Abstract
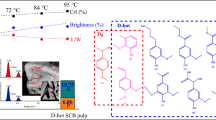
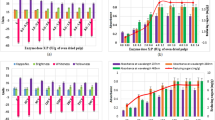
This work describes the effect of the hot chlorine dioxide delignification (DHT) on the properties of bagasse fiber and the formation of AOX. The bagasse pulp was subjected to both DHT and normal temperature chlorine dioxide delignification (D0), and the AOX contents in the effluent were determined respectively. The GC–MS results showed that the main components of the D0 stage wastewater were chlorinated hydrocarbons and chlorinated diphenyls. In contrast, those AOXs in the DHT stage wastewater were very few. The GC–MS, ATR-FTIR, and XPS results showed the DHT process is more effective in the removal of the residual phenolic lignin and the hemicellulose-linked HexA compared with D0. Furthermore, in comparison, the AOX content could be reduced by 50% with DHT. The fully bleached pulp obtained via DHTEpD process has a higher brightness than that obtained by D0EpD, which provides a reliable theoretical basis for industrial application.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balabanič D, Filipič M, Klemenčič AK, Žegura B (2017) Raw and biologically treated paper mill wastewater effluents and the recipient surface waters: Cytotoxic and genotoxic activity and the presence of endocrine disrupting compounds. Sci Total Environ 574:78–89
Björklund M, Germgård U, Basta J (2004) Formation of AOX and OCI in ECF bleaching of birch pulp. Tappi J 3:7–12
Cadena EM et al (2011) On hexenuronic acid (HexA) removal and mediator coupling to pulp fiber in the laccase/mediator treatment. Biores Technol 102:3911–3917
Candido RG, Godoy GG, Gonçalves AR (2017) Characterization and application of cellulose acetate synthesized from sugarcane bagasse. Carbohyd Polym
Chaparro TR, Pires EC (2015) Post-treatment of anaerobic effluent by ozone and ozone/UV of a kraft cellulose pulp mill. Water Sci Technol 71:382–389
Deshmukh NS, Lapsiya KL, Savant DV, Chiplonkar SA, Yeole TY, Dhakephalkar PK, Ranade DR (2009) Upflow anaerobic filter for the degradation of adsorbable organic halides (AOX) from bleach composite wastewater of pulp and paper industry. Chemosphere 75:1179–1185
Eiras BM, Maria K (2002) Optimisation of the high temperature chlorine dioxide bleaching stage for eucalyptus kraft pulp. Visosa Federal University
Gomes CM, Colodette JL, Delantonio NR, Mounteer AH, Silva CM (2007) Effect of hot acid hydrolysis and hot chlorine dioxide stage on bleaching effluent biodegradability. Water Sci Technol 55:39–46
Gray DG, Weller M, Ulkem N, Lejeune A (2010) Composition of lignocellulosic surfaces: comments on the interpretation of XPS spectra. Cellulose 17:117–124
Jiang Z-H, Bouchard J, Berry R (2006) Evidence for the formation of lignin-hexenuronic acid-xylan complexes during modified kraft pulping processes. Holzforschung 60(2):137–142
Juutilainen S, Vilpponen A, Pikka O, Vuorinen T, Henricson K (1999) Combining chlorine dioxide bleaching of birch kraft pulp with an A stage at high temperatures. Tappi J 2:645–651
Lachenal D, Chirat C (1998) High temperature chlorine dioxide delignification: a breakthrough in ECF bleaching of hardwood kraft pulp. In: Tappi pulping conference
Magara K, Ikeda T, Sugimoto T, Hosoya S (2006) Reduction of AOX by prolonged ClO2 bleaching under high temperature and acidic pH conditions Japan. Tappi J 60:761–772
Malhotra R, Prakash D, Shukla SK, Kim T, Kumar S, Rao NJ (2013) Comparative study of toxic chlorophenolic compounds generated in various bleaching sequences of wheat straw pulp. Clean Technol Environ Policy 15:999–1011
Mcdonough TJ, Uno S, Rudie AW, Courchene CE (2009) Optimization of ECF bleaching of kraft pulp: II. Effects of acid prehydrolysis on hardwood pulp bleachability. Tappi J 8:10–18
Mjm B, Seco IM, Fernandes PM, Ferreira LM, Castro JA (2001) Reduction of AOX in the bleach plant of a pulp mill. Environ Sci Technol 35:4390–4393
Nie S et al (2014) Kinetics study of oxidation of the lignin model compounds by chlorine dioxide. Chem Eng J 241:410–417
Nie S, Wang S, Qin C, Yao S, Ebonka JF, Song X, Li K (2015) Removal of hexenuronic acid by xylanase to reduce adsorbable organic halides formation in chlorine dioxide bleaching of bagasse pulp. Biores Technol 196:413–417
Nie S, Yao S, Wang S, Qin C (2016) Absorbable organic halide (AOX) reduction in elemental chlorine-free (ECF) bleaching of bagasse pulp from the addition of sodium sulphide. Bioresources 11:713–723
Osman WH, Abdullah SR, Mohamad AB, Kadhum AA, Rahman RA (2013) Simultaneous removal of AOX and COD from real recycled paper wastewater using GAC-SBBR. J Environ Manag 121:80–86
Petit-Breuilh X, Melo R, Zaror C (2004) Environmental implications of hexenuronic acid removal from Eucalyptus globulus kraft pulp using peroxymonosulfuric acid. Chil Chem Soc 49:355–360
Reis CL, Silva LM, Rodrigues TH, Félix AK, Santiago-Aguiar RS, Canuto KM, Rocha MV (2017) Pretreatment of cashew apple bagasse using protic ionic liquids: enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis. Biores Technol 224:694
Savant DV, Abdulrahman R, Ranade DR (2006) Anaerobic degradation of adsorbable organic halides (AOX) from pulp and paper industry wastewater. Biores Technol 97:1092–1104
Sharma A, Thakur VV, Shrivastava A, Jain RK, Mathur RM, Gupta R, Kuhad RC (2014) Xylanase and laccase based enzymatic kraft pulp bleaching reduces adsorbable organic halogen (AOX) in bleach effluents: a pilot scale study. Biores Technol 169:96
Singh P, Thakur IS (2006) Colour removal of anaerobically treated pulp and paper mill effluent by microorganisms in two steps bioreactor. Biores Technol 97:218–223
Tarvo V (2010a) The effect of process variables in chlorine dioxide prebleaching of birch kraft pulp. Part 1. Inorganic chlorine compounds, kappa number, lignin, and hexenuronic acid content. J Wood Chem Technol 30:1–18
Tarvo V (2010b) The effect of process variables in chlorine dioxide prebleaching of birch kraft pulp. Part 2. AOX and OX formation. J Wood Chem Technol 30:19–30
Tiku DK, Kumar A, Chaturvedi R, Makhijani SD, Manoharan A, Kumar R (2010) Holistic bioremediation of pulp mill effluents using autochthonous bacteria. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 64:173–183
Ventorim G (2005) The fate of chlorine species during high temperature chlorine dioxide bleaching. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 20:007–011
Wang J et al (2011) Combining renewable gum rosin and lignin: towards hydrophobic polymer composites by controlled polymerization. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 49:3728–3738
Yao S, Gao C, Zhu H, Zhang Y, Wang S, Qin C (2016) Effects of additives on absorbable organic halide reduction in elemental chlorine-free bleaching of bagasse kraft pulp. Bioresources 11:996–1006
Yao S, Nie S, Zhu H, Wang S, Song X, Qin C (2017) Extraction of hemicellulose by hot water to reduce adsorbable organic halogen formation in chlorine dioxide bleaching of bagasse pulp. Ind Crops Prod 96:178–185
Zhang C, Chen J, Wen Z (2012) Alternative policy assessment for water pollution control in China’s pulp and paper industry. Resour Conserv Recycl 66:15–26
Zhou Z, Jääskeläinen AS, Vuorinen T (2008) Oxidation of cellulose and carboxylic acids by hypochlorous acid: kinetics and mechanisms. J Pulp Pap Sci 34:212–218
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by the Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education (YCSW2017046), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31660182 & 21466004), the Scientific Research Foundation of Guangxi University (Grant No. XGZ160166), the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation of China (2016GXNSFBA380234 & 2013GXNSFFA019005), and the Middle-young age Ability Enhancement Program of Guangxi (KY2016YB037).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Nie, S., Qin, C. et al. Effect of hot chlorine dioxide delignification on AOX in bagasse pulp wastewater. Cellulose 25, 2037–2049 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1670-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1670-1