Abstract
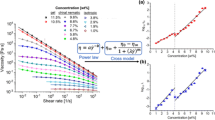
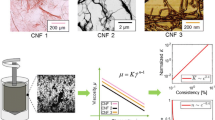
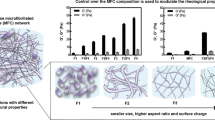
Cellulose nanomaterials provide a promising avenue for combining composite materials with natural polymers or bio-based plastics, however, current studies on rheological characterization at high shear rates is limited. In this study, a capillary rheometer was employed to investigate the rheological characteristics of aqueous cellulose nanofibril (CNF) suspensions at room temperature and shear rates above 1000 s\(^{-1}\). The shear rate-dependent viscosity of aqueous CNFs was characterized and monitored for viscosity-related indicators of fibril decomposition or entanglement due to the stresses induced by the high shear-rate flow. Traditional capillary rheology corrections for entrance pressure loss and irregular flow profiles were attempted to compare apparent and true rheological behaviors. Large entanglements of fibrils made the characterization of the suspensions difficult due to their ability to clog the capillary. However, appropriate preprocessing steps enabled better measurement resolution and enhanced dispersion of cellulose nanofibers, as verified by atomic force microscopy. The suspensions display shear thinning behavior and demonstrate higher entrance pressures for lower shear rates. Similar preprocessing techniques could be implemented on a large scale to enhance fibril distribution in CNF suspensions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availibility
Data may be made available to individuals upon request.
References
Bledzki AK, Faruk O, Sperber VE (2006) Cars from bio-fibres. Macromol Mater Eng 291(5):449–457. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.200600113
Camarero Espinosa S, Kuhnt T, Foster EJ, Weder C (2013) Isolation of thermally stable cellulose nanocrystals by phosphoric acid hydrolysis. Biomacromol 14(4):1223–1230. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm400219u
Chakrabarty A, Teramoto Y (2018) Recent advances in nanocellulose composites with polymers: a guide for choosing partners and how to incorporate them. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050517
Clarkson CM, El Awad Azrak SM, Forti ES, Schueneman GT, Moon RJ, Youngblood JP (2021) Recent developments in cellulose nanomaterial composites. Adv Mater 33(28):e2000718. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202000718
CSA Group (2014) Cellulosic nanomaterials—test methods for characterization. Tech. Rep. Z5100-14, CSA Group. https://www.csagroup.org/store/product/2422955/
Dospisil D, Kubát J, Plešek M, Sáha P (1994) Extrusion of short fibre reinforced PP: fibre length reduction during single screw extrusion. Int Polym Process 9(4):303–309. https://doi.org/10.3139/217.940303
Faruk O, Bledzki AK, Fink HP, Sain M (2014) Progress report on natural fiber reinforced composites. Macromol Mater Eng 299(1):9–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201300008
Foster EJ, Moon RJ, Agarwal UP et al (2018) Current characterization methods for cellulose nanomaterials. Chem Soc Rev 47(8):2609–2679. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cs00895j
Franzén B, Klason C, Kubát J, Kitano T (1989) Fibre degradation during processing of short fibre reinforced thermoplastics. Composites 20(1):65–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-4361(89)90684-8
Hubbe MA, Rojas OJ, Lucia LA, Sain M (2008) Cellulosic nanocomposites a review. BioResources 3(3):929–980. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.3.3.929-980
Hubbe MA, Tayeb P, Joyce M, Tyagi P, Kehoe M, Dimic-Misic K, Pal L (2017) Rheology of nanocellulose-rich aqueous suspensions: a review. BioResources 12(4):9556–9661. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.12.4.hubbe
Iotti M, Gregersen ØW, Moe S, Lenes M (2011) Rheological studies of microfibrillar cellulose water dispersions. J Polym Environ 19(1):137–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-010-0248-2
Iwatake A, Nogi M, Yano H (2008) Cellulose nanofiber-reinforced polylactic acid. Compos Sci Technol 68(9):2103–2106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2008.03.006
Kang K, Koelling KW, Lee LJ (2006) Microdevice end pressure evaluations with bagley correction. Microfluid Nanofluidics 2(3):223–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-005-0067-2
Karppinen A, Saarinen T, Salmela J, Laukkanen A, Nuopponen M, Seppälä J (2012) Flocculation of microfibrillated cellulose in shear flow. Cellulose 19(6):1807–1819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9766-5
Lauri J, Haavisto S, Salmela J, Miettinen A, Fabritius T, Koponen AI (2021) Online measurement of floc size, viscosity, and consistency of cellulose microfibril suspensions with optical coherence tomography. Cellulose 28(6):3373–3387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03745-6
Lee KY, Tammelin T, Schulfter K, Kiiskinen H, Samela J, Bismarck A (2012) High performance cellulose nanocomposites: comparing the reinforcing ability of bacterial cellulose and nanofibrillated cellulose. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(8):4078–4086. https://doi.org/10.1021/am300852a
Li B, Guo Y, Steeman P, Bulters M, Yu W (2021) Wall effect on the rheology of short-fiber suspensions under shear. J Rheol 65(6):1169–1185. https://doi.org/10.1122/8.0000292
Marett J, Aning A, Foster EJ (2017) The isolation of cellulose nanocrystals from pistachio shells via acid hydrolysis. Ind Crops Prod 109:869–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.09.039
McHugh TW, Harrell ER, Powell JW, Chartoff RP (1972) End corrections in capillary flow of polymer melts with nonzero exit pressures. Trans Soc Rheol 16(2):331–337. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.549246
Mendelson RA, Finger FL, Bagley EB (1971) Die swell and recoverable shear strain in polyethylene extrusion. J Polym Sci C Polym Sympos 35:177–188
Mitsoulis E, Hatzikiriakos SG (2003) Bagley correction: the effect of contraction angle and its prediction. Rheol Acta 42(4):309–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-003-0294-y
Moon RJ, Schueneman GT, Simonsen J (2016) Overview of cellulose nanomaterials, their capabilities and applications. JOM 68(9):2383–2394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-016-2018-7
Pinto A, Ciesla JH, Palucci A, Sutliff BP, Nomura CT (2016) Chemically intractable no more: in vivo incorporation of “Click’’-Ready fatty acids into Poly-[(R)-3-hydroxyalkanoates] in escherichia coli. ACS Macro Lett 5(2):215–219. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.5b00823
Puls J, Wilson SA, Hölter D (2011) Degradation of cellulose acetate-based materials: a review. J Polym Environ 19(1):152–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-010-0258-0
Saarinen T, Haavisto S, Sorvari A, Salmela J, Seppälä J (2014) The effect of wall depletion on the rheology of microfibrillated cellulose water suspensions by optical coherence tomography. Cellulose 21(3):1261–1275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0187-5
Salinas A, Pittman JFT (1981) Bending and breaking fibers in sheared suspensions. Polym Eng Sci 21(1):23–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.760210105
Scheel RA, Fusi AD, Min BC, Thomas CM, Ramarao BV, Nomura CT (2019) Increased production of the value-added biopolymers poly(r-3-hydroxyalkanoate) and Poly(\(\gamma\)-Glutamic acid) from hydrolyzed paper recycling waste fines. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:409. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00409
Sutliff BP, Das A, Youngblood J, Bortner MJ (2020) High shear capillary rheometry of cellulose nanocrystals for industrially relevant processing. Carbohydr Polym 231(115):735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115735
Tanaka R, Saito T, Hondo H, Isogai A (2015) Influence of flexibility and dimensions of nanocelluloses on the flow properties of their aqueous dispersions. Biomacromol 16(7):2127–2131. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.5b00539
Tappel RC, Pan W, Bergey NS, Wang Q, Patterson IL, Ozumba OA, Matsumoto K, Taguchi S, Nomura CT (2014) Engineering Escherichia coli for improved production of short-chain-length-co-medium-chain-length poly[(R)-3-hydroxyalkanoate] (SCL-co-MCL PHA) copolymers from renewable nonfatty acid feedstocks. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2(7):1879–1887. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc500217p
Thompson RC, Swan SH, Moore CJ, vom Saal FS (2009) Our plastic age. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 364(1526):1973–1976. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0054
Vadodaria SS, Onyianta AJ, Sun D (2018) High-shear rate rheometry of micro-nanofibrillated cellulose (CMF/CNF) suspensions using rotational rheometer. Cellulose 25(10):5535–5552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1963-4
Wang C, Li KZ, Li HJ, Jiao GS, Lu J, Hou DS (2008) Effect of carbon fiber dispersion on the mechanical properties of carbon fiber-reinforced cement-based composites. Mater Sci Eng A 487(1):52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.09.073
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Materials Characterization Laboratory at Virginia Tech for the use of the Jupiter AFM and assistance with obtaining neat AFM images.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.P.S.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing - Original Draft, Writing - Review and Editing. A.J.K.: Methodology, Formal Analysis, Investigation. S.S. and S.O.: Methodology, Investigation. M.J.B. Conceptualization, Writing - Review and Editing, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary information:
Supplementary information should be included with the online version of this article. (628 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sutliff, B.P., Kaplan, A.J., Stutz, S. et al. Preprocessing considerations for floc reduction in cellulose nanofibril suspensions. Cellulose 30, 6907–6915 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05315-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05315-4