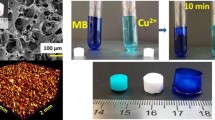
Abstract
Hydrogels were prepared from enzymatically synthesized (1 → 6)-α-D-glucan (dextran) and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) by crosslinking with ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether. The resulting dextran/CMC hydrogel was transparent, highly swellable, and self-standing. Analyses revealed that the swelling ratio of the hydrogels increased as the CMC content increased. Further, the CMC hydrogel was hard but brittle, with a relatively high elastic modulus (15.8 kPa) and low fracture strain (10.5%). With increasing dextran content, the dextran/CMC hydrogels became softer and more flexible, the elastic modulus decreased, and the fracture strain increased. The oven-dried samples of the dextran/CMC hydrogel exhibited the ability to restore their shape and size when immersed in deionized water. The adsorption of heavy metal Cu2+ ions and methylene blue dye on the dextran/CMC hydrogel was well described by pseudo-second-order kinetics and Freundlich isotherm models. The reusability test showed that the dextran/CMC hydrogel is a potential adsorbent that can be reused multiple times.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed EM (2015) Hydrogel: preparation, characterization, and applications: a review. J Adv Res 6:105–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2013.07.006
Baldwin AD, Kiick KL (2010) Polysaccharide-modified synthetic polymeric biomaterials. Peptide Sci 94:120–140. https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.21334
Benoit L, Cailiez C, Gehin A et al (1995) Carboxymethyl cellulase and avicelase activities from a cellulolytic clostridium strain A11. Curr Microbiol 30:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00295506
Bessbousse H, Rhlalou T, Verchere JF, Lebrun L (2008) Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by filtration with a novel complexing membrane containing poly(ethyleneimine) in a poly (vinyl alcohol) matrix. J Membr Sci 307:249–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2007.09.027
Capanema NSV, Mansur AAP, De Jesus AC et al (2018) Superabsorbent crosslinked carboxymethyl cellulose-PEG hydrogels for potential wound dressing applications. Int J Biol Macromol 106:1218–1234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.124
Chang CY, He M, Zhou JP, Zhang LN (2011) Swelling behaviors of pH- and salt-responsive cellulose-based hydrogels. Macromolecules 44:1642–1648. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma102801f
Dabrowski A, Hubicki Z, Podkoscielny P, Robens E (2004) Selective removal of the heavy metal ions from waters and industrial wastewaters by ion-exchange method. Chemosphere 56:91–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.03.006
Dahlan NA, Veeramachineni AK, Langford SJ, Pushpamalar J (2017) Developing of a magnetite film of carboxymethyl cellulose grafted carboxymethyl polyvinyl alcohol (CMC-g-CMPVA) for copper removal. Carbohydr Polym 173:619–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.06.008
Díaz-Montes E (2021) Dextran: sources, structures, and properties. Polysaccharides 2:554–565. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides2030033
He QF, Kobayashi K, Kusumi R et al (2020) In vitro synthesis of branchless Linear (1 → 6)-alpha-D-glucan by glucosyltransferase K: mechanical and swelling properties of its hydrogels crosslinked with diglycidyl ethers. ACS Omega 5:31272–31280. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c04699
Hong HJ, Lim JS, Hwang JY et al (2018) Carboxymethlyated cellulose nanofibrils (CMCNFs) embedded in polyurethane foam as a modular adsorbent of heavy metal ions. Carbohydr Polym 195:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.081
Huang ZH, Wu QL, Liu SX et al (2013) A novel biodegradable beta-cyclodextrin-based hydrogel for the removal of heavy metal ions. Carbohydr Polym 97:496–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.04.047
Isobe N, Chen XX, Kim UJ et al (2013) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose hydrogel as a high-capacity and reusable heavy metal ion adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 260:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.05.024
Karaer H, Kaya İ (2016) Synthesis, characterization of magnetic chitosan/active charcoal composite and using at the adsorption of methylene blue and reactive blue4. Micropor Mesopor Mater 232:26–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.06.006
Khare AR, Peppas NA (1995) Swelling/deswelling of anionic copolymer gels. Biomaterials 16:559–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-9612(95)91130-Q
Kono H (2014) Characterization and properties of carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels crosslinked by polyethylene glycol. Carbohydr Polym 105:84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.02.020
Kono H, Onishi K, Nakamura T (2013) Characterization and bisphenol a adsorption capacity of beta-cyclodextrin-carboxymethylcellulose-based hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym 98:784–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.06.065
Luo J, Fan C, Xiao Z et al (2019) Novel graphene oxide/carboxymethyl chitosan aerogels via vacuum-assisted self-assembly for heavy metal adsorption capacity. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 578:123584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123584
Mittal H, Al Alili A, Morajkar PP, Alhassan SM (2021) Go crosslinked hydrogel nanocomposites of chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose - a versatile adsorbent for the treatment of dyes contaminated wastewater. Int J Biol Macromol 167:1248–1261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.11.079
Mohtashami R, Shang JQ (2019) Treatment of automotive paint wastewater in continuous-flow electroflotation reactor. J Clean Prod 218:335–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.326
Panchan N, Niamnuy C, Dittanet P, Devahastin S (2018) Optimization of synthesis condition for carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel from rice straw by microwave-assisted method and its application in heavy metal ions removal. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 93:413–425. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5370
Qi XL, Wei W, Li JJ et al (2015) Fabrication and characterization of a novel anticancer drug delivery system: salecan/poly (methacrylic acid) semi-interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 1:1287–1299. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5b00346
Qi XL, Wei W, Su T et al (2018) Fabrication of a new polysaccharide-based adsorbent for water purification. Carbohydr Polym 195:368–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.112
Simpson CL, Cheetham NWH, Giffard PM, Jacques NA (1995) Four glucosyltransferases, GtfJ, GtfK, GtfL and GtfM, from Streptococcus salivarius ATCC 25975. Microbiology 141:1451–1460. https://doi.org/10.1099/13500872-141-6-1451
Wu F, Zhang Y, Liu L, Yao JM (2012) Synthesis and characterization of a novel cellulose-g-poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) superabsorbent composite based on flax yarn waste. Carbohydr Polym 87:2519–2525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.11.028
Xu XH, Bai B, Ding CX et al (2015) Synthesis and properties of an ecofriendly superabsorbent composite by grafting the poly (acrylic acid) onto the surface of dopamine-coated sea buckthorn branches. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:3268–3278. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b00092
Zennifer A, Senthilvelan P, Sethuraman S, Sundaramurthi D (2021) Key advances of carboxymethyl cellulose in tissue engineering and 3D bioprinting applications. Carbohydr Polym 256:117561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117561
Zhang M, Wang R, Shi ZQ et al (2017) Multi-responsive, tough and reversible hydrogels with tunable swelling property. J Hazard Mater 322:499–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.016
Zhu XW, Chen JJ, Hu YX et al (2021) Tuning complexation of carboxymethyl cellulose/ cationic chitosan to stabilize Pickering emulsion for curcumin encapsulation. Food Hydrocoll 110:106135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106135
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Advanced Low Carbon Technology Research and Development Program (ALCA) of the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) (JPMJAL1502) and JSPS KAKENHI (19H03018). The author Y. Zhang thanks Japanese Government (MEXT) Scholarships for the personal financial support.
Funding
Advanced Low Carbon Technology Research and Development Program, JPMJAL1502, Masahisa Wada, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, 19H03018, Masahisa Wada
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ: Writing—original draft, Investigation, Data curation. QH: Methodology, Investigation. KK: Methodology, Investigation. RK: Methodology, Investigation. MW: Writing—review and editing, Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., He, Q., Kobayashi, K. et al. Hydrogels from dextran/carboxymethyl cellulose exhibiting high post-drying swelling ratios and recovery. Cellulose 30, 263–276 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04886-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04886-y