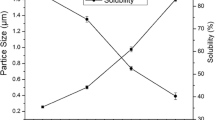
Abstract
Biodegradability and multifunctionality (ultraviolet (UV) shielding and antioxidant/antimicrobial properties) are desirable properties for future food packaging materials. Despite its potential as a biodegradable packaging material, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) has critical disadvantages like low mechanical strength, poor water vapor/UV barrier, and lack of antioxidant/antimicrobial properties. In this study, cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) and apple peel extract (APE) were incorporated into a PVA matrix to overcome these limitations. CNCs are expected to improve the mechanical/water vapor barrier properties of the PVA/CNC/APE composite, while APE can provide UV shielding and antioxidant/antimicrobial features. The mechanical strength, water barrier properties, and UV protection factor of the PVA/CNC/APE 20% film (20 wt.% APE in a PVA/CNC matrix containing 5 wt.% CNCs) were improved by factors of 1.39, 1.14, and 4.88, respectively, compared to those of pure PVA film. The antioxidant/antimicrobial activity of PVA/CNC/APE composites was evaluated and demonstrated by 2, 2-azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS) assay, packaging test with fresh pear, and antimicrobial simulation test with fresh milk.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Abral H, Ikhsan M, Rahmadiawan D et al (2022) Anti-UV, antibacterial, strong, and high thermal resistant polyvinyl alcohol/uncaria gambir extract biocomposite film. J Mater Res Technol 17:2193–2202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.01.120
Agarwal UP, Reiner RS, Ralph SA (2010) Cellulose I crystallinity determination using FT-Raman spectroscopy: univariate and multivariate methods. Cellulose 17(4):721–733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9420-z
Anthony R, Sharara MA, Runge TM et al (2017) Life cycle comparison of petroleum- and bio-based paper binder from distillers grains (DG). Ind Crop Prod 96:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.11.014
Apjok R, Cozmuta AM, Peter A et al (2019) Active packaging based on cellulose-chitosan-Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite for storage of clarified butter. Cellulose 26(3):1923–1946. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-02226-7
Bitalebi S, Nikoo M, Rahmanifarah K et al (2019) Effect of apple peel extract as natural antioxidant on lipid and protein oxidation of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) mince. Int Aquat Res 11(2):135–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40071-019-0224-y
Carvalho DO, Curto AF, Guido LF (2015) Determination of phenolic content in different barley varieties and corresponding malts by liquid chromatography-diode array detection-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Antioxidants 4(3):563–576. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox4030563
Chaudhary BU, Lingayat S, Banerjee AN et al (2021) Development of multifunctional food packaging films based on waste garlic peel extract and chitosan. Int J Biol Macromol 192:479–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.031
Chen W, Chen F, Zhang G et al (2019) Fabrication of cellulose nanocrystal composite filter papers for rapid and highly efficient removal of bacteria from aqueous solutions. Cellulose 26(12):7027–7035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02620-9
Dasgupta A, Klein K (2014) Antioxidants in food, vitamins, and supplements: Prevention and treatment of disease. Elsevier, Amsterdam
de Oliveira Filho JG, Albiero BR, Cipriano L et al (2021) Arrowroot starch-based films incorporated with a carnauba wax nanoemulsion, cellulose nanocrystals, and essential oils: a new functional material for food packaging applications. Cellulose 28(10):6499–6511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03945-0
Diñeiro García Y, Valles BS, Picinelli Lobo A (2009) Phenolic and antioxidant composition of by-products from the cider industry: Apple pomace. Food Chem 117(4):731–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.04.049
Farooq U (2019) Inhibition of escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococcus aureus and enterococcus feacalis through malus domestica extracts to eliminate food borne illness. Am J Biomed Sci 3(5):391–397. https://doi.org/10.34297/ajbsr.2019.03.000701
Fasihnia SH, Peighambardoust SH, Peighambardoust SJ et al (2020) Migration analysis, antioxidant, and mechanical characterization of polypropylene-based active food packaging films loaded with BHA, BHT, and TBHQ. J Food Sci 85(8):2317–2328. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15337
Felter SP, Zhang XL, Thompson C (2021) Butylated hydroxyanisole: Carcinogenic food additive to be avoided or harmless antioxidant important to protect food supply. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 121:104887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2021.104887
Ferreira AS, Nunes C, Castro A et al (2014) Influence of grape pomace extract incorporation on chitosan films properties. Carbohyd Polym 113:490–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.07.032
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21(2):885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
French AD (2020) Increment in evolution of cellulose crystallinity analysis. Cellulose 27(10):5445–5448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03172-z
Gaikwad KK, Lee JY, Lee YS (2016) Development of polyvinyl alcohol and apple pomace bio-composite film with antioxidant properties for active food packaging application. J Food Sci Tech Mys 53(3):1608–1619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-2104-9
Gasti T, Hiremani VD, Kesti SS et al (2021) Physicochemical and antibacterial evaluation of poly (vinyl alcohol)/guar gum/silver nanocomposite films for food packaging applications. J Polym Environ 29(10):3347–3363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02123-4
Gasti T, Dixit S, Sataraddi SP et al (2020) Physicochemical and biological evaluation of different extracts of edible solanum nigrumL. leaves incorporated chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) composite films. J Polym Environ 28(11):2918–2930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01832-6
Gore AH, Prajapat AL (2022) Biopolymer nanocomposites for sustainable UV protective packaging. Front Mater 9:855727. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2022.855727
Hivechi A, Bahrami SH, Siegel RA et al (2019) In vitro and in vivo studies of biaxially electrospun poly(caprolactone)/gelatin nanofibers, reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals, for wound healing applications. Cellulose 27(9):5179–5196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03106-9
Huang J, Zhou JJ, Liu MJ (2022) Interphase in Polymer Nanocomposites JACS Au 2(2):280–291. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacsau.1c00430
Jahan Z, Niazi MBK, Gregersen ØW (2018) Mechanical, thermal and swelling properties of cellulose nanocrystals/PVA nanocomposites membranes. J Ind Eng Chem 57:113–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.08.014
Jayalakshmi CP, Sharma JD (1986) Effect of butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) on rat erythrocytes. Environ Res 41(1):235–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-9351(86)80185-2
Kang XY, Kuga S, Wang C et al (2018) Green preparation of cellulose nanocrystal and its application. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(3):2954–2960. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02363
Kubacka A, Diez MS, Rojo D et al (2014) Understanding the antimicrobial mechanism of TiO2-based nanocomposite films in a pathogenic bacterium. Sci Rep 4:4143. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04134
Lan W, Wang S, Zhang Z et al (2021) Development of red apple pomace extract/chitosan-based films reinforced by TiO2 nanoparticles as a multifunctional packaging material. Int J Biol Macromol 168:105–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.051
Lee WJ, Clancy AJ, Kontturi E et al (2016) Strong and stiff: High-performance cellulose nanocrystal/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite fibers. ACS Appl Mater Inter 8(46):31500–31504. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b11578
Li S, Yan Y, Guan X et al (2020) Preparation of a hordein-quercetin-chitosan antioxidant electrospun nanofibre film for food packaging and improvement of the film hydrophobic properties by heat treatment. Food Packaging Shelf 23:100466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2020.100466
Liu CP, Dai CA, Chao CY et al (2014) Novel proton exchange membrane based on crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) for direct methanol fuel cells. J Power Sources 249:285–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.10.117
Lyu Y, Gu X, Mao Y (2020) Green composite of instant coffee and poly(vinyl alcohol): An excellent transparent UV-shielding material with superior thermal oxidative stability. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:8640–8648. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c00413
Matta E, Tavera-Quiroz MJ, Bertola N (2019) Active edible films of methylcellulose with extracts of green apple (Granny Smith) skin. Int J Biol Macromol 124:1292–1298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.114
Nguyen SV, Lee BK (2022a) Polyvinyl alcohol/alkyl ketene dimer films with excellent water resistance and water vapor barrier properties. Mater Lett 307:131045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.131045
Nguyen SV, Lee BK (2022b) Polyvinyl alcohol/cellulose nanocrystals/alkyl ketene dimer nanocomposite as a novel biodegradable food packing material. Int J Biol Macromol 207:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.02.184
Nguyen SV, Lee BK (2022c) PVA/CNC/TiO2 nanocomposite for food-packaging: Improved mechanical, UV/water vapor barrier, and antimicrobial properties. Carbohydr Polym 298:120064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120064
Park Y, You M, Shin J et al (2019) Thermal conductivity enhancement in electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(vinyl alcohol)/cellulose nanocrystal composite nanofibers. Sci Rep 9:3026. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39825-8
Passaretti MG, Ninago MD, Di Anibal C et al (2019) Composite films with UV barrier capacity to minimize flavored waters degradation. Food Packaging Shelf Life 21:100334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2019.100334
Patel M, Bastioli C, Marini L, Würdinger E (2002) Environmental assessment of bio-based polymers and natural fibres. Utrecht University
Pingret D, Fabiano-Tixier AS, Bourvellec CL et al (2012) Lab and pilot-scale ultrasound-assisted water extraction of polyphenols from apple pomace. J Food Eng 111(1):73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2012.01.026
Popescu MC (2017) Structure and sorption properties of CNC reinforced PVA films. Int J Biol Macromol 101:783–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.03.168
Popescu MC, Dogaru BI, Goanta M et al (2018) Structural and morphological evaluation of CNC reinforced PVA/Starch biodegradable films. Int J Biol Macromol 116:385–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.036
Qiu Z, Niu W, Wang S et al (2021) Multifunctional composite film based on biodegradable grape skin and polyvinyl alcohol. Cellulose 28(10):6467–6479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03968-7
Rabelo SC, Filho RM, Costa AC (2013) Lime pretreatment and fermentation of enzymatically hydrolyzed sugarcane bagasse. Appl Biochem Biotech 169(5):1696–1712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0097-2
Rahman MM, Afrin S, Haque P (2014) Characterization of crystalline cellulose of jute reinforced poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) biocomposite film for potential biomedical applications. Prog Biomater 3(1):23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40204-014-0023-x
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A et al (1999) Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radical Bio Med 26(9–10):1231–1237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00315-3
Riaz A, Lagnika C, Abdin M et al (2020) Preparation and characterization of chitosan/gelatin-based active food packaging films containing apple peel nanoparticles. J Polym Environ 28(2):411–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01619-4
Riaz A, Lei S, Akhtar HMS et al (2018) Preparation and characterization of chitosan-based antimicrobial active food packaging film incorporated with apple peel polyphenols. Int J Biol Macromol 114:547–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.126
Rukmanikrishnan B, Ramalingam S, Kim SS et al (2021) Rheological and anti-microbial study of silica and silver nanoparticles-reinforced k-carrageenan/hydroxyethyl cellulose composites for food packaging applications. Cellulose 28(9):5577–5590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03873-z
Sarwar MS, Niazi MBK, Jahan Z et al (2018) Preparation and characterization of PVA/nanocellulose/Ag nanocomposite films for antimicrobial food packaging. Carbohydr Polym 184:453–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.12.068
Simkovic I, Surina I, Vrican M (2003) Primary reactions of sucrose thermal degradation. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 70(2):493–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-2370(03)00007-X
Sonker AK, Teotia AK, Kumar A et al (2017) Development of polyvinyl alcohol based high strength biocompatible composite films. Macromol Chem Phys 218(15):1700130. https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.201700130
Subhashree SN, Sunoj S, Xue J et al (2017) Quantification of browning in apples using colour and textural features by image analysis. Food Qual Saf 1(3):221–226. https://doi.org/10.1093/fqsafe/fyx021
Suganthi S, Vignesh S, Sundar JK et al (2020) Fabrication of PVA polymer films with improved antibacterial activity by fine-tuning via organic acids for food packaging applications. Appl Water Sci 10(4):100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-1162-y
Tan R, Li F, Zhang Y et al (2021) High-performance biocomposite polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) films modified with cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs), tannic acid (TA), and chitosan (CS) for food packaging. J Nanomater 2021:4821717. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4821717
Terzioglu P, Guney F, Parin FN et al (2021) Biowaste orange peel incorporated chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol composite films for food packaging applications. Food Packaging Shelf Life 30:100742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2021.100742
Ting ASY, Chin JE (2020) Biogenic synthesis of iron nanoparticles from apple peel extracts for decolorization of malachite green dye. Water Air Soil Poll 231(6):278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04658-z
Trache D, Hussin MH, Haafiz MKM et al (2017) Recent progress in cellulose nanocrystals: Sources and production. Nanoscale 9(5):1763–1786. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6nr09494e
Tran TN, Mai BT, Setti C et al (2020) Transparent bioplastic derived from CO2-based polymer functionalized with oregano waste extract toward active food packaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(41):46667–46677. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c12789
Urbina L, Eceiza A, Gabilondo N et al (2019) Valorization of apple waste for active packaging: multicomponent polyhydroxyalkanoate coated nanopapers with improved hydrophobicity and antioxidant capacity. Food Packaging Shelf Life 21:100356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2019.100356
Veiga-Santos P, Oliveira LM, Cereda MP et al (2007) Sucrose and inverted sugar as plasticizer. Effect on cassava starch-gelatin film mechanical properties, hydrophilicity and water activity. Food Chem 103(2):255–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.07.048
Vera R, Figueredo F, Díaz-Gómez A et al (2018) Evaluation of Fuji apple peel extract as a corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in a saline medium. Int J Electrochem Sc 13(5):4139–4159. https://doi.org/10.20964/2018.05.57
Wu LY, Guo YL, Cao LL et al (2016) Application of NaOH–HCl-modified apple pomace to binding epigallocatechin gallate. Food Bioprocess Tech 9(6):917–923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1683-4
Yang W, Qi G, Kenny JM et al (2020) Effect of cellulose nanocrystals and lignin nanoparticles on mechanical, antioxidant and water vapour barrier properties of glutaraldehyde crosslinked PVA films. Polymers 12(6):1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061364
Zhang W, He X, Li C et al (2014) High performance poly (vinyl alcohol)/cellulose nanocrystals nanocomposites manufactured by injection molding. Cellulose 21(1):485–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0141-y
Zhang X, Liu YP, Yong HM et al (2019) Development of multifunctional food packaging films based on chitosan, TiO2 nanoparticles and anthocyanin-rich black plum peel extract. Food Hydrocolloids 94:80–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0141-y
Zhou X, Dai Q, Huang X et al (2021) Preparation and characterizations of antibacterial-antioxidant film from soy protein isolate incorporated with mangosteen peel extract. E-Polymers 21(1):575–589. https://doi.org/10.1515/epoly-2021-0058
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (NRF-2020R1A2C2007603).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Van Nguyen, S., Lee, BK. Multifunctional food packaging polymer composites based on polyvinyl alcohol/cellulose nanocrystals/apple peel extract. Cellulose 30, 1697–1716 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04976-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04976-x