Abstract
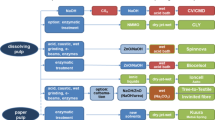
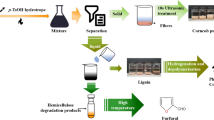
In this study, dissolving pulp was prepared from corncob via alkali extraction, kraft cooking, metal ion removal, and H2O2 bleaching. Two cooking schemes were used to prepare unbleached corncob pulp samples with degrees of polymerization of 735 and 565. Employing an acid treatment with sodium ethylenediamine tetraacetate (EDTA) and sodium hexametaphosphate (SHMP) effectively reduced the ash and iron contents of the pulp; the optimal treatment conditions were pH 1.5, 0.4 wt% EDTA, and 0.4 wt% SHMP, which afforded pulp with iron and ash contents of 8.5 ppm and 0.02 wt%, respectively. A single-factor experiment was used to study the effects of H2O2 dosage and bleaching time on the brightness of the obtained pulp. The optimal bleaching parameters were determined as an H2O2 dosage of 3 wt% and a bleaching time of 70 min, which led to a brightness value greater than 82%. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy results confirmed that the main component of corncob pulp was cellulose, and the fiber adopted twine-like morphologies with numerous spiral folds on the surface. The wet corncob pulp was used directly as the raw material for spinning lyocell fibers, and the results indicated that the corncob pulp had good spinnability.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Ahuja V, Dasgupta D, Kshirsagar S, Ghosh P, More S, Gupta P, Behera B, Bhaskar T (2022) Crystalline xylitol production from corncob biomass with oral toxicity analysis. Ind Crop Prod 187:115407
Arumugam A, Malolan VV, Ponnusami V (2021) Contemporary pretreatment strategies for bioethanol production from corncobs: a comprehensive review. Waste Biomass Valoriz 12(2):577–612
Behin J, Zeyghami M (2009) Dissolving pulp from corn stalk residue and waste water of Merox unit. Chem Eng J 152(1):26–35
Boonchuay P, Techapun C, Leksawasdi N, Seesuriyachan P, Hanmoungjai P, Watanabe M, Takenaka S, Chaiyaso T (2018) An integrated process for xylooligosaccharide and bioethanol production from corncob. Bioresource Technol 256:399–407
Borbély É (2008) Lyocell, the new generation of regenerated cellulose. Acta Polytech Hung 5(3):11–18
Cardona-Barrau D, Lachenal D, Chirat C (2001) Affinity of metal ions for kraft pulps studied by ESR Inhibition of their catalytic action in oxygen bleaching. J wood chem Technol 21(3):247–261. https://doi.org/10.1081/wct-100105375
Chang S, Guo Y, Wu B, He B (2017) Extracellular expression of alkali tolerant xylanase from Bacillus subtilis Lucky9 in E. coli and application for xylooligosaccharides production from agro-industrial waste. Int J Biol Macromol 96:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.11.032
Ditzel FI, Prestes E, Carvalho BM, Demiate IM, Pinheiro LA (2017) Nanocrystalline cellulose extracted from pine wood and corncob. Carbohyd Polym 157:1577–1585
Fan Y, Zhang D, Zheng A, Zhao Z, Li H, Yang T (2019) Selective production of anhydrosugars and furfural from fast pyrolysis of corncobs using sulfuric acid as an inhibitor and catalyst. Chem Eng J 358:743–751
Fink HP, Weigel P, Purz HJ, Ganster J (2001) Structure formation of regenerated cellulose materials from NMMO-solutions. Prog Polym Sci 26(9):1473–1524
Granholm K, Harju L, Ivaska A (2010) Desorption of metal ions from kraft pulps. Part 1. Chelation of hardwood and softwood kraft pulp with EDTA BioResources 5(1): 206–226
Hao X, Xu F, Zhang J (2022) Effect of pretreatments on production of xylooligosaccharides and monosaccharides from corncob by a two-step hydrolysis. Carbohyd Polym 285:119217
Huang GQ, Zhang Z, Han KT, Zhan HY, Zheng ZT (1998) Modified kraft pulping of eucalyptus wood. Proceedings of the international symposium on emerging technologies of pulping and papermaking of fast-growing wood, Guangzhou, China
Jiang Z, Hu C (2016) Selective extraction and conversion of lignin in actual biomass to monophenols: a review. J Energy Chem 25(6):947–956
Kahar P, Taku K, Tanaka S (2010) Enzymatic digestion of corncobs pretreated with low strength of sulfuric acid for bioethanol production. J Biosci Bioeng 110(4):453–458
Klimont Z, Kupiainen K, Heyes C, Purohit P, Cofala J, Rafaj P, Borken-Kleefeld J, Schöpp W (2017) Global anthropogenic emissions of particulate matter including black carbon. Atmos Chem Phys 17(14):8681–8723
Kumar V, Sandhu PP, Ahluwalia V, Mishra BB, Yadav SK (2019) Improved upstream processing for detoxification and recovery of xylitol produced from corncob. Bioresource Technol 291:121931
Liu R, Yu H, Huang Y (2005) Structure and morphology of cellulose in wheat straw. Cellulose 12(1):25–34
Luo Q, Liu HB (1998) A Kappa number mathematical model for batch kraft pulping control. Proceedings of the international symposium on emerging technologies of pulping and papermaking of fast-growing wood, Guangzhou, China
Lv X, Li Q, Jiang Z, Wang Y, Li J, Hu C (2018) Structure characterization and pyrolysis behavior of organosolv lignin isolated from corncob residue. J Anal Appl Pyrol 136:115–124
Mateos-Espejel E, Radiotis T, Jemaa N (2013) Implications of converting a kraft pulp mill to a dissolving pulp operation with a hemicellulose extraction stage. Tappi J 12(2):29–38
Perepelkin KE (2007) Lyocell fibres based on direct dissolution of cellulose in N-methylmorpholine N-oxide: development and prospects. Fibre Chem 39(2):163–172
Qin C, Yang L, Li C, Chen Y (2008) Effect of transition metal ions on hydrogen peroxide bleaching of recycled pulp. J Guangxi Univ (Nat Sci Ed) (2): 156–158
Qing Q, Guo Q, Zhou L, Wan Y, Xu Y, Ji H, Gao X, Zhang Y (2017) Catalytic conversion of corncob and corncob pretreatment hydrolysate to furfural in a biphasic system with addition of sodium chloride. Bioresource Technol 226:247–254
Rosenau T, Potthast A, Sixta H, Kosma P (2001) The chemistry of side reactions and byproduct formation in the system NMMO/cellulose (Lyocell process). Prog Polym Sci 26(9):1763–1837
Rosenau T, Potthast A, Adorjan I, Hofinger A, Sixta H, Firgo H, Kosma P (2002) Cellulose solutions in N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO)−degradation processes and stabilizers. Cellulose 9(3–4):283–291
Rosenau T, Potthast A, Milacher W, Adorjan I, Hofinger A, Kosma P (2005) Discoloration of cellulose solutions in N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (Lyocell). Part 2: isolation and identification of chromophores. Cellulose 12:197–208
Shao X, Wang J, Liu Z, Hu N, Liu M, Xu Y (2020) Preparation and characterization of porous microcrystalline cellulose from corncob. Ind Crop Prod 151:112457
Shatalov AA, Pereira H (2005) Arundo donax L reed: new perspectives for pulping and bleaching Part 4 Peroxide bleaching of organosolv pulps. Bioresour Technol 96(8):865–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.09.005
Sun XF, Xu F, Sun RC, Fowler P, Baird MS (2005) Characteristics of degraded cellulose obtained from steam-exploded wheat straw. Carbohyd Res 340(1):97–106
Tao S, Ru MY, Du W, Zhu X, Zhong QR, Li BG, Shen GF, Pan XL, Meng WJ, Chen YL (2018) Quantifying the rural residential energy transition in China from 1992 to 2012 through a representative national survey. Nat Energy 3(7):567–573
Wang H, Zhang X, Wang D, Cui C, Gao C, Wang L, Wang Y, Bi Y (2016) Estimation and utilization of corncob resources in China. J China Agr Resour Reg Plan 37(1):1–8
Wendler F, Kolbe A, Meister F, Heinze T (2005) Thermostability of Lyocell Dopes Modified with Surface-Active Additives. Macromol Mater Eng 290(8):826–832
Wendler F, Konkin A, Heinze T (2008) Studies on the stabilization of modified Lyocell solutions. Macromol Symposia 262(1):72–84
Weyant CL, Chen P, Vaidya A, Li C, Zhang Q, Thompson R, Ellis J, Chen Y, Kang S, Shrestha GR (2019) Emission measurements from traditional biomass cookstoves in South Asia and Tibet. Environ Sci Technol 53(6):3306–3314
Wu Q, Fan G, Yu T, Sun B, Tang H, Teng C, Yang R, Li X (2019) Biochemical characteristics of the mutant xylanase T-XynC (122) C (166) and production of xylooligosaccharides from corncobs. Ind Crop Prod 142:111848
Wu J, Kong S, Yan Y, Yao L, Yan Q, Liu D, Shen G, Zhang X, Qi S (2022) Neglected biomass burning emissions of air pollutants in China-views from the corncob burning test, emission estimation, and simulations. Atmos Environ 278:119082
Xiao B, Sun X, Sun R (2001) Chemical, structural, and thermal characterizations of alkali-soluble lignins and hemicelluloses, and cellulose from maize stems, rye straw, and rice straw. Polym Degrad Stabil 74(2):307–319
Xu X, Liu Q (2016) Eucalyptus kraft pulping with pretreatment of cold alkali impregnation and compression. Trans China Pulp Paper 31(3):7–11
Yang G, Yang Y, Zhang H, Shao H (2021) Influences of stabilizers on lyocell spinning dope and fiber properties. Polym Test 99:107228
Yang G, Peng K, Zhang H, Song X, Zhou Y, Shao H (2022) Structure and properties of flame-retardant lyocell fibers prepared by blending method. Polym Eng Sci 62(10):3476–3486
Zhang H, Zhang H, Tong M, Shao H, Hu X (2008) Comparison of the structures and properties of lyocell fibers from high hemicellulose pulp and high α-cellulose pulp. J Appl Polym Sci 107(1):636–641
Zhang H, Xu Y, Yu S (2017) Co-production of functional xylooligosaccharides and fermentable sugars from corncob with effective acetic acid prehydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 234:343–349
Zhao L, Yuan Z, Kapu N, Chang X, Beatson R, Trajano H, Martinez D (2017) Increasing efficiency of enzymatic hemicellulose removal from bamboo for production of high-grade dissolving pulp. Bioresour Technol 223:40–46
Zhu M, He J, Ren Y (2014) Study on extraction cooking process of cellulose from cotton stalk using organic solvent. Shanghai Textile Sci Technol 42(8):37–39
Zong Z, Wang X, Tian C, Chen Y, Qu L, Ji L, Zhang G (2016) Source apportionment of PM 2.5 at a regional background site in North China using PMF linked with radiocarbon analysis: insight into the contribution of biomass burning. Atmos Chem Phys 16(17):11249–11265
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the financial support from the National Key R&D Program of China (2020YFC1910303). We also thank Suzanne Adam, PhD, from Liwen Bianji (Edanz) (http://www.liwenbianji.cn/) for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
National Key Research and Development Program of China, 2020YFC1910303
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GY: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—original draft, review & editing, Funding acquisition, Project administration. YZ: Resources, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation, Formal analysis. HZ: Conceptualization, Methodology. SW: Investigation, Visualization. XY: Formal analysis, Validation. HS: Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, G., Zhou, Y., Zhang, H. et al. Preparation and characterization of dissolving pulp and lyocell fibers from corncob. Cellulose 30, 4841–4853 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05179-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05179-8