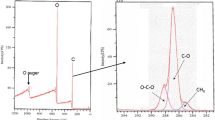
Abstract
Cheap, disposable bio-diagnostic devices are becoming increasingly prevalent in the field of biosensing. Earlier we had reported the ability of cellulosic surface to control the nucleation of plasmonic silver nanoparticles and in this report we utilize this nucleation controlling property to demonstrate a new plasmonic sensing mechanism based on paper substrates to quantitatively detect proteins. On contrary to conventional paper based diagnostic devices which use the cellulosic part of paper as a support structure, the proposed method takes advantage of cellulose as nucleation controller during silver nanoparticle formation. Reduction of silver ions interacting competitively with nucleation controlling cellulosic surface and reduction suppressing amino acids of protein (via complexation) resulted in silver nanoparticles whose size–shape dependent plasmonic property quantitatively reflected the concentration of protein on paper, characterized using UV–Vis and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopies. As a proof-of-concept, bovine serum albumin (BSA) was tested as the target analyte. UV–Vis spectroscopy based BSA quantification was sensitive in the concentration range 10–60 mg ml−1 while that for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy extended well below 10 mg ml−1, thus demonstrating the potential of this simple method to quantitatively detect a wide range of proteins relevant to the field of biodiagnostics.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- PTAP:
-
4-Aminothiophenol
- SERS:
-
Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy
- UV–Vis:
-
Ultra violet–visible light
- XPS:
-
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
References
Cheng C, Martinez AW, Gong J, Mace CR, Phillips ST, Carrilho E, Mirica KA, Whitesides GM (2010) Paper-based ELISA. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:4771–4774. doi:10.1002/anie.201001005
Choi S, Choi EY, Kim DJ, Kim JH, Kim TS, Oh SW (2004) A rapid, simple measurement of human albumin in whole blood using a fluorescence immunoassay (I). Clin Chim Acta 339:147–156. doi:10.1016/j.cccn.2003.10.002
Jin H, Kettunen M, Laiho A, Pynnolnen H, Paltakari J, Marmur A, Ikkala O, Ras RHA (2011) Superhydrophobic and superoleophobic nanocellulose aerogel membranes as bioinspired cargo carriers on water and oil. Langmuir 27:1930–1934. doi:10.1021/la103877r
Kim J-H, Kang K, Yun S, Yang S, Lee M-H, Kim J-H, Kim J (2008) Cellulose electroactive paper (EAPap): the potential for a novel electronic material. MRS Proc. doi:10.1557/PROC-1129-V05-02
Kim J, Lee H, Kim HS (2010) Beam vibration control using cellulose-based electro-active paper sensor. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 11:823–827. doi:10.1007/s12541-010-0099-8
Lee SW, Kim JH, Kim J, Kim HS (2009) Characterization and sensor application of cellulose electro-active paper (EAPap). Chin Sci Bull 54:2703–2707. doi:10.1007/s11434-009-0219-y
Lee CH, Hankus ME, Tian L, Pellegrino PM, Singamaneni S (2011) Highly sensitive surface enhanced Raman scattering substrates based on filter paper loaded with plasmonic nanostructures. Anal Chem 83:8953–8958. doi:10.1021/ac2016882
Liu Q, Wang J, Wang B, Li Z, Huang H, Li C, Yu X, Chu PK (2014) Paper-based plasmonic platform for sensitive, noninvasive, and rapid cancer screening. Biosens Bioelectron 54:128–134. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2013.10.067
Lokanathan AR, Uddin KMA, Rojas OJ, Laine J (2014) Cellulose nanocrystal-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: role of sulfate groups in nucleation phenomena. Biomacromolecules 15:373–379. doi:10.1021/bm401613h
Martinez AW, Phillips ST, Whitesides GM, Carrilho E (2010) Diagnostics for the developing world: microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal Chem 82:3–10. doi:10.1021/ac9013989
Merril CR (1990) Silver staining of proteins and DNA. Nature 343:779–780
Morones RJ, Frey W (2007) Environmentally sensitive silver nanoparticles of controlled size synthesized with PNIPAM as a nucleating and capping agent. Langmuir 23:8180–8186. doi:10.1021/la7008336
Nie Z, Nijhuis CA, Gong J, Chen X, Kumachev A, Andres MW, Narovlyansky M, Whitesides GM (2010) Electrochemical sensing in paper-based microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 10:477–483. doi:10.1039/B917150A
Rozand C (2014) Paper-based analytical devices for point-of-care infectious disease testing. Eur J Clin Microbiol 33:147–156. doi:10.1007/s10096-013-1945-2
Wandowski T, Malinowski P, Ostachowicz WM (2011) Damage detection with concentrated configurations of piezoelectric transducers. Smart Mater Struct 20:025002–025016
Yu J, Ge L, Huang J, Wang S, Ge S (2011) Microfluidic paper-based chemiluminescence biosensor for simultaneous determination of glucose and uric acid. Lab Chip 11:1286–1291. doi:10.1039/C0LC00524J
Yuan J, Gaponik N, Eychmuller A (2012) Application of polymer quantum dot-enzyme hybrids in the biosensor development and test paper fabrication. Anal Chem 84:5047–5052. doi:10.1021/ac300714j
Yun G, Kim J, Kim J, Kim S (2010) Fabrication and testing of cellulose EAPap actuators for haptic application. Sens Actuators A Phys 164:68–73. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2010.09.005
Zheng J, Zhou Y, Li X, Ji Y, Lu T, Gu R (2003) Surface-enhanced raman scattering of 4-aminothiophenol in assemblies of nanosized particles and the macroscopic surface of silver. Langmuir 19:632–636. doi:10.1021/la011706p
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank the Academy of Finland for funding this study through its Centres of Excellence Programme (2014–2019) and under Project 132723612 HYBER. Authors also thank Joseph Campbell for XPS measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arcot, L.R., Uddin, K.M.A., Chen, X. et al. Paper-based plasmon-enhanced protein sensing by controlled nucleation of silver nanoparticles on cellulose. Cellulose 22, 4027–4034 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0783-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0783-z