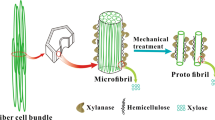
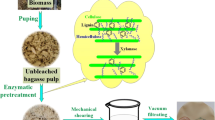
Abstract
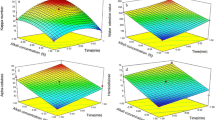
In this work, the effects of lignin on the thermal stability of bagasse cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) were investigated. The CNFs were prepared with different lignin content bagasse pulp using ultrafine grinding combined with high-pressure homogenization. Scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and thermogravimetric analysis were used to study the influence mechanisms of lignin content on the thermal stability of the CNFs. The thermal stability of cellulose was tested by thermogravimetric analyzer at different heating rates, and the activation energy of bagasse cellulose nanofibrils was calculated by Flynn-Wall-Ozawa method. The results showed that the average width of CNFs prepared by the mechanical method was approximately 20 nm. The higher the lignin contents in the CNFs, the lower the crystallinity and the better the thermal stability. The thermal decomposition activation energy of CNF fluctuates with the change of conversion rate. Under the same conversion rate, the higher the lignin contents in the CNFs, the larger the activation energy value. The average activation energies of NO-LCNF, L-LCNF, ML-LCNF, MH-LCNF, and H-LCNF were 208.14, 254.49, 412.95, 530.54 and 652.10 kJ/mol, respectively, during the conversion rate of 20% to 90%. The research results provide a theoretical basis for the pyrolysis mechanism and high value utilization of CNFs and have a profound impact on promoting the application and development of CNFs in emerging nanocomposites.
Graphic abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemdar A, Sain M (2008) Isolation and characterization of nanofibers from agricultural residues: wheat straw and soy hulls. Bioresour Technol 99:1664–1671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.04.029
Bradbury AG, Sakai Y, Shafizadeh F (1979) A kinetic model for pyrolysis of cellulose. J Appl Polym Sci 23:3271–3280
Brown ME, Dollimore D, Galwey AK (1980) Reactions in the solid state, vol 22. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Chen W, Yu H, Liu Y, Chen P, Zhang M, Hai Y (2011) Individualization of cellulose nanofibers from wood using high-intensity ultrasonication combined with chemical pretreatments. Carbohydr Polym 83:1804–1811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.040
Dhaundiyal A, Singh SB, Hanon MM, Rawat R (2018) Determination of kinetic parameters for the thermal decomposition of parthenium hysterophorus. Environ Clim Technol 22:5–21. https://doi.org/10.1515/rtuect-2018-0001
Dong F et al (2019) Sulfadiazine destruction by chlorination in a pilot-scale water distribution system: kinetics, pathway, and bacterial community structure. J Hazard Mater 366:88–97
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Gwon JG, Lee SY, Doh GH, Kim JH (2010) Characterization of chemically modified wood fibers using FTIR spectroscopy for biocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.31746
Hassan M, Berglund L, Hassan E, Abou-Zeid R, Oksman K (2018) Effect of xylanase pretreatment of rice straw unbleached soda and neutral sulfite pulps on isolation of nanofibers and their properties. Cellulose 25:2939–2953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1779-2
Hoareau W, Trindade WG, Siegmund B, Castellan A, Frollini E (2004) Sugar cane bagasse and curaua lignins oxidized by chlorine dioxide and reacted with furfuryl alcohol: characterization and stability. Polym Degrad Stab 86:567–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2004.07.005
Hoeger IC, Nair SS, Ragauskas AJ, Deng Y, Rojas OJ, Zhu JY (2013) Mechanical deconstruction of lignocellulose cell walls and their enzymatic saccharification. Cellulose 20:807–818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9867-9
Huang C, He J, Du L, Min D, Yong Q (2016) Structural characterization of the lignins from the green and yellow bamboo of bamboo culm (Phyllostachys pubescens). J Wood Chem Technol 36:157–172
Huang C, Dong H, Su Y, Wu Y, Narron R, Yong Q (2019) Synthesis of carbon quantum dot nanoparticles derived from byproducts in bio-refinery process for cell imaging and in vivo bioimaging. Nanomaterials 9:387
Isaac A, de Paula J, Viana CM, Henriques AB, Malachias A, Montoro LA (2018) From nano- to micrometer scale: the role of microwave-assisted acid and alkali pretreatments in the sugarcane biomass structure. Biotechnol Biofuels 11:73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1071-6
Kačuráková M, Belton PS, Wilson RH, Hirsch J, Ebringerova A (1998) Hydration properties of xylan-type structures an FTIR study of xylooligosaccharides. J Sci Food Agric 77:38–44
Kutscha NP, Gray JR (1970) The potential of lignin research. Maine Agricultural Experiment Station. Technical Bulletin 41
Li X, Xu R, Yang J, Nie S, Liu D, Liu Y, Si C (2019) Production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and levulinic acid from lignocellulosic biomass and catalytic upgradation. Ind Crops Prod 130:184–197
Liao Q et al (2018) Highly cuboid-shaped heterobimetallic metal-organic frameworks derived from porous Co/ZnO/C microrods with improved electromagnetic wave absorption capabilities. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:29136–29144. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b09093
Lin X, Wu Z, Zhang C, Liu S, Nie S (2018) Enzymatic pulping of lignocellulosic biomass. Ind Crops Prod 120:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.04.033
Nair SS, Yan N (2015) Effect of high residual lignin on the thermal stability of nanofibrils and its enhanced mechanical performance in aqueous environments. Cellulose 22:3137–3150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0737-5
Nair SS, Kuo P-Y, Chen H, Yan N (2017) Investigating the effect of lignin on the mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of cellulose nanofibril reinforced epoxy composite. Ind Crops Prod 100:208–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.02.032
Nie S et al (2014) Kinetics study of oxidation of the lignin model compounds by chlorine dioxide. Chem Eng J 241:410–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.10.068
Nie S, Wang S, Qin C, Yao S, Ebonka JF, Song X, Li K (2015) Removal of hexenuronic acid by xylanase to reduce adsorbable organic halides formation in chlorine dioxide bleaching of bagasse pulp. Bioresour Technol 196:413–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.07.115
Nie S, Zhang C, Zhang Q, Zhang K, Zhang Y, Tao P, Wang S (2018a) Enzymatic and cold alkaline pretreatments of sugarcane bagasse pulp to produce cellulose nanofibrils using a mechanical method. Ind Crops Prod 124:435–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.08.033
Nie S, Zhang K, Lin X, Zhang C, Yan D, Liang H, Wang S (2018b) Enzymatic pretreatment for the improvement of dispersion and film properties of cellulose nanofibrils. Carbohydr Polym 181:1136–1142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.020
Pei Y, Wang S, Qin C, Su J, Nie S, Song X (2016) Optimization of laccase-aided chlorine dioxide bleaching of bagasse pulp. BioResources 11:696–712
Peng Y, Nair SS, Chen H, Yan N, Cao J (2018) Effects of lignin content on mechanical and thermal properties of polypropylene composites reinforced with micro particles of spray dried cellulose nanofibrils. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:11078–11086. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02544
Penttila PA et al (2013) Xylan as limiting factor in enzymatic hydrolysis of nanocellulose. Bioresour Technol 129:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.11.017
Rojo E, Peresin MS, Sampson WW, Hoeger IC, Vartiainen J, Laine J, Rojas OJ (2015) Comprehensive elucidation of the effect of residual lignin on the physical, barrier, mechanical and surface properties of nanocellulose films. Green Chem 17:1853–1866. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4gc02398f
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the x-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29:786–794
Shafizadeh F (1982) Introduction to pyrolysis of biomass. J Anal Appl Pyrol 3:283–305
Solala I et al (2012) Mechanoradical formation and its effects on birch kraft pulp during the preparation of nanofibrillated cellulose with Masuko refining. Holzforschung. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf.2011.183
Spence KL, Venditti RA, Rojas OJ, Habibi Y, Pawlak JJ (2010) The effect of chemical composition on microfibrillar cellulose films from wood pulps: water interactions and physical properties for packaging applications. Cellulose 17:835–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9424-8
Sugimoto T, Morishita T, Matsumoto Y, Meshitsuka G (2005) Effect of oxygen pressure on the oxidation of syringyl alcohol initiated by manganese(III) acetate. Holzforschung 54:262–268
Sun JX, Sun XF, Sun RC, Su YQ (2004) Fractional extraction and structural characterization of sugarcane bagasse hemicelluloses. Carbohydr Polym 56:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2004.02.002
Tao P, Wu Z, Xing C, Zhang Q, Wei Z, Nie S (2019a) Effect of enzymatic treatment on the thermal stability of cellulose nanofibrils. Cellulose 26:1–10
Tao P, Zhang Y, Wu Z, Liao X, Nie S (2019b) Enzymatic pretreatment for cellulose nanofibrils isolation from bagasse pulp: transition of cellulose crystal structure. Carbohydr Polym 214:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.03.012
TAPPI (1992) TAPPI test methods. TAPPI, Peachtree Corners
Tian X, Lu P, Song X, Nie S, Liu Y, Liu M, Wang Z (2017) Enzyme-assisted mechanical production of microfibrillated cellulose from northern bleached softwood kraft pulp. Cellulose 24:3929–3942
Tynell T, Giri A, Gaskins J, Hopkins PE, Mele P, Miyazaki K, Karppinen M (2014) Efficiently suppressed thermal conductivity in ZnO thin films via periodic introduction of organic layers. J Mater Chem A 2:12150–12152
Wang LW, Fu H, Liu HJ, Yu KF, Wang YH, Ma JM (2018) In-situ packaging ultra-uniform 3D hematite nanotubes by polyaniline and their improved gas sensing properties. Mater Res Bull 107:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.06.034
Wu X, Li S, Coumes F, Darcos V, Lai KHJ, Bron P (2013) Modeling and self-assembly behavior of PEG-PLA-PEG triblock copolymers in aqueous solution. Nanoscale 5:9010–9017
Xing J, Tao P, Wu Z, Xing C, Liao X, Nie S (2019) Nanocellulose-graphene composites—a promising nanomaterial for flexible supercapacitors. Carbohydr Polym 207:447–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.010
Yao S, Nie S, Yuan Y, Wang S, Qin C (2015) Efficient extraction of bagasse hemicelluloses and characterization of solid remainder. Bioresour Technol 185:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.02.052
Yao S, Nie S, Zhu H, Wang S, Song X, Qin C (2017) Extraction of hemicellulose by hot water to reduce adsorbable organic halogen formation in chlorine dioxide bleaching of bagasse pulp. Ind Crops Prod 96:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.11.046
Yoon B, Lee BH, George SM (2012) Highly conductive and transparent hybrid organic−inorganic zincone thin films using atomic and molecular layer deposition. J Phys Chem C 116:24787–24791
Yu H et al (2018) Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose from waste paper fibers by cationic polymers addition. Carbohydr Polym 200:248
Zhang H, Nie S, Qin C, Zhang K, Wang S (2018a) Effect of hot chlorine dioxide delignification on AOX in bagasse pulp wastewater. Cellulose 25:2037–2049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1670-1
Zhang H, Qin C, Nie S, Wang S (2018b) Effects of D-hot pretreatment on micro-distribution of residual lignin in sugarcane bagasse pulp and fiber properties. Cellulose 25:4423–4435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1883-3
Zhang K, Zhang Y, Yan D, Zhang C, Nie S (2018c) Enzyme-assisted mechanical production of cellulose nanofibrils: thermal stability. Cellulose 25:5049–5061. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1928-7
Zhang H, Nie S, Qin C, Wang S (2019a) Removal of hexenuronic acid to reduce AOX formation in hot chlorine dioxide bleaching of bagasse pulp. Ind Crops Prod 128:338–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.11.025
Zhang K, Tao P, Zhang Y, Liao X, Nie S (2019b) Highly thermal conductivity of CNF/AlN hybrid films for thermal management of flexible energy storage devices. Carbohydr Polym 213:228–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.02.087
Zhu H et al (2016) Wood-derived materials for green electronics, biological devices, and energy applications. Chem Rev 116:9305–9374. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00225
Acknowledgments
This Project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31760192) and the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation of China (2018GXNSFDA281050).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, N., Tao, P., Lu, Y. et al. Effect of lignin on the thermal stability of cellulose nanofibrils produced from bagasse pulp. Cellulose 26, 7823–7835 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02657-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02657-w