Abstract
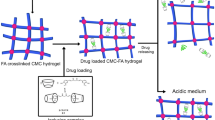
Although cellulose hydrogels are one of promising biomaterials for drug release carrier, their passive manner of drug release and the absence of remote stimuli response limit their further applications. Herein, we report a simple one-pot method for the synthesis of magnetic β-cyclodextrin (β-CD)/cellulose hydrogel beads, which exhibited rapid swelling–deswelling properties under an external magnetic field (EMF) to remotely control drug release from passive release to stepwise release. The grafted β-CD endows the hydrogel with high drug loading capacity and, simultaneously, the incorporation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles provide the force for stepwise drug release through EMF induced rapid and reversible deformation of 3D network. We demonstrate that the efficiency of the hydrogel in the stepwise drug release dose and rate can be controlled by switching on–off the EMF and adjusting the content of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Additionally, results from cytotoxicity tests confirmed the excellent biocompatibility of the developed hydrogel, which is promising to be used in the biomedical field.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amolidiva M, Sadighibonabi R, Pourghazi K (2017) Switchable on/off drug release from gold nanoparticles-grafted dual light- and temperature-responsive hydrogel for controlled drug delivery. Mater Sci Eng, C 76:242–248
Bai X, Bao Z, Bi S, Li Y, Yu X, Hu S, Tian M, Zhang X, Cheng X, Chen X (2018) Chitosan-based thermo/pH double sensitive hydrogel for controlled drug delivery. Macromol Biosci 18:1700305
Banerjee SS, Chen D (2008) Cyclodextrin conjugated magnetic colloidal nanoparticles as a nanocarrier for targeted anticancer drug delivery. Nanotechnology 19:265602
Brown W, Wikström R (1965) A viscosity-molecular weight relationship for cellulose in cadoxen and a hydrodynamic interpretation. Eur Polym J 1(1):1–10
Celebioglu A, Demirci S, Uyar T (2014) Cyclodextrin-grafted electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibers via “Click” reaction for removal of phenanthrene. Appl Surf Sci 305:581–588
Chen P, Song H, Yao S, Tu X, Su M, Zhou L (2017) Magnetic targeted nanoparticles based on β-cyclodextrin and chitosan for hydrophobic drug delivery and a study of their mechanism. RSC Adv 7:29025–29034
Chen W, Yu H, Lee SY, Wei T, Li J, Fan Z (2018) Nanocellulose: a promising nanomaterial for advanced electrochemical energy storage. Chem Soc Rev 47:2837–2872
Dai H, Zhang H, Ma L, Zhou H, Yu Y, Guo T, Zhang Y, Huang H (2019) Green pH/magnetic sensitive hydrogels based on pineapple peel cellulose and polyvinyl alcohol: synthesis, characterization and naringin prolonged release. Carbohydr Polym 209:51–61
Das S, Subuddhi U (2013) Cyclodextrin mediated controlled release of naproxen from pH-sensitive chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels for colon targeted delivery. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:14192–14200
Esmaeilnejadahranjani P, Kazemeini M, Singh G, Arpanaei A (2016) Study of molecular conformation and activity-related properties of lipase immobilized onto core–shell structured polyacrylic acid-coated magnetic silica nanocomposite particles. Langmuir 32:3242–3252
Dhar P, Kumar A, Katiyar V (2016) Magnetic cellulose nanocrystals-based anisotropic polylactic acid nanocomposite films: influence on electrical, magnetic, thermal and mechanical properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:18393–18409
Ge J, Neofytou E, Iii TJC, Beygui RE, Zare RN (2012) Drug release from electric-field-responsive nanoparticles. ACS Nano 6:227–233
Hayashi K, Ono K, Suzuki H, Sawada M, Moriya M, Sakamoto W, Yogo T (2010) High-frequency, magnetic-field-responsive drug release from magnetic nanoparticle/organic hybrid based on hyperthermic effect. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:1903–1911
Hu K, Zhou N, Li Y, Ma S, Guo Z, Cao M, Zhang Q, Sun J, Zhang T, Gu N (2016) Sliced magnetic polyacrylamide hydrogel with cell-adhesive microarray interface: a novel multicellular spheroid culturing platform. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:15113–15119
Jin L, Liu Q, Sun Z, Ni X, Wei M (2010) Preparation of 5-fluorouracil/β-cyclodextrin complex intercalated in layered double hydroxide and the controlled drug release properties. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:11176–11181
Kang DH, Jung HS, Ahn N, Yang SM, Seo S, Suh KY, Chang PS, Jeon NL, Kim J, Kim K (2014) Janus-compartmental alginate microbeads having polydiacetylene liposomes and magnetic nanoparticles for visual lead (II) detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:10631–10637
Kondaveeti S, Semeano A, Cornejo DR, Ulrich H, Petri D (2018) Magnetic hydrogels for levodopa release and cell stimulation triggered by external magnetic field. Colloids Surf B 167:415–424
Lei J, Kim JH, Jeon YS (2008) Preparation and properties of alginate/polyaspartate composite hydrogels. Macromol Res 16:45–50
Li Y, Huang G, Zhang X, Li B, Chen Y, Lu T, Tian JL, Feng X (2013) Magnetic hydrogels and their potential biomedical applications. Adv Funct Mater 23:660–672
Li D, Deng M, Yu Z, Liu W, Zhou G, Li W, Wang X, Yang DP, Zhang W (2018) Biocompatible and stable GO-coated Fe3O4 nanocomposite: a robust drug delivery carrier for simultaneous tumor MR imaging and targeted therapy. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 4:2143–2154
Lin N, Dufresne A (2013) Supramolecular hydrogels from in situ host-guest inclusion between chemically modified cellulose nanocrystals and cyclodextrin. Biomacromol 14:871–880
Lin F, You Y, Yang X, Jiang X, Lu Q, Wang T, Huang B, Lu B (2017) Microwave-assisted facile synthesis of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose beads with high adsorption capacity for organic dyes. Cellulose 24:1–16
Lin F, Zheng R, Chen J, Su W, Dong B, Lin C, Huang B, Lu B (2019) Microfibrillated cellulose enhancement to mechanical and conductive properties of biocompatible hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym 205:244–254
Liu T, Hu S, Liu T, Liu D, Chen S (2006) Magnetic-sensitive behavior of intelligent ferrogels for controlled release of drug. Langmuir 22:5974–5978
Mahdavinia GR, Rahmani Z, Karami S, Pourjavadi A (2014) Magnetic/pH-sensitive κ-carrageenan/sodium alginate hydrogel nanocomposite beads: preparation, swelling behavior, and drug delivery. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 25:1891–1906
Malakootikhah J, Rezayan AH, Negahdari B, Nasseri S, Rastegar H (2017) Glucose reinforced Fe3O4@cellulose mediated amino acid: reusable magnetic glyconanoparticles with enhanced bacteria capture efficiency. Carbohydr Polym 170:190–197
Peng N, Wu B, Wang L, He W, Ai Z, Zhang X, Wang Y, Fan L, Ye Q (2016) High drug loading and pH-responsive targeted nanocarriers from alginate-modified SPIONs for anti-tumor chemotherapy. Biomater sci 4:1802–1813
Peng N, Ding X, Wang Z, Cheng Y, Gong Z, Xu X, Guo X, Cai Q, Huang S, Liu Y (2019) Novel dual responsive alginate-based magnetic nanogels for onco-theranostics. Carbohydr Polym 204:32–41
Peters C, Hoop M, Pané S, Nelson BJ, Hierold C (2016) Degradable magnetic composites for minimally invasive interventions: device fabrication, targeted drug delivery, and cytotoxicity tests. Adv Mater 28:533–538
Piazza RD, Nunes E, Viali WR, Da SS, Aragón FH, Coaquira J, De PM, Marques R, Jafelicci JM (2017) Magnetic nanohydrogel obtained by miniemulsion polymerization of poly(acrylic acid) grafted onto derivatized dextran. Carbohydr Polym 178:378–385
Shete PB, Patil RM, Ningthoujam RS, Ghosh SJ, Pawar SH (2013) Magnetic core–shell structures for magnetic fluid hyperthermia therapy application. New J Chem 37:3784–3792
Sinha A, Basiruddin SK, Chakraborty A, Jana NR (2015) β-cyclodextrin functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica colloid for cholesterol separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:1340–1347
Solanki A, Sanghvi S, Devkar R, Thakore S (2016) β-Cyclodextrin based magnetic nanoconjugates for targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy. RSC Adv 6:98693–98707
Tofzikovskaya Z, Mcnamara M (2012) Synthesis, characterisation and photo-stability of a folate-modified β-cyclodextrin as a functional food additive. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 74:437–445
Tokarev I, Minko S (2010) Stimuli-responsive porous hydrogels at interfaces for molecular filtration, separation, controlled release, and gating in capsules and membranes. Adv Mater 22:3446–3462
Ulbrich K, Holá K, Šubr V, Bakandritsos A, Tuček J, Zbořil R (2016) Targeted drug delivery with polymers and magnetic nanoparticles: covalent and noncovalent approaches, release control, and clinical studies. Chem Rev 116:5338–5431
Wang Q, Xie X, Zhang X, Zhang J, Wang A (2010) Preparation and swelling properties of pH-sensitive composite hydrogel beads based on chitosan-g-poly (acrylic acid)/vermiculite and sodium alginate for diclofenac controlled release. Int J Biol Macromol 46:356–362
Wang L, Zheng W, Chen S, Han Y, Jiang J (2016) Development of rectal delivered thermo-reversible gelling film encapsulating a 5-fluorouracil hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex. Carbohydr Polym 137:9–18
Wang Y, Zhang J, Qiu C, Li J, Cao Z, Ma C, Zheng J, Huang G (2018) Self-recovery magnetic hydrogel with high strength and toughness using nanofibrillated cellulose as a dispersing agent and filler. Carbohydr Poly 196:82–91
Winter A, Chavan A, Wawroschek F (2018) Magnetic resonance imaging of sentinel lymph nodes using intraprostatic injection of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in prostate cancer patients: first-in-human results. Eur Urol Suppl 73:813–814
Xu X, Huang Z, Huang Z, Zhang X, He S, Sun X, Shen Y, Yan M, Zhao C (2017) Injectable, NIR/pH-responsive nanocomposite hydrogel as long-acting implant for chemo-photothermal synergistic cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:20361–20375
Xu Q, Ji Y, Sun Q, Fu Y, Xu Y, Jin L (2019) Fabrication of cellulose nanocrystal/chitosan hydrogel for controlled drug release. Nanomaterials 9:253
Yan F, Yang G, Xiao K, Li Y (2017) Surface-imprinted magnetic carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals for the highly selective extraction of six fluoroquinolones from egg samples. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:1759–1769
Zhang L, Zhou J, Zhang L (2013) Structure and properties of β-cyclodextrin/cellulose hydrogels prepared in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Carbohydr Polym 94:386–393
Zhang H, Luan Q, Tang H, Huang F, Zheng M, Deng Q, Xiang X, Yang C, Shi J, Zheng C (2016) Removal of methyl orange from aqueous solutions by adsorption on cellulose hydrogel assisted with Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Cellulose 24:1–12
Zhang W, Jin X, Li H, Zhang R, Wu C (2018) Injectable and body temperature sensitive hydrogels based on chitosan and hyaluronic acid for pH sensitive drug release. Carbohydr Polym 186:82–90
Zhao Q, Wang S, Cheng X, Yam RC, Kong D, Li R (2010) Surface modification of cellulose fiber via supramolecular assembly of biodegradable polyesters by the aid of host-guest inclusion complexation. Biomacromol 11:1364–1369
Zhao R, Wang Y, Li X, Sun B, Wang C (2015) Synthesis of β-cyclodextrin-based electrospun nanofiber membranes for highly efficient adsorption and separation of methylene blue. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:26649–26657
Zhao D, Huang J, Zhong Y, Li K, Zhang L, Cai J (2016) High-strength and high-toughness double-cross-linked cellulose hydrogels: a new strategy using sequential chemical and physical cross-linking. Adv Funct Mater 26:6279–6287
Zhou L, He B, Zhang F (2011) Facile one-pot synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles cross-linked magnetic poly (vinyl alcohol) gel beads for drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:192–199
Zhou Y, Fu S, Zhang L, Zhan H, Levit M (2014a) Use of carboxylated cellulose nanofibrils-filled magnetic chitosan hydrogel beads as adsorbents for Pb(II). Carbohydr Polym 101:75–82
Zhou Y, Huang L, Li E, Yang Y, Dong C, Li B, Shuang S, Wang H (2014b) β-Cyclodextrin derivatives hybrid Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as the drug delivery for ketoprofen. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 80:209–215
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the generous financial support of the Special Scientific Research Fund for Public Service Sectors of Forestry (No. 201504603), Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (No. xjq201503), Scientific Research Foundation of Graduate School of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (No. 324-1122yb041). B. Lu also thanks the support of the outstanding youth scientific research personnel training plan of colleges and universities in Fujian Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, F., Zheng, J., Guo, W. et al. Smart cellulose-derived magnetic hydrogel with rapid swelling and deswelling properties for remotely controlled drug release. Cellulose 26, 6861–6877 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02572-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02572-0