Abstract
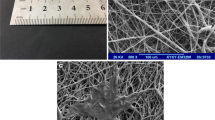
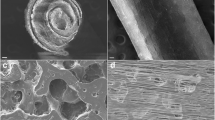
The current study aimed to enhance the efficacy of peripheral nerve regeneration using a biodegradable porous neural guidance conduit as a carrier to transplant allogeneic Schwann cells (SCs). The conduit was prepared from polyurethane (PU) and gelatin nanofibrils (GNFs) using thermally induced phase separation technique and filled with melatonin (MLT) and platelet-rich plasma (PRP). The prepared conduit had the porosity of 87.17 ± 1.89%, the contact angle of 78.17 ± 5.30° and the ultimate tensile strength and Young’s modulus of 5.40 ± 0.98 MPa and 3.13 ± 0.65 GPa, respectively. The conduit lost about 14% of its weight after 60 days in distilled water. The produced conduit enhanced the proliferation of SCs demonstrated by a tetrazolium salt-based assay. For functional analysis, the conduit was seeded with 1.50 × 104 SCs (PU/GNFs/PRP/MLT/SCs) and implanted into a 10-mm sciatic nerve defect of Wistar rat. Three control groups were used: (1) PU/GNFs/SCs, (2) PU/GNFs/PRP/SCs, and (3) Autograft. The results of sciatic functional index, hot plate latency, compound muscle action potential amplitude and latency, weight-loss percentage of wet gastrocnemius muscle and histopathological examination using hematoxylin–eosin and Luxol fast blue staining, demonstrated that using the PU/GNFs/PRP/MLT conduit to transplant SCs to the sciatic nerve defect resulted in a higher regenerative outcome than the PU/GNFs and PU/GNFs/PRP conduits.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasipour-Dalivand S, Mohammadi R, Mohammadi V (2015) Effects of local administration of platelet rich plasma on functional recovery after bridging sciatic nerve defect using silicone rubber chamber; an experimental study. Bull Emerg Trauma 3:1
Atik B, Erkutlu I, Tercan M, Buyukhatipoglu H, Bekerecioglu M, Pence S (2011) The effects of exogenous melatonin on peripheral nerve regeneration and collagen formation in rats. J Surg Res 166:330–336
Chan-Chan L, Solis-Correa R, Vargas-Coronado R, Cervantes-Uc J, Cauich-Rodríguez J, Quintana P, Bartolo-Pérez P (2010) Degradation studies on segmented polyurethanes prepared with HMDI, PCL and different chain extenders. Acta Biomater 6:2035–2044
Chang HM, Liu CH, Hsu WM, Chen LY, Wang HP, Wu TH, Chen KY, Ho WH, Liao WC (2014) Proliferative effects of melatonin on Schwann cells: implication for nerve regeneration following peripheral nerve injury. J Pineal Res 56:322–332
Chen J, Dong R, Ge J, Guo B, Ma PX (2015) Biocompatible, biodegradable, and electroactive polyurethane-urea elastomers with tunable hydrophilicity for skeletal muscle tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:28273–28285
Chen L, Li B, Chen B, Shao Y, Luo Q, Shi X, Chen Y (2016) Thymoquinone alleviates the experimental diabetic peripheral neuropathy by modulation of inflammation. Sci Rep 6:31656
Corfas G, Velardez MO, Ko C-P, Ratner N, Peles E (2004) Mechanisms and roles of axon-Schwann cell interactions. J Neurosci 24:9250–9260
Cui T, Yan Y, Zhang R, Liu L, Xu W, Wang X (2008) Rapid prototyping of a double-layer polyurethane–collagen conduit for peripheral nerve regeneration. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 15:1–9
Dai LG, Huang GS, Hsu Sh (2013) Sciatic nerve regeneration by cocultured Schwann cells and stem cells on microporous nerve conduits. Cell Transpl 22:2029–2039
Danielsen N, Pettmann B, Vahlsing H, Manthorpe M, Varon S (1988) Fibroblast growth factor effects on peripheral nerve regeneration in a silicone chamber model. J Neurosci Res 20:320–330
Davis JB, Stroobant P (1990) Platelet-derived growth factors and fibroblast growth factors are mitogens for rat Schwann cells. J Cell Biol 110:1353–1360
De Luca AC, Lacour SP, Raffoul W, Di Summa PG (2014) Extracellular matrix components in peripheral nerve repair: how to affect neural cellular response and nerve regeneration? Neural Regen Res 9:1943
De Ruiter GC, Malessy MJ, Yaszemski MJ, Windebank AJ, Spinner RJ (2009) Designing ideal conduits for peripheral nerve repair. Neurosurg Focus 26:E5
Dijkstra JR, Meek MF, Robinson PH, Gramsbergen A (2000) Methods to evaluate functional nerve recovery in adult rats: walking track analysis, video analysis and the withdrawal reflex. J Neurosci Methods 96:89–96
El-Shekeil Y, Sapuan S, Abdan K, Zainudin E (2012) Influence of fiber content on the mechanical and thermal properties of Kenaf fiber reinforced thermoplastic polyurethane composites. Mater Des 40:299–303
Evans PJ, Mackinnon SE, Best TJ, Wade JA, Awerbuck DC, Makino AP, Hunter DA, Midha R (1995) Regeneration across preserved peripheral nerve grafts. Muscle Nerve 18:1128–1138
Farrag TY, Lehar M, Verhaegen P, Carson KA, Byrne PJ (2007) Effect of platelet rich plasma and fibrin sealant on facial nerve regeneration in a rat model. Laryngoscope 117:157–165
Frattini F, Pereira Lopes FR, Almeida FM, Rodrigues RF, Boldrini LC, Tomaz MA, Baptista AF, Melo PA, Martinez AMB (2012) Mesenchymal stem cells in a polycaprolactone conduit promote sciatic nerve regeneration and sensory neuron survival after nerve injury. Tissue Eng Part A 18:2030–2039
Ghasemi-Mobarakeh L, Prabhakaran MP, Morshed M, Nasr-Esfahani M-H, Ramakrishna S (2008) Electrospun poly (ɛ-caprolactone)/gelatin nanofibrous scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. Biomaterials 29:4532–4539
Gristina AG, Naylor PT, Myrvik QN (1990) Biomaterial-centered infections: microbial adhesion versus tissue integration. In: Wadström T, Eliasson I, Holder I, Ljungh A (eds) Pathogenesis of wound and biomaterial-associated infections. Springer, London, pp 193–216
Kajikawa Y, Morihara T, Sakamoto H, Ki Matsuda, Oshima Y, Yoshida A, Nagae M, Arai Y, Kawata M, Kubo T (2008) Platelet-rich plasma enhances the initial mobilization of circulation-derived cells for tendon healing. J Cell Physiol 215:837–845
Kong X, Li X, Cai Z, Yang N, Liu Y, Shu J, Pan L, Zuo P (2008) Melatonin regulates the viability and differentiation of rat midbrain neural stem cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 28:569–579
Liu X, Smith LA, Hu J, Ma PX (2009) Biomimetic nanofibrous gelatin/apatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 30:2252–2258
Liu H, Ding X, Zhou G, Li P, Wei X, Fan Y (2013) Electrospinning of nanofibers for tissue engineering applications. J Nanomater 2013:3
Lu W, Ma M, Xu H, Zhang B, Cao X, Guo Y (2015) Gelatin nanofibers prepared by spiral-electrospinning and cross-linked by vapor and liquid-phase glutaraldehyde. Mater Lett 140:1–4
Luo L, Gan L, Liu Y, Tian W, Tong Z, Wang X, Huselstein C, Chen Y (2015) Construction of nerve guide conduits from cellulose/soy protein composite membranes combined with Schwann cells and pyrroloquinoline quinone for the repair of peripheral nerve defect. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 457:507–513
Naseri-Nosar M, Salehi M, Ghorbani S, Beiranvand SP, Goodarzi A, Azami M (2016) Characterization of wet-electrospun cellulose acetate based 3-dimensional scaffolds for skin tissue engineering applications: influence of cellulose acetate concentration. Cellulose 23:3239–3248
Naseri-Nosar M, Salehi M, Hojjati-Emami S (2017) Cellulose acetate/poly lactic acid coaxial wet-electrospun scaffold containing citalopram-loaded gelatin nanocarriers for neural tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol 103:701–708
Nectow AR, Marra KG, Kaplan DL (2012) Biomaterials for the development of peripheral nerve guidance conduits. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 18:40–50
Odaci E, Kaplan S (2009) Melatonin and nerve regeneration. Int Rev Neurobiol 87:317–335
Ogata T, Yamamoto SI, Tanaka S (2006) Signaling axis in schwann cell proliferation and differentiation. Mol Neurobiol 33:51–61
Parenteau-Bareil R, Gauvin R, Berthod F (2010) Collagen-based biomaterials for tissue engineering applications. Materials 3:1863–1887
Pfister LA, Papaloïzos M, Merkle HP, Gander B (2007) Nerve conduits and growth factor delivery in peripheral nerve repair. J Peripher Nerv Syst 12:65–82
Ridley AJ, Davis JB, Stroobant P, Land H (1989) Transforming growth factors-beta 1 and beta 2 are mitogens for rat Schwann cells. J Cell Biol 109:3419–3424
Salehi M, Naseri-Nosar M, Amani A, Azami M, Tavakol S, Ghanbari H (2015) Preparation of Pure PLLA, Pure Chitosan, and PLLA/Chitosan blend porous tissue engineering scaffolds by thermally induced phase separation method and evaluation of the corresponding mechanical and biological properties. Int J Polym Mater 64:675–682
Salehi M, Naseri-Nosar M, Azami M, Nodooshan SJ, Arish J (2016a) Comparative study of poly(l-lactic acid) scaffolds coated with chitosan nanoparticles prepared via ultrasonication and ionic gelation techniques. Tissue Eng Regen Med 13:498–506
Salehi M, Farzamfar S, Bastami F, Tajerian R (2016b) Fabrication and characterization of electrospun PLLA/collagen nanofibrous scaffold coated with chitosan to sustain release of aloe vera gel for skin tissue engineering. Biomed Eng (Singap.) 28:1650035
Salehi M, Naseri-Nosar M, Ebrahimi-Barough S, Nourani M, Khojasteh A, Hamidieh A-A, Amani A, Farzamfar S, Ai J (2017) Sciatic nerve regeneration by transplantation of schwann cells via erythropoietin controlled-releasing polylactic acid/multi-walled carbon nanotubes/gelatin nanofibrils neural guidance conduit. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater
Shi X, Chen Y, Nadeem L, Xu G (2013) Beneficial effect of TNF-α inhibition on diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Neuroinflammation 10:1
Sondell M, Lundborg G, Kanje M (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor has neurotrophic activity and stimulates axonal outgrowth, enhancing cell survival and Schwann cell proliferation in the peripheral nervous system. J Neurosci 19:5731–5740
Stavisky RC, Britt JM, Zuzek A, Truong E, Bittner GD (2005) Melatonin enhances the in vitro and in vivo repair of severed rat sciatic axons. Neurosci Lett 376:98–101
Sun X-H, Che Y-Q, Tong X-J, Zhang L-X, Feng Y, Xu A-H, Tong L, Jia H, Zhang X (2009) Improving nerve regeneration of acellular nerve allografts seeded with SCs bridging the sciatic nerve defects of rat. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29:347–353
Turgut M, Kaplan S (2011) Effects of melatonin on peripheral nerve regeneration. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov 5:100–108
Wang S, Yaszemski MJ, Knight AM, Gruetzmacher JA, Windebank AJ, Lu L (2009) Photo-crosslinked poly (ε-caprolactone fumarate) networks for guided peripheral nerve regeneration: material properties and preliminary biological evaluations. Acta Biomater 5:1531–1542
Wang X, Ding B, Li B (2013) Biomimetic electrospun nanofibrous structures for tissue engineering. Mater Today 16:229–241
Webber CA, Christie KJ, Cheng C, Martinez JA, Singh B, Singh V, Thomas D, Zochodne DW (2011) Schwann cells direct peripheral nerve regeneration through the Netrin-1 receptors, DCC and Unc5H2. Glia 59:1503–1517
Wu M, Zhao G, Yang X, Peng C, Zhao J, Liu J, Li R, Gao Z (2014) Puerarin accelerates neural regeneration after sciatic nerve injury. Neural Regen Res 9:589
Yu W, Zhao W, Zhu C, Zhang X, Ye D, Zhang W, Zhou Y, Jiang X, Zhang Z (2011) Sciatic nerve regeneration in rats by a promising electrospun collagen/poly (ε-caprolactone) nerve conduit with tailored degradation rate. BMC Neurosci 12:1
Acknowledgement
This study was funded by Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. 95-01-87-31294).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salehi, M., Naseri-Nosar, M., Ebrahimi-Barough, S. et al. Polyurethane/Gelatin Nanofibrils Neural Guidance Conduit Containing Platelet-Rich Plasma and Melatonin for Transplantation of Schwann Cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38, 703–713 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0535-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0535-8