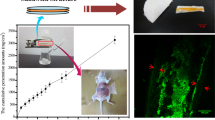
Abstract
Pectin/bacteria cellulose (BC) hydrogel composites with various BC contents have been fabricated for the purpose of electrically controlled transdermal drug delivery. A conductive polymer, polypyrrole, was successfully incorporated into the pectin/BC hydrogel composite as a host of drug encapsulation for controlled release under applied electric field. Ibuprofen as a model drug was studied for its release behavior based on the effects of matrix composition, pH stimulation, matrix mesh size, and applied electrical potential by using a modified Franz diffusion cell. The drug release was optimized at 30 wt% BC and increased with applying electrical potential. The highest amount of drug release was 78% which was obtained on a drug-loaded polypyrrole-incorporated composite under applied electrical potential at 7 V. The hydrogel composites also presented the remarkable benefit of antibacterial activity for gram-positive bacteria. Thus, the hydrogel composites are valuable alternative materials for transdermal drug delivery.
Graphic abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya M, Mishra S, Sahoo RN, Mallick S (2017) Infrared spectroscopy for analysis of co-processed ibuprofen and magnesium trisilicate at milling and freeze drying. Acta Chimica Slovenica 64(1):45–54. https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2016.2772
AL-Janabi AAHS (2010) In vitro antibacterial activity of ibuprofen and acetaminophen. J Glob Infect Dis 2(2):105. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-777X.62880
Bala P, Jathar S, Kale S, Pal K (2014) Transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS)-A multifaceted approach for drug delivery. J Pharm Res 8(12):1805–1835
Boutherin B, Mazeau K, Tvaroska I (1997) Conformational statistics of pectin substances in solution by a metropolis monte carlo study. Carbohydr Polym 32(3–4):255–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(96)00161-0
Cacicedo ML, Islan GA, Drachemberg MF, Alvarez VA, Bartel LC, Bolzán AD, Castro GR (2018) Hybrid bacterial cellulose–pectin films for delivery of bioactive molecules. New J Chem 42(9):7457–7467. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NJ03973E
Caló E, Khutoryanskiy VV (2015) Biomedical applications of hydrogels: a review of patents and commercial products. Eur Polym J 65:252–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.11.024
Chang CC, Imae T (2018) Synergistic performance of composite supercapacitors between carbon nanohorn and conducting polymer. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(4):5162–5172. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b04813
Chansai P, Sirivat A, Niamlang S, Chotpattananont D, Viravaidya-Pasuwat K (2009) Controlled transdermal iontophoresis of sulfosalicylic acid from polypyrrole/poly (acrylic acid) hydrogel. Int J Pharm 381(1):25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.07.019
Dhote V, Bhatnagar P, Mishra PK, Mahajan SC, Mishra DK (2012) Iontophoresis: a potential emergence of a transdermal drug delivery system. Sci Pharm 80:1–28. https://doi.org/10.3797/scipharm.1108-20
Esa F, Tasirin SM, Rahman NA (2014) Overview of bacterial cellulose production and application. Agric Agric Sci Procedia 2(1):113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aaspro.2014.11.017
Gallegos AMA, Carrera SH, Parra R, Keshavarz T, Iqbal HM (2016) Bacterial cellulose: a sustainable source to develop value-added products—a review. BioResources 11(2):5641–5655. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.11.2.Gallegos
Gawkowska D, Cybulska J, Zdunek A (2018) Structure-related gelling of pectins and linking with other natural compounds: a review. Polymers 10(7):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070762
Gea S, Reynolds CT, Roohpour N, Wirjosentono B, Soykeabkaew N, Bilotti E, Peijs T (2011) Investigation into the structural, morphological, mechanical and thermal behaviour of bacterial cellulose after a two-step purification process. Bioresour Technol 102(19):9105–9110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.04.077
Grijalvo S, Eritja R, Díaz Díaz D (2019) On the race for more stretchable and tough hydrogels. Gels 5(2):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels5020024
Halib N, Amin M, Ahmad I (2012) Physicochemical properties and characterization of nata de coco from local food industries as a source of cellulose. Sains Malays 41(2):205–211. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639045.2013.819882
Indermun S, Choonara YE, Kumar P, Du Toit LC, Modi G, Luttge R, Pillay V (2014) An interfacially plasticized electro-responsive hydrogel for transdermal electro-activated and modulated (TEAM) drug delivery. Int J Pharm 462(1–2):52–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.11.014
Jonas R, Farah LF (1998) Production and application of microbial cellulose. Polym Degrad Stab 59(1–3):101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-3910(97)00197-3
Juntanon K, Niamlang S, Rujiravanit R, Sirivat A (2008) Electrically controlled release of sulfosalicylic acid from crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel. Int J Pharm 356(1–2):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.12.023
Krathumkhet N, Sabrina IT, Krafft MP (2021) Nitric oxide gas in carbon nanohorn/fluorinated dendrimer/fluorinated poly (ethylene glycol)-based hierarchical nanocomposites as therapeutic nanocarriers. ACS Appl Bio Mater 4(3):2591–2600. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.0c01577
Kumar R, Philip A (2007) Modified transdermal technologies: breaking the barriers of drug permeation via the skin. Trop J Pharm Res 6(1):633–644. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v6i1.14641
Lin D, Liu Z, Shen R, Chen S, Yang X (2020) Bacterial cellulose in food industry: current research and future prospects. Int J Biol Macromol 158(1):1007–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.230
Liu Y, Yan K, Jiang G, Xiong Y, Du Y (2014) Shi X (2014) Electrical signal guided ibuprofen release from electrodeposited chitosan hydrogel. Int J Polym Sci 2014:8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/736898
Masuelli MA (2011) Viscometric study of pectin. Effect of temperature on the hydrodynamic properties. Int J Biol Macromol 48(2):286–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.11.014
Mavondo GAA, Tagumirwa MC (2016) Asiatic acid-pectin hydrogel matrix patch transdermal delivery system influences parasitaemia suppression and inflammation reduction in P. berghei murine malaria infected Sprague-Dawley rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med 9(12):1172–1180
Mongkolkitikul S, Paradee N, Sirivat A (2018) Electrically controlled release of ibuprofen from conductive poly (3-methoxydiphenylamine)/crosslinked pectin hydrogel. Eur J Pharm Sci 112:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2017.10.043
Moore N, Pollack C, Butkerait P (2015) Adverse drug reactions and drug–drug interactions with over-the-counter NSAIDs. Ther Clin Risk Manag 11:1061–1075. https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S79135
Morris G, Foster T, Harding S (2002) A hydrodynamic study of the depolymerisation of a high methoxy pectin at elevated temperatures. Carbohydr Polym 48(4):361–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(01)00270-3
Neves SC, Gomes DB, Sousa A, Bidarra SJ, Petrini P, Moroni L, Granja PL (2015) Biofunctionalized pectin hydrogels as 3D cellular microenvironments. J Mater Chem B 3(10):2096–2108. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00885E
Niamlang S, Paradee N, Sirivat A (2018) Hybrid transdermal drug delivery patch made from poly (p-phenylene vinylene)/natural rubber latex and controlled by an electric field. Polym Int 67(6):747–754. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.5566
Pairatwachapun S, Paradee N, Sirivat A (2016) Controlled release of acetylsalicylic acid from polythiophene/carrageenan hydrogel via electrical stimulation. Carbohydr Polym 137:214–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.10.026
Paradee N, Sirivat A, Niamlang S, Prissanaroon-Ouajai W (2012) Effects of crosslinking ratio, model drugs, and electric field strength on electrically controlled release for alginate-based hydrogel. J Mater Sci Mater Med 23(4):999–1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-012-4571-0
Peppas NA, Merrill EW (1977) Crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels as swollen elastic networks. J Appl Polym Sci 21(7):1763–1770. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1977.070210704
Peppas NA, Sahlin JJ (1989) A simple equation for the description of solute release. III. Coupling of diffusion and relaxation. Int J Pharm 57(2):169–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5173(89)90306-2
Peppas NA, Wright SL (1996) Solute diffusion in poly (vinyl alcohol)/poly (acrylic acid) interpenetrating networks. Macromolecules 29(27):8798–8804. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma9613392
Portela R, Leal CR, Almeida PL, Sobral RG (2019) Bacterial cellulose: a versatile biopolymer for wound dressing applications. Microb Biotechnol 12(4):586–610. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13392
Rastogi V, Yadav P (2014) Transdermal drug delivery system: an overview. Asian J Pharm Free Full Text Artic Asian J Pharm. https://doi.org/10.22377/ajp.v6i3.51
Rizwan M, Yahya R, Hassan A, Yar M, Azzahari AD, Selvanathan V, Abouloula CN (2017) pH sensitive hydrogels in drug delivery: brief history, properties, swelling, and release mechanism, material selection and applications. Polymers 9(4):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9040137
Samanta D, Meiser JL, Zare RN (2015) Polypyrrole nanoparticles for tunable, pH-sensitive and sustained drug release. Nanoscale 7(21):9497–9504. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR02196K
Sannino A, Demitri C, Madaghiele M (2009) Biodegradable cellulose-based hydrogels: design and applications. Mater 2(2):353–373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2020353
Seixas F, Turbiani F, Salomão P, Souza R, Gimenes M (2013) Biofilms composed of alginate and pectin: effect of concentration of crosslinker and plasticizer agents. Chem Eng Trans 32:1693–1698. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1332283
Shi X, Zheng Y, Wang C, Yue L, Qiao K, Wang G, Wang L, Quan H (2015) Dual stimulus responsive drug release under the interaction of pH value and pulsatile electric field for a bacterial cellulose/sodium alginate/multi-walled carbon nanotube hybrid hydrogel. RSC Adv 5(52):41820–41829. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA04897D
Siepmann J, Peppas NA (2012) Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:163–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-409x(01)00112-0
Sittiwong J, Niamlang S, Paradee N, Sirivat A (2012) Electric field-controlled benzoic acid and sulphanilamide delivery from poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel. AAPS PharmSciTech 13(4):1407–1415. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-012-9869-1
Suksaeree J, Prasomkij J, Panrat K, Pichayakorn W (2018) Comparison of pectin layers for nicotine transdermal patch preparation. Adv Pharm Bull 8(3):401 https://doi.org/10.15171/apb.2018.047
Treesuppharat W, Rojanapanthu P, Siangsanoh C, Manuspiya H, Ummartyotin S (2017) Synthesis and characterization of bacterial cellulose and gelatin-based hydrogel composites for drug-delivery systems. Biotechnol Rep 15:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2017.07.002
Wells L, Sheardown H (2011) Photosensitive controlled release with polyethylene glycol–anthracene modified alginate. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 79(2):304–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2011.03.023
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi under KMUTT Research Center of Excellence Project and Thailand Science Research and Innovation (TSRI) Basic Research Fund: Fiscal year 2021 under project number 64A306000039. NK give thanks to National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taiwan, for the financial support by a student scholarship. The authors would like to acknowledge Professor Paripok Phitsuwan from LigniTech-Lignin Technology Research Group, School of Bioresources and Technology, Bioresources and Technology, King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi for teaching technical experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NK: Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, visualization, writing—original draft the manuscript. TI: Supervision, visualization, writing—review and editing the manuscript. NP: Supervision, conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition, writing—review and editing draft the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Ethical approval
This manuscript does not include human participants or animal studies in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krathumkhet, N., Imae, T. & Paradee, N. Electrically controlled transdermal ibuprofen delivery consisting of pectin-bacterial cellulose/polypyrrole hydrogel composites. Cellulose 28, 11451–11463 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04259-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04259-x