Memantine improves outcomes after repetitive traumatic brain injury. Behav Brain Res 340:195–204
Menezes FP, Da SR (2017) The influence of temperature on adult zebrafish sensitivity to pentylenetetrazole. Epilepsy Res 135:14–18
Mercado-Gomez OF, Cordova-Davalos L, Garcia-Betanzo D, Rocha L, Alonso-Vanegas MA, Cienfuegos J, Guevara-Guzman R (2018) Overexpression of inflammatory-related and nitric oxide synthase genes in olfactory bulbs from frontal lobe epilepsy patients. Epilepsy Res 148:37–43
Michel PP, Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2016) Understanding dopaminergic cell death pathways in parkinson disease. Neuron 90(4):675–691
Ohnishi M, Monda A, Takemoto R, Fujimoto Y, Sugitani M, Iwamura T, Hiroyasu T, Inoue A (2014) High-mobility group box 1 up-regulates aquaporin 4 expression via microglia-astrocyte interaction. Neurochem Int 75:32–38
Paoletti P, Neyton J (2007) NMDA receptor subunits: function and pharmacology. Curr Opin Pharmacol 7(1):39–47
Patterson KP, Brennan GP, Curran M, Kinney-Lang E, Dube C, Rashid F, Ly C, Obenaus A, Baram TZ (2015) Rapid, coordinate inflammatory responses after experimental febrile status epilepticus: implications for epileptogenesis. Eneuro. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0034-15.2015
Paxinos G, Watson C (1996) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 3rd edn. Academic Press, New York
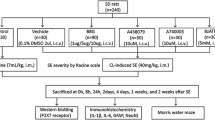
Racine RJ (1972) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation II motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32(3):281–294
Ridder DA, Schwaninger M (2009) NF-kappaB signaling in cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 158(3):995–1006
Rozov A, Burnashev N (2016) Fast interaction between AMPA and NMDA receptors by intracellular calcium. Cell Calcium 60(6):407–414
Schrattenholz A, Soskic V (2006) NMDA receptors are not alone: dynamic regulation of NMDA receptor structure and function by neuregulins and transient cholesterol-rich membrane domains leads to disease-specific nuances of glutamate-signalling. Curr Top Med Chem 6(7):663–686
Shi Y, Zhang L, Teng J, Miao W (2018) HMGB1 mediates microglia activation via the TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway in coriaria lactone induced epilepsy. Mol Med Rep 17(4):5125–5131
Shin HJ, Kim H, Heo RW, Kim HJ, Choi WS, Kwon HM, Roh GS (2014) Tonicity-responsive enhancer binding protein haplodeficiency attenuates seizure severity and NF-kappaB-mediated neuroinflammation in kainic acid-induced seizures. Cell Death Differ 21(7):1095–1106
Skowronska K, Obara-Michlewska M, Czarnecka A, Dabrowska K, Zielinska M, Albrecht J (2019) Persistent overexposure to N-Methyl-d-Aspartate (NMDA) calcium-dependently downregulates glutamine synthetase, Aquaporin 4, and Kir4.1 channel in mouse cortical astrocytes. Neurotoxicity Res. 35(1):271–280
Sun L, Li M, Ma X, Feng H, Song J, Lv C, He Y (2017) Inhibition of HMGB1 reduces rat spinal cord astrocytic swelling and AQP4 expression after oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation via TLR4 and NF-kappaB signaling in an IL-6-dependent manner. J Neuroinflamm 14(1):231
Sun L, Li M, Ma X, Zhang L, Song J, Lv C, He Y (2018) Inhibiting high mobility group box-1 reduces early spinal cord edema and attenuates astrocyte activation and Aquaporin-4 expression after spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurotrauma. 36(3):421–435
Szepetowski P (2017) Genetics of human epilepsies: continuing progress. Presse Med. 47(3):218–226
Tovar KR, Westbrook GL (1999) The incorporation of NMDA receptors with a distinct subunit composition at nascent hippocampal synapses in vitro. J Neurosci 19(10):4180–4188
van Vliet EA, Da CAS, Redeker S, van Schaik R, Aronica E, Gorter JA (2007) Blood-brain barrier leakage may lead to progression of temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 130(Pt 2):521–534
Verkman AS, Smith AJ, Phuan PW, Tradtrantip L, Anderson MO (2017) The aquaporin-4 water channel as a potential drug target in neurological disorders. Expert Opin Ther Targets 21(12):1161–1170
Wang XX, Li YH, Gong HQ, Liang PJ, Zhang PM, Lu QC (2017a) The subiculum: a potential site of ictogenesis in a neonatal seizure model. Front Neurol 8:147
Wang X, An F, Wang S, An Z, Wang S (2017b) Orientin attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat model through the AQP-4 and TLR4/NF-kappaB/TNF-alpha Signaling Pathway. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 26(10):2199–2214
Wang C, Yan M, Jiang H, Wang Q, He S, Chen J, Wang C (2018) Mechanism of aquaporin 4 (AQP 4) up-regulation in rat cerebral edema under hypobaric hypoxia and the preventative effect of puerarin. Life Sci 193:270–281
Wu X, Zhang JT, Li D, Zhou J, Yang J, Zheng HL, Chen JG, Wang F (2017) Aquaporin-4 deficiency facilitates fear memory extinction in the hippocampus through excessive activation of extrasynaptic GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors. Neuropharmacology 112(Pt A):124–134
Xie Y, Huang XF (2018) Commentary: GLYX-13 ameliorates schizophrenia-like phenotype induced by MK-801 in mice: role of hippocampal NR2B and DISC1. Front Mol Neurosci 11:315
Yang Y, Tian X, Xu D, Zheng F, Lu X, Zhang Y, Ma Y, Li Y, Xu X, Zhu B, Wang X (2018) GPR40 modulates epileptic seizure and NMDA receptor function. Sci Adv 4(10):u2357
Yin J, Zhang H, Chen H, Lv Q, Jin X (2018) Hypertonic saline alleviates brain edema after traumatic brain injury via downregulation of aquaporin 4 in rats. Med Sci Monit 24:1863–1870
Yu H, Chen L, Ma M (2015) Effect on the expression of NF- κB p65、IL-1β、IL-6 and TNF-α in the hippocampus of chronic epilepsy rats by acetazolamide. J Apoplexy Nerv Dis 08:730–733
Yu H, Qi GL, Wang J, Chen L, Deng Z, Zhao YS, Lei SS, Zhu XQ (2016) Aquaporin 4 inhibition decreased synthesis of cytokines by acetazolamide in the hippocampus of rats with pentrazol-induced chronic epilepsy. Genet Mol Res 15(3):15039012
Zhou Y, Li HL, Zhao R, Yang LT, Dong Y, Yue X, Ma YY, Wang Z, Chen J, Cui CL, Yu AC (2010) Astrocytes express N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits in development, ischemia and post-ischemia. Neurochem Res 35(12):2124–2134
Zhou D, Lv D, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Wang C (2018) GLYX-13 ameliorates schizophrenia-like phenotype induced by MK-801 in mice: ROLE of hippocampal NR2B and DISC1. Front Mol Neurosci 11:121
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81771401, 81870992, 81870856, 81603681, U1603281), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province of China (2020A1515010986), Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province of China (2017ZC0234), a technology project of Guangzhou (2018-1202-SF-0019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. SL, XZ, and PX designed the study. YH, ZZ, ZL, YL, YH, SD, and XC performed the research. XC analyzed the data. YH wrote the manuscript. XZ and PX revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were following the ethical standards of the Experimental Animal Care and Ethics Committee of Experimental Animal Center of Guangzhou Medical University (GY2017-038).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, S., He, Y., Zhu, Z. et al. Inhibition of NMDA Receptors Downregulates Astrocytic AQP4 to Suppress Seizures. Cell Mol Neurobiol 40, 1283–1295 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00813-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00813-6