Abstract
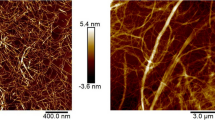
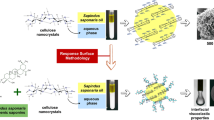
Stabilization of emulsion using plant-derived nanomaterial has been of great research interest. In this regard, cellulose nanofibers (CNF) showed good potential in conventional emulsion system. Thus, it creates the scope to develop an efficient CNF-based stabilizer for high internal phase emulsion (HIPE) using a convenient process. Herein, we prepared oil-in-water (o/w) HIPEs or emulsion gels using amphiphile-grafted CNFs termed as cellulosic gelators (CLGs). The CLGs were obtained by grafting a poly(ethylene glycol)-based amphiphile (PGLE) onto CNFs by one-step etherification reaction at different degree of PGLE substitution (DS). The HIPEs remained stable at very high oil volume (upto 96.3%) and they were characterized by optical and electron microscopy, rheology and differential scanning calorimetry. The efficacy of stabilization and oil-droplet sizes were highly dependent to the DS, concentration of CLG, and the volume of aqueous phase. The beneficial effect of CNF in CLGs was observed from the higher thermal stability (control, 31.4 °C; CLG, 57.0 °C) and improved viscoelasticity (critical strain γc: control, 0.3%; CLG, 1.0%). This approach will pave the way to the application of CNFs in producing commercial HIPEs to be used in food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability and materials
Kyoto University Research Information Repository.
References
Aaen R, Brodin FW, Simon S et al (2019) Oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by cellulose nanofibrils—the effects of ionic strength and pH. Nanomaterials 9:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020259
Barbetta A, Cameron NR (2004) Morphology and surface area of emulsion-derived (PolyHIPE) solid foams prepared with oil-phase soluble porogenic solvents: three-component surfactant system. Macromolecules 37:3202–3213. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma035944y
Binks BP, Lumsdon SO (2000) Catastrophic phase inversion of water-in-oil emulsions stabilized by hydrophobie silica. Langmuir 16:2539–2547. https://doi.org/10.1021/la991081j
Bizmark N, Du X, Ioannidis MA (2020) High internal phase pickering emulsions as templates for a cellulosic functional porous material. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:3664–3672. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b06577
Cai J, Zhang L, Zhou J et al (2007) Multifilament fibers based on dissolution of cellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solution: structure and properties. Adv Mater 19:821–825. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200601521
Capron I, Cathala B (2013) Surfactant-free high internal phase emulsions stabilized by cellulose nanocrystals. Biomacromol 14:291–296. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm301871k
Chakrabarty A, Teramoto Y (2018) Recent advances in nanocellulose composites with polymers: a guide for choosing partners and how to incorporate them. Polymers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050517
Chakrabarty A, Teramoto Y (2020) Scalable Pickering stabilization to design cellulose nanofiber-wrapped block copolymer microspheres for thermal energy storage. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:4623–4632. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00687
Chakrabarty A, Maiti M, Miyagi K, Teramoto Y (2018) Gel emulsion based on amphiphilic block copolymer: a template to develop porous polymeric monolith for the efficient adsorption of volatile organic compounds. ACS Appl Nano Mater 1:1569–1578. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.8b00068
Chen QH, Zheng J, Xu YT et al (2018) Surface modification improves fabrication of pickering high internal phase emulsions stabilized by cellulose nanocrystals. Food Hydrocoll 75:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.09.005
Chen L, Ao F, Ge X, Shen W (2020) Food-grade pickering emulsions: preparation, stabilization and applications. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143202
Colver PJ, Bon SAF (2007) Cellular polymer monoliths made via pickering high internal phase emulsions. Chem Mater 19:1537–1539. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0628810
Destribats M, Faure B, Birot M et al (2012) Tailored silica macrocellular foams: combining limited coalescence-based pickering emulsion and Sol-Gel process. Adv Funct Mater 22:2642–2654. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201102564
French DJ, Brown AT, Schofield AB et al (2016) The secret life of Pickering emulsions: particle exchange revealed using two colours of particle. Sci Rep 6:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31401
Goi Y, Fujisawa S, Saito T et al (2019) Dual functions of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers in oil-in-water emulsions: a Pickering emulsifier and a unique dispersion stabilizer. Langmuir 35:10920–10926. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b01977
Gonzalez Ortiz D, Pochat-Bohatier C, Cambedouzou J et al (2020) Current trends in Pickering emulsions: particle morphology and applications. Engineering 6:468–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2019.08.017
Horozov TS, Binks BP (2006) Particle-stabilized emulsions: a bilayer or a bridging monolayer? Angew Chemie - Int Ed 45:773–776. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200503131
Ifuku S, Nogi M, Abe K et al (2007) Surface modification of bacterial cellulose nanofibers for property enhancement of optically transparent composites: Dependence on acetyl-group DS. Biomacromol 8:1973–1978. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm070113b
Isogai A, Usuda M (1990) Crystallinity indexes of cellulosic materials. Sen’i Gakkaishi 46:324–329. https://doi.org/10.2115/fiber.46.8_324
Jiménez-Saelices C, Seantier B, Grohens Y, Capron I (2018) Thermal superinsulating materials made from nanofibrillated cellulose-stabilized pickering emulsions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:16193–16202. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b02418
Kedzior SA, Gabriel VA, Dubé MA, Cranston ED (2020) Nanocellulose in emulsions and heterogeneous water-based polymer systems: a review. Adv Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202002404
Kim K, Kim S, Ryu J et al (2017) Processable high internal phase Pickering emulsions using depletion attraction. Nat Commun 8:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14305
Kloser E, Gray DG (2010) Surface grafting of cellulose nanocrystals with poly(ethylene oxide) in aqueous media. Langmuir 26:13450–13456. https://doi.org/10.1021/la101795s
Lee KY, Blaker JJ, Murakami R et al (2014) Phase behavior of medium and high internal phase water-in-oil emulsions stabilized solely by hydrophobized bacterial cellulose nanofibrils. Langmuir 30:452–460. https://doi.org/10.1021/la4032514
Lissant KJ (1966) The geometry of high-internal-phase-ratio emulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 22:462–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(66)90091-9
Liu X, Qi X, Guan Y et al (2019) Transparent and strong polymer nanocomposites generated from Pickering emulsion gels stabilized by cellulose nanofibrils. Carbohydr Polym 224:115202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115202
Li X, Li J, Kuang Y et al (2020) Stabilization of pickering emulsions with cellulose nanofibers derived from oil palm fruit bunch. Cellulose 27:839–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02803-4
Miao C, Tayebi M, Hamad WY (2018) Investigation of the formation mechanisms in high internal phase pickering emulsions stabilized by cellulose nanocrystals. Philos Trans R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2017.0039
Murray BS (2019) Pickering emulsions for food and drinks. Curr Opin Food Sci 27:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2019.05.004
Nalawade AC, Ghorpade RV, Shadbar S et al (2016) Inverse high internal phase emulsion polymerization (i-HIPE) of GMMA, HEMA and GDMA for the preparation of superporous hydrogels as a tissue engineering scaffold. J Mater Chem B 4:450–460. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5tb01873k
Okano T, Sarko A (1984) Mercerization of cellulose. I. X-ray diffraction evidence for intermediate structures. J Appl Polym Sci 29:4175–4182. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1984.070291247
Peng J, Xia H, Liu K et al (2009) Water-in-oil gel emulsions from a cholesterol derivative: structure and unusual properties. J Colloid Interface Sci 336:780–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.04.055
Perrin E, Bizot H, Cathala B, Capron I (2014) Chitin nanocrystals for pickering high internal phase emulsions. Biomacromol 15:3766–3771. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm5010417
Pickering SU (1907) Emulsions. J Chem Soc Trans 91:2001–2021
Ramsden W (1903) Separation of solids in the surface-layers of solutions and suspensions. Proc R Soc London 72:156–164
Roy S, Maiti M, Roy A (2017) A new class of boronic acid-derived amphiphile-based gel emulsions capable of entrapping and releasing vitamin B12 and doxorubicin. ChemistrySelect 2:6929–6939. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201701397
Sarkar A, Dickinson E (2020) Sustainable food-grade Pickering emulsions stabilized by plant-based particles. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 49:69–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2020.04.004
Sun G, Li Z, Ngai T (2010) Inversion of particle-stabilized emulsions to form high-internal-phase emulsions. Angew Chemie 122:2209–2212. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.200907175
Tang C, Spinney S, Shi Z et al (2018) Amphiphilic cellulose nanocrystals for enhanced Pickering emulsion stabilization. Langmuir 34:12897–12905. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b02437
Yokota S, Kamada K, Sugiyama A, Kondo T (2019) Pickering emulsion stabilization by using amphiphilic cellulose nanofibrils prepared by aqueous counter collision. Carbohydr Polym 226:115293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115293
Zhang B, Zhang J, Liu C et al (2016) High-internal-phase emulsions stabilized by metal-organic frameworks and derivation of ultralight metal-organic aerogels. Sci Rep 6:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21401
Zhang N, Zhong S, Chen T et al (2017) Emulsion-derived hierarchically porous polystyrene solid foam for oil removal from aqueous environment. RSC Adv 7:22946–22953. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra02953e
Zhang T, Sanguramath RA, Israel S, Silverstein MS (2019) Emulsion templating: porous polymers and beyond. Macromolecules 52:5445–5479. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.8b02576
Zhang T, Zhao Y, Silverstein MS (2020) Cellulose-based, highly porous polyurethanes templated within non-aqueous high internal phase emulsions. Cellulose 27:4007–4018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03059-z
Zheng Z, Zheng X, Wang H, Du Q (2013) Macroporous graphene oxide-polymer composite prepared through Pickering high internal phase emulsions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:7974–7982. https://doi.org/10.1021/am4020549
Zheng X, Zhang Y, Wang H, Du Q (2014) Interconnected macroporous polymers synthesized from silica particle stabilized high internal phase emulsions. Macromolecules 47:6847–6855. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma501253u
Zhu Y, Huan S, Bai L et al (2020) High internal phase oil-in-water pickering emulsions stabilized by chitin nanofibrils: 3D structuring and Solid foam. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:11240–11251. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b23430
Acknowledgments
AC is thankful to Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) for the postdoctoral fellowship (Award No. P18395). The Authors are thankful to Prof. Hiroshi Watanabe, Kyoto University for rheological measurements. The Authors are also thankful to Prof. Hiroshi Kamitakahara, Kyoto University for the surface tension and zeta potential measurements. The Authors thank to Dr. Tatsuya Awano, Kyoto University for TEM observation.
Funding
This work was supported by the JSPS Postdoctoral Fellowship (Grant no. P18395) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
There is no animal studies or human participants involved in this study. Therefore, the authors have no ethical approval to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakrabarty, A., Teramoto, Y. Cellulose nanofiber-derived efficient stabilizer for oil-in-water high-internal-phase emulsion. Cellulose 28, 6253–6268 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03948-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03948-x