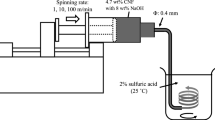
Abstract
This work demonstrates a simple fabrication of cellulose nanofibers by direct electrospinning of dissolved cellulose solutions. The hard- and softwood pulps and the outer mantles of tunicate were dissolved in a mixture of trifluoroacetic acid and dichloroethane by stirring and ultrasonication to give highly viscoelastic, clear solutions. These solutions were electrospun to form continuous nanofibers made of unsubstituted cellulose, which were confirmed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and IR spectroscopy. Statistical analysis of the SEM images of the nanofibers suggested that there are positive correlations between diameters of the nanofibers and concentration of the cellulose solution. The mean diameters of the nanofibers obtained from softwood pulp (DP of cellulose ≈ 1200) solutions were larger than those from hardwood pulp (DP of cellulose ≈ 500) at the same concentrations. This indicates that the DP of cellulose is one of the important parameters to control the diameters of the electrospun cellulose nanofibers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abitbol T, Rivkin A, Cao Y, Nevo Y, Abraham E, Ben-Shalom T, Lapidot S, Shoseyov O (2016) Nanocellulose, a tiny fiber with huge applications. Curr Opin Biotechnol 39:76–88
Cai J, Zhang L (2005) Rapid dissolution of cellulose in LiOH/urea and NaOH/urea aqueous solutions. Macromol Biosci 5:539–548
Chanzy H, Peguy A, Chaunis S, Monzie P (1980) Oriented cellulose films and fibers from a mesophase system. J Polym Sci Polym Phys Ed 18:1137–1144
Eichhorn SJ, Dufresne A, Aranguren M, Marcovich NE, Capadona JR, Rowan SJ, Weder C, Thielemans W, Roman M, Renneckar S, Gindl W, Veigel S, Keckes J, Yano H, Abe K, Nogi M, Nakagaito AN, Mangalam A, Simonsen J, Benight AS, Bismarck A, Berglund LA, Peijs T (2010) Review: current international research into cellulose nanofibres and nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 45:1–33
Freire MG, Teles ARR, Ferreira RAS, Carlos LD, Lopes-da-Silva JA, Coutinho JAP (2011) Electrospun nanosized cellulose fibers using ionic liquids at room temperature. Green Chem 13:3173–3180
Hasegawa M, Isogai A, Onabe F, Usuda M (1992) Dissolving states of cellulose and chitosan in trifluoroacetic acid. J Appl Polym Sci 45:1857–1863
Heinze T, Dicke R, Koschella A, Kull AH, Klohr E-A, Koch W (2000) Effective preparation of cellulose derivatives in a new simple cellulose solvent. Macromol Chem Phys 201:627–631
Khadka DB, Haynie DT (2012) Protein- and peptide-based electrospun nanofibers in medical biomaterials. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 8:1242–1262
Klemm D, Kramer F, Moritz S, Lindström T, Ankerfors M, Gray D, Dorris A (2011) Nanocelluloses: a new family of nature-based materials. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:5438–5466
Kulpinski P (2005) Cellulose nanofibers prepared by the N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide method. J Appl Polym Sci 98:1855–1859
Li M, Mondrinos MJ, Gandhi MR, Ko FK, Weiss AS, Lelkes PI (2005) Electrospun protein fibers as matrices for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 26:5999–6008
Liu H, Hsieh Y-L (2002) Ultrafine fibrous cellulose membranes from electrospinning of cellulose acetate. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 40:2119–2129
McCormick CL, Callais PA, Hutchinson BH (1985) Solution studies of cellulose in lithium chloride and N,N-dimethylacetamide. Macromolecules 18:2394–2401
Ohkawa K (2008) Electrospinning of natural and bio-related polymeric materials. Seni Gakkaishi 64:36–44
Ohkawa K (2015) Nanofibers of cellulose and its derivatives fabricated using direct electrospinning. Molecules 20:9139–9154
Ohkawa K, Hayashi S, Nishida A, Yamamoto H, Ducreux J (2009) Preparation of pure cellulose nanofiber via electrospinning. Text Res J 79:1396–1401
Ono Y, Tanaka R, Funahashi R, Takeuchi M, Saito T, Isogai A (2016) SEC–MALLS analysis of ethylenediamine-pretreated native celluloses in LiCl/N,N-dimethylacetamide: softwood kraft pulp and highly crystalline bacterial, tunicate, and algal celluloses. Cellulose 23:1639–1647
Patel DL, Gilbert RD (1981) Lyotropic mesomorphic formation of cellulose in trifluoroacetic acid-chlorinated-alkane solvent mixtures at room temperature. J Polym Sci Polym Phys Ed 19:1231–1236
Quan S-L, Kang S-G, Chin I-J (2010) Characterization of cellulose fibers electrospun using ionic liquid. Cellulose 17:223–230
Schiffman JD, Schauer CL (2008) A review: electrospinning of biopolymer nanofibers and their applications. Polym Rev 48:317–352
Sill TJ, von Recum HA (2008) Electrospinning: applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 29:1989–2006
Tamai N, Tatsumi D, Matsumoto T (2004) Rheological properties and molecular structure of tunicate cellulose in LiCl/1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone. Biomacromol 5:422–432
Zhang L, Ruan D, Gao S (2002) Dissolution and regeneration of cellulose in NaOH/thiourea aqueous solution. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 40:1521–1529
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Institut Carnot PolyNat (ANR-11-CANR-0007-01), ANR “sweetmemory” project (ANR-14-CE08-0021), and the CNRS. The authors thank Dr. B. Carré, Dr. B. Arnoul-Jarriault, and Dr. D. Lachenal for providing the soft- and hardwood pulp samples. The authors also thank Dr. Y. Nishiyama for providing the tunicate samples and Dr. C. Lancelon-Pin for SEM observation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Otsuka, I., Njinang, C.N. & Borsali, R. Simple fabrication of cellulose nanofibers via electrospinning of dissolving pulp and tunicate. Cellulose 24, 3281–3288 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1360-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1360-4