Abstract
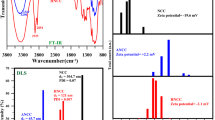
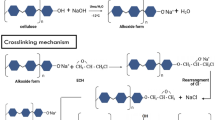
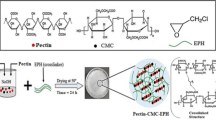
Nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) was modified with (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APTES) and hexadecyltrimethoxysilane (HDTMS) to obtain NCC-APTES and NCC-HDTMS respectively. The modification was confirmed by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analyses (TGA), dynamic light scattering and zeta potential analyses. A series of poly(acrylic acid) (PAA)/NCC, PAA/NCC-APTES, and PAA/NCC-HDTMS hydrogel nanocomposites with various amounts of nanoparticles were synthesized by in situ radical polymerization method. Nanocomposites were characterized using XRD, TGA and field emission scanning electron microscopy. Also, swelling behavior of hydrogel nanocomposites showed that NCC and NCC-APTES helped swelling of hydrogels whereas CNN-HDTMS decreased swelling ratio. The hydrogel nanocomposites were also used as adsorbents for removal of methylene Blue from aqueous solution at different pH values. Results showed that the adsorption capacity for dye increased with increasing pH and contact time. Introducing NCC into hydrogel nanocomposite network affected adsorption capacity. Finally, adsorption kinetics was studied by three kinetic models including pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order and intra-particle diffusion models.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdeen Z, Mohammad SG (2014) Study of the adsorption efficiency of an eco-friendly carbohydrate polymer for contaminated aqueous solution by organophosphorus pesticide. Open J Org Polym Mater 4:16–28. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojopm.2014.41004
Abdollahi E, Abdouss M, Salami-Kalajahi M, Mohammadi A (2016) Molecular recognition ability of molecularly imprinted polymer nano- and micro-particles by reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization. Polym Rev 56:557–583. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2015.1119162
Abdollahi E, Khalafi-Nezhad A, Mohammadi A, Abdouss M, Salami-Kalajahi M (2018) Synthesis of new molecularly imprinted polymer via reversible addition fragmentation transfer polymerization as a drug delivery system. Polymer 143:245–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2018.03.058
Ahmad A, Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Ibrahim MH, Hashim R (2009) Scavenging behaviour of meranti sawdust in the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 170:357–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.087
Ahvenainen P, Kontro I, Svedström K (2016) Comparison of sample crystallinity determination methods by X-ray diffraction for challenging cellulose I materials. Cellulose 23:1073–1086. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0881-6
Akkaya MÇ, Emik S, Güçlü G, İyim TB, Özgümüş S (2009) Removal of basic dyes from aqueous solutions by crosslinked-acrylic acid/acrylamidopropane sulfonic acid hydrogels. J Appl Polym Sci 114:1150–1159. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.30704
Almeida CAP, Debacher NA, Downs AJ, Cottet L, Mello CAD (2009) Removal of methylene blue from colored effluents by adsorption on montmorillonite clay. J Colloid Interface Sci 332:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2008.12.012
Amirshaqaqi N, Salami-Kalajahi M, Mahdavian M (2014) Corrosion behavior of aluminum/silica/polystyrene nanostructured hybrid flakes. Iran Polym J 23:699–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-014-0264-5
Anirudhan TS, Rejeena SR (2012) Poly (acrylic acid)-modified poly (glycidylmethacrylate)-grafted nanocellulose as matrices for the adsorption of lysozyme from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 187:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.113
Annadurai G, Juang R, Lee DJ (2002) Use of cellulose-based wastes for adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 92:263–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(02)00017-1
Atta AM, Ismail HS, Elsaaed AM (2012) Application of anionic acrylamide-based hydrogels in the removal of heavy metals from waste water. J Appl Polym Sci 123:2500–2510. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.34798
Banaei M, Salami-Kalajahi M (2015) Synthesis of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)-grafted poly(aminoamide) dendrimers as polymeric nanostructures. Colloid Polym Sci 293:1553–1559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3559-y
Bashir S, Teo YY, Naeem S, Ramesh S, Ramesh K (2017) pH responsive N-succinyl chitosan/poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels and in vitro release of 5-fluorouracil. PLoS ONE 12:e0179250. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179250
Bekiari V, Sotiropoulou M, Bokias G, Lianos P (2008) Use of poly(N, Ndimethylacrylamide- co-sodium acrylate) hydrogel to extract cationic dyes and metals from water. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Asp 312:214–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.06.053
Bhatia M, Rajulapati SB, Sonawane S, Girdhar A (2017) Synthesis and implication of novel poly (acrylic acid)/nanosorbent embedded hydrogel composite for lead ion removal. Sci Rep 7:16413. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15642-9
Blus K, Czechowski J, Koziróg A (2014) New eco-friendly method for paper dyeing. Fibres Text East Eur 22:121–125
Bulut Y, Karaer H (2015) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by crosslinked chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid)/bentonite composite. Chem Eng Commun 202:1635–1644. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2014.968713
Cha R, He Z, Ni Y (2012) Preparation and characterization of thermal/pH-sensitive hydrogel from carboxylated nanocrystalline cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 88:713–718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.01.026
Chen H, Wang A (2009) Adsorption characteristics of Cu(II) from aqueous solution onto poly(acrylamide)/attapulgite composite. J Hazard Mater 165:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.097
Cheng HL, Feng QH, Liao CA, Liu Y, Wu DB, Wang QG (2016) Removal of methylene blue with hemicellulose/clay hybrid hydrogels. Chin J Polym Sci 34:709–719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-016-1788-2
Ciardelli G, Corsi L, Marcucci M (2001) Membrane separation for wastewater reuse in the textile industry. Resour Conserv Recycl 31:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-3449(00)00079-3
Crini G (2006) Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresour Technol 97:1061–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.05.001
de Paiva SD, da Silva IB, de Moura Santos ECM, Rocha IMV, Martínez-Huitle CA, dos Santos EV (2018) Coupled Electrochemical Processes for Removing Dye from Soil and Water. J Electrochem Soc 165:E318–E324. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0391809jes
Dehghani E, Salami-Kalajahi M, Roghani-Mamaqani H (2019) Fabricating cauliflower-like and dumbbell-like Janus particles: loading and simultaneous release of DOX and ibuprofen. Colloids Surf B-Biointerfaces 173:155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.09.068
Fallahi-Sambaran M, Salami-Kalajahi M, Dehghani E, Abbasi F (2018) Investigation of different core-shell toward Janus morphologies by variation of surfactant and feeding composition: a study on the kinetics of DOX release. Colloids Surf B-Biointerfaces 170:578–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.06.064
Fallahi-Samberan M, Salami-Kalajahi M, Dehghani E, Abbasi F (2019) Investigating Janus morphology development of poly(acrylic acid)/poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) composite particles: an experimental study and mathematical modeling of DOX release. Microchem J 145:492–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.11.017
Gao Q, Zhu Q, Yang CQ (2009) Formation of highly hydrophobic surfaces on cotton and polyester fabrics using silica sol nanoparticles and nonfluorinated alkylsilane. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:9797–9803. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie9005518
Ghosh D, Bhattacharyya KG (2002) Adsorption of methylene blue on kaolinite. Appl Clay Sci 20:295–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-1317(01)00081-3
Golshan M, Salami-Kalajahi M, Roghani-Mamaqani H, Mohammadi M (2017) Poly(propylene imine) dendrimer-grafted nanocrystalline cellulose: doxorubicin loading and release behavior. Polymer 117:287–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2017.04.047
Guerra E, Llompart M, Garcia-Jares C (2018) Analysis of dyes in cosmetics: challenges and recent developments. Cosmetics 5:47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics5030047
Gupta VK, Kumar R, Nayak A, Saleh TA, Barakat MA (2013) Adsorptive removal of dyes from aqueous solution onto carbon nanotubes: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 193:24–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2013.03.003
Habibi Y (2014) Key advances in the chemical modification of nanocelluloses. Chem Soc Rev 43:1519–1542. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60204D
Haqani M, Roghani-Mamaqani H, Salami-Kalajahi M (2017) Synthesis of dual-sensitive nanocrystalline cellulose-grafted block copolymers of N-isopropylacrylamide and acrylic acid by reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization. Cellulose 24:2241–2254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1249-2
Hernandez-Martínez AR, Lujan-Montelongo JA, Silva-Cuevas C, Mota-Morales JD, Cortez-Valadez M, de Jesus Ruíz-Baltazar A, Cruz M, Herrera-Ordonez J (2018) Swelling and methylene blue adsorption of poly (N, N-dimethylacrylamide-co-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogel. React Funct Polym 122:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2017.11.008
Hou K, Li Y, Liu Y, Zhang R, Hsiao BS, Zhu M (2017) Continuous fabrication of cellulose nanocrystal/poly (ethylene glycol) diacrylate hydrogel fiber from nanocomposite dispersion: rheology, preparation and characterization. Polymer 123:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2017.06.034
Ibrahim SM, El Salmawi KM, Zahran AH (2007) Synthesis of crosslinked superabsorbent carboxymethyl cellulose/acrylamide hydrogels through electron-beam irradiation. J Appl Polym Sci 104:2003–2008. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.25916
Kargarzadeh H, Ahmad I, Abdullah I, Dufresne A, Zainudin SY, Sheltami RM (2012) Effects of hydrolysis conditions on the morphology, crystallinity, and thermal stability of cellulose nanocrystals extracted from kenaf bast fibers. Cellulose 19:855–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9684-6
Kaşgöz H, Durmus A (2008) Dye removal by a novel hydrogel-clay nanocomposite with enhanced swelling properties. Polym Adv Technol 19:838–845. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.1045
Kumar A, Negi YS, Choudhary V, Bhardwaj NK (2014) Characterization of cellulose nanocrystals produced by acid-hydrolysis from sugarcane bagasse as agro-waste. J Mater Phys Chem 2:1–8. https://doi.org/10.12691/jmpc-2-1-1
Kurdtabar M, Koutenaee RN, Bardajee GR (2018) Synthesis and characterization of a novel pH-responsive nanocomposite hydrogel based on chitosan for targeted drug release. J Polym Res 25:119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-018-1499-1
Li S, Zhang H, Feng J, Xu R, Liu X (2011) Facile preparation of poly (acrylic acid–acrylamide) hydrogels by frontal polymerization and their use in removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution. Desalination 280:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.06.056
Lim LS, Ahmad I (2014) Chemical crosslinking of acrylic acid to form biocompatible pH sensitive hydrogel reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals (CNC). AIP Conf Proc 1614:366–370. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4895224
Lim LS, Ahmad I, Lazim MASM (2015) pH sensitive hydrogel based on poly(acrylic acid) and cellulose nanocrystals. Sains Malaysiana 44:779–785. https://doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2015-4406-02
Lim LS, Rosli NA, Ahmad I, Lazim MASM, Amin MCIM (2017) Synthesis and swelling behavior of pH-sensitive semi-IPN superabsorbent hydrogels based on poly (acrylic acid) reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals. Nanomaterials 7:399. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7110399
Liu Y, Zheng Y, Wang A (2010) Enhanced adsorption of Methylene Blue from aqueous solution by chitosan-g-poly (acrylic acid)/vermiculite hydrogel composites. J Environ Sci 22:486–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60134-0
Liu J, Liu G, Liu W (2014) Preparation of water-soluble β-cyclodextrin/poly(acrylic acid)/graphene oxide nanocomposites as new adsorbents to remove cationic dyes from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 25:299–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.021
Lu B, Tarn MD, Pamme N, Georgiou TK (2015a) Tailoring pH-responsive acrylic acid microgels with hydrophobic crosslinks for drug release. J Mater Chem 3:4524–4529. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00222B
Lu T, Xiang T, Huang XL, Li C, Zhao WF, Zhang Q, Zhao CS (2015b) Post-crosslinking towards stimuli-responsive sodium alginate beads for the removal of dye and heavy metals. Carbohydr Polym 133:587–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.07.048
Luo X, Zhang L (2009) High effective adsorption of organic dyes on magnetic cellulose beads entrapping activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 171:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.009
Luo JH, Li YY, Wang PM, Xia BB, He LP, Yang BW, Jiang B (2017) A facial route for preparation of hydrophobic nano-silica modified by silane coupling agents. Key Eng Mater 727:353–358. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.727.353
Luo M-T, Li H-L, Huang C, Zhang H-R, Xiong L, Chen X-F, Chen X-D (2018) Cellulose-based absorbent production from bacterial cellulose and acrylic acid: synthesis and performance. Polymers 10:702. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070702
Maiti S, Jayaramudu J, Das K, Reddy SM, Sadiku R, Ray SS, Liu D (2013) Preparation and characterization of nano-cellulose with new shape from different precursor. Carbohydr Polym 98:562–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.06.029
Malik PK, Saha SK (2003) Oxidation of direct dyes with hydrogen peroxide using ferrous ion as catalyst. Sep Purif Technol 31:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-5866(02)00200-9
Mall ID, Srivastava VC, Agarwal NK, Mishra IM (2005) Removal of congo red from aqueous solution by bagasse fly ash and activated carbon: kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analyses. Chemosphere 61:492–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.065
Mazlita Y, Lee HV, Hamid SBA (2016) Preparation of cellulose nanocrystals bio-polymer from agro-industrial wastes: separation and characterization. Polym Polym Compos 24:719–728. https://doi.org/10.1177/096739111602400907
Melo BC, Paulino FA, Cardoso VA, Pereira AG, Fajardo AR, Rodrigues FH (2018) Cellulose nanowhiskers improve the methylene blue adsorption capacity of chitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid) hydrogel. Carbohydr Polym 181:358–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.10.079
Modarresi-Saryazdi SM, Haddadi-Asl V, Salami-Kalajahi M (2018) N,N’-methylenebis(acrylamide)-crosslinked poly(acrylic acid) particles as doxorubicin carriers: a comparison between release behavior of physically loaded drug and conjugated drug via acid-labile hydrazone linkage. J Biomed Mater Res A 106:342–348. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36240
Moqadam S, Salami-Kalajahi M, Mahdavian M (2018) Synthesis and characterization of sunflower oil-based polysulfide polymer/cloisite 30B nanocomposites. Iran J Chem Chem Eng 37:185–192
Nath J, Dolui SK (2018) Synthesis of carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(acrylic acid)/LDH hydrogel for in vitro controlled release of vitamin B12. Appl Clay Sci 155:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.01.004
Nikravan G, Haddadi-Asl V, Salami-Kalajahi M (2018a) Synthesis of pH-responsive magnetic yolk-shell nanoparticles: a comparison between the conventional etching and new deswelling approaches. Appl Organometal Chem 32:e4272. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4272
Nikravan G, Haddadi-Asl V, Salami-Kalajahi M (2018b) Synthesis of dual temperature– and pH-responsive yolk-shell nanoparticles by conventional etching and new deswelling approaches: DOX release behavior. Colloids Surf B-Biointerfaces 165:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.02.010
Nilsson C (2017) Preparation and characterization of nanocellulose from wheat bran, Lund University. http://lup.lub.lu.se/student-papers/record/8906333
Noein L, Haddadi-Asl V, Salami-Kalajahi M (2017) Grafting of pH-sensitive poly (N, N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate-co-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) onto halloysite nanotubes via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization for controllable drug release. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 66:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2016.1190927
Panahian P, Salami-Kalajahi M, Hosseini MS (2014) Synthesis of dual thermoresponsive and pH-sensitive hollow nanospheres by atom transfer radical polymerization. J Polym Res 21:455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-014-0455-y
Panswed J, Wongchaisuwan S (1986) Mechanisms of dye wastewater colour removal by magnesium carbonate-hydrated basic. Water Sci Technol 18:139–144. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.1986.0045
Patil PS, Phugare SS, Jadhav SB, Jadhav JP (2010) Communal action of microbial cultures for Red HE3B degradation. J Hazard Mater 181:263–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.05.093
Pirayesh A, Salami-Kalajahi M, Roghani-Mamaqani H, Dehghani E (2018) Amine-modified graphene oxide as co-curing agent of epoxidized polysulfide prepolymer: thermophysical and mechanical properties of nanocomposites. Diamond Relat Mater 86:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2018.04.025
Qi X, Wu L, Su T, Zhang J, Dong W (2018) Polysaccharide-based cationic hydrogels for dye adsorption. Colloids Surf B-Biointerfaces 170:364–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.06.036
Rahchamani J, Mousavi HZ, Behzad M (2011) Adsorption of methyl violet from aqueous solution by polyacrylamide as an adsorbent: isotherm and kinetic studies. Desalination 267:256–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.09.036
Rashidzadeh A, Olad A, Salari D (2015) The effective removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions by NaAlg-g-poly (acrylic acid-co-acryl amide)/clinoptilolite hydrogel nanocomposite. Fib Polym 16:354–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-015-0354-9
Seema HS, Deepika L, Ambika B (2018) a comparative study on discharge printing using conventional and ecological recipe. Trends Text Eng Fashion Technol 3:TTEFT.000552.2018. https://doi.org/10.31031/TTEFT.2018.03.000552
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29:786–794. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051755902901003
Shankar S, Rhim JW (2016) Preparation of nanocellulose from micro-crystalline cellulose: the effect on the performance and properties of agar-based composite films. Carbohydr Polym 135:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.08.082
Sharifzadeh E, Salami-Kalajahi M, Hosseini MS, Aghjeh MKR (2016) A temperature-controlled method to produce Janus nanoparticles using high internal interface systems: experimental and theoretical approaches. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 506:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.06.006
Sharma R, Kaith BS, Kalia S, Pathania D, Kumar A, Sharma N, Street RM, Schauer C (2015) Biodegradable and conducting hydrogels based on Guar gum polysaccharide for antibacterial and dye removal applications. J Environ Manag 162:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.07.044
Singh T, Singhal R (2015) Kinetics and thermodynamics of cationic dye adsorption onto dry and swollen hydrogels pol (acrylic acid-sodium acrylate-acrylamide) sodium humate. Desalin Water Treat 53:3668–3680. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.871342
Soleimani K, Tehrani AD, Adeli ADM (2018) Bioconjugated graphene oxide hydrogel as an effective adsorbent for cationic dyes removal. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.08.021
Şolpan D, Duran S, Saraydin D, Güven O (2003) Adsorption of methyl violet in aqueous solutions by poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels. Rad Phys Chem 66:117–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-806X(02)00384-5
Suo A, Qian J, Yao Y, Zhang W (2007) Synthesis and properties of carboxymethyl cellulose-graft-poly (acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) as a novel cellulose-based superabsorbent. J Appl Polym Sci 103:1382–1388. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.23948
Vakili M, Rafatullah M, Salamatinia B, Abdullah AZ, Ibrahim MH, Tan KB, Amouzgar P (2014) Application of chitosan and its derivatives as adsorbents for dye removal from water and wastewater. Carbohydr Polym 113:115–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.07.007
Varaprasad K, Jayaramudu T (2017) Removal of dye by carboxymethyl cellulose, acrylamide and graphene oxide via a free radical polymerization process. Carbohydr Polym 164:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.01.094
Wang S, Peng Y (2010) Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 156:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.10.029
Wang J, Wang W, Wang A (2010) Synthesis, characterization and swelling behaviors of hydroxyethyl cellulose-g-poly(acrylic acid)/attapulgite superabsorbent composite. Polym Eng Sci 50:1019–1027. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.21500
Yamada K, Yoshii S, Kumagai S, Fujiwara I, Nishio K, Okuda M, Matsukawa N, Yamashita I (2006) High-density and highly surface selective adsorption of protein–nanoparticle complexes by controlling electrostatic interaction. Jpn J Appl Phys 45:4259. https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.45.4259
Yang J (2017) Manufacturing of nanocrystalline cellulose, Aalto University. http://urn.fi/URN:NBN:fi:aalto-201709046803
Yang J, Han CR, Duan JF, Ma MG, Zhang XM, Xu F, Sun RC, Xie XM (2012) Studies on the properties and formation mechanism of flexible nanocomposite hydrogels from cellulose nanocrystals and poly(acrylic acid). J Mater Chem 22:22467–22480. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM35498E
Yassin S, Su K, Lin H, Gladden LF, Zeitler JA (2015) Diffusion and swelling measurements in pharmaceutical powder compacts using terahertz pulsed imaging. J Pharm Sci 104:1658–1667. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.24376
Yetimoğlu K, Kahraman MV, Ercan O, Akdemir ZS, Apohan NK (2007) Nvinylpyrrolidone/acrylic acid/2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid based hydrogels: synthesis, characterization and their application in the removal of heavy metals. React Funct Polym 67:451–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2007.02.007
Zarezadeh-Mehrizi M, Karimi M, Qomi M (2017) Removal of methylene blue using polyacrylic acid/octavinyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanocomposite. J Nanoanalysis 4:134–141. https://doi.org/10.22034/jna.2017.02.006
Zendehdel M, Barati A, Alikhani H, Hekmat A (2010) Removal of methylene blue dye from wastewater by adsorption onto semi-inpenetrating polymer network hydrogels composed of acrylamide and acrylic acid copolymer and polyvinyl alcohol. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 7:431–436
Zhang H, Song SP, She Y, Lang Q, Pu JW (2012) Modification of NCC for Improving the wetting property with polyurethane. Adv Mater Res 528:164–167. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.528.164
Zheng Y, Wang A (2009) Evaluation of ammonium removal using a chitosan-g-poly (acrylic acid)/rectorite hydrogel composite. J Hazard Mater 171:671–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.05
Zhou Y, Fu S, Liu H, Yang S, Zhan H (2011) Removal of methylene blue dyes from wastewater using cellulose-based superadsorbent hydrogels. Polym Eng Sci 51:2417–2424. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.22020
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10570_2019_2490_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Materials; Preparation of NCC from MCC; Characterization; FE-SEM images of MCC and CNC; TGA results of nanocomposite hydrogels; XRD diffractograms of nanocomposite hydrogels; Swelling ratios of hydrogel nanocomposites; Modeling results of hydrogel nanocomposites (DOCX 2996 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safavi-Mirmahalleh, SA., Salami-Kalajahi, M. & Roghani-Mamaqani, H. Effect of surface chemistry and content of nanocrystalline cellulose on removal of methylene blue from wastewater by poly(acrylic acid)/nanocrystalline cellulose nanocomposite hydrogels. Cellulose 26, 5603–5619 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02490-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02490-1