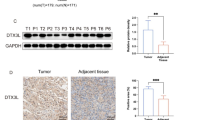
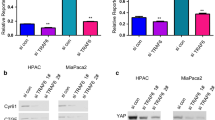
Abstract
The prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is poor despite diagnostic progress and new chemotherapeutic regimens. Constitutive activation of NF-κB is frequently observed in PDAC. In this study, we found that YEATS2, a scaffolding protein of ATAC complex, was highly expressed in human PDAC. Depletion of YEATS2 reduced the growth, survival, and tumorigenesis of PDAC cells. The binding of YEATS2 is crucial for maintaining TAK1 activation and NF-κB transcriptional activity. Of importance, our results reveal that YEATS2 promotes NF-κB transcriptional activity through modulating TAK1 abundance and directly interacting with NF-κB as a co-transcriptional factor.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary information files.
References
Ahmed N, Zeng M, Sinha I, Polin L, Wei WZ, Rathinam C, Flavell R, Massoumi R, Venuprasad K. The E3 ligase Itch and deubiquitinase Cyld act together to regulate Tak1 and inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:1176–83.
Buscail L, Bournet B, Cordelier P. Role of oncogenic KRAS in the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;17:153–68.
Chen J, Archer TK. Regulating SWI/SNF subunit levels via protein-protein interactions and proteasomal degradation: BAF155 and BAF170 limit expression of BAF57. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:9016–27.
Chen F, Castranova V, Shi X. New insights into the role of nuclear factor-kappaB in cell growth regulation. Am J Pathol. 2001;159:387–97.
Guttridge DC, Albanese C, Reuther JY, Pestell RG, Baldwin AS Jr. NF-kappaB controls cell growth and differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:5785–99.
Hanada M, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Komaki K, Ohnishi M, Katsura K, Kanamaru R, Matsumoto K, Tamura S. Regulation of the TAK1 signaling pathway by protein phosphatase 2C. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:5753–9.
Helmlinger D, Papai G, Devys D, Tora L. What do the structures of GCN5-containing complexes teach us about their function? Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021;1864:194614.
Hinz M, Krappmann D, Eichten A, Heder A, Scheidereit C, Strauss M. NF-kappaB function in growth control: regulation of cyclin D1 expression and G0/G1-to-S-phase transition. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:2690–8.
Ishikawa K, Makanae K, Iwasaki S, Ingolia NT, Moriya H. Post-translational dosage compensation buffers genetic perturbations to stoichiometry of protein complexes. PLoS Genet. 2017;13:e1006554.
Joyce D, Bouzahzah B, Fu M, Albanese C, D’amico M, Steer J, Klein JU, Lee RJ, Segall JE, Westwick JK, Der CJ, Pestell RG. Integration of Rac-dependent regulation of cyclin D1 transcription through a nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:25245–9.
Kajino T, Ren H, Iemura S, Natsume T, Stefansson B, Brautigan DL, Matsumoto K, Ninomiya-Tsuji J. Protein phosphatase 6 down-regulates TAK1 kinase activation in the IL-1 signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:39891–6.
Kanayama A, Seth RB, Sun L, Ea CK, Hong M, Shaito A, Chiu YH, Deng L, Chen ZJ. TAB2 and TAB3 activate the NF-kappaB pathway through binding to polyubiquitin chains. Mol Cell. 2004;15:535–48.
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR, Li ZW. NF-kappaB in cancer: from innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:301–10.
Keppler BR, Archer TK. Ubiquitin-dependent and ubiquitin-independent control of subunit stoichiometry in the SWI/SNF complex. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:35665–74.
Kishimoto K, Matsumoto K, Ninomiya-Tsuji J. TAK1 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase is activated by autophosphorylation within its activation loop. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:7359–64.
Klein BJ, Vann KR, Andrews FH, Wang WW, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Beloglazkina AA, Mi W, Li Y, Li H, Shi X, Kutateladze AG, Strahl BD, Liu WR, Kutateladze TG. Structural insights into the π-π-π stacking mechanism and DNA-binding activity of the YEATS domain. Nat Commun. 2018;9:4574.
Lee TH, Shank J, Cusson N, Kelliher MA. The kinase activity of Rip1 is not required for tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced IkappaB kinase or p38 MAP kinase activation or for the ubiquitination of Rip1 by Traf2. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:33185–91.
Melisi D, Xia Q, Paradiso G, Ling J, Moccia T, Carbone C, Budillon A, Abbruzzese JL, Chiao PJ. Modulation of pancreatic cancer chemoresistance by inhibition of TAK1. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103:1190–204.
Mettouchi A, Cabon F, Montreau N, Dejong V, Vernier P, Gherzi R, Mercier G, Binétruy B. The c-Jun-induced transformation process involves complex regulation of tenascin-C expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17:3202–9.
Mi W, Guan H, Lyu J, Zhao D, Xi Y, Jiang S, Andrews FH, Wang X, Gagea M, Wen H, Tora L, Dent SYR, Kutateladze TG, Li W, Li H, Shi X. YEATS2 links histone acetylation to tumorigenesis of non-small cell lung cancer. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1088.
Mihaly SR, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Morioka S. TAK1 control of cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21:1667–76.
Mukhopadhyay H, Lee NY. Multifaceted roles of TAK1 signaling in cancer. Oncogene. 2020;39:1402–13.
Neoptolemos JP, Kleeff J, Michl P, Costello E, Greenhalf W, Palmer DH. Therapeutic developments in pancreatic cancer: current and future perspectives. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:333–48.
Prabhu L, Mundade R, Korc M, Loehrer PJ, Lu T. Critical role of NF-kappaB in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 2014;5:10969–75.
Sakurai H, Miyoshi H, Mizukami J, Sugita T. Phosphorylation-dependent activation of TAK1 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase by TAB1. FEBS Lett. 2000;474:141–5.
Scholz R, Sidler CL, Thali RF, Winssinger N, Cheung PC, Neumann D. Autoactivation of transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 is a sequential bimolecular process. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:25753–66.
Singhirunnusorn P, Suzuki S, Kawasaki N, Saiki I, Sakurai H. Critical roles of threonine 187 phosphorylation in cellular stress-induced rapid and transient activation of transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) in a signaling complex containing TAK1-binding protein TAB1 and TAB2. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:7359–68.
Takaesu G, Surabhi RM, Park KJ, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Matsumoto K, Gaynor RB. TAK1 is critical for IkappaB kinase-mediated activation of the NF-kappaB pathway. J Mol Biol. 2003;326:105–15.
Taniguchi K, Karin M. NF-kappaB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: coming of age. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18:309–24.
Tripathi V, Shin JH, Stuelten CH, Zhang YE. TGF-β-induced alternative splicing of TAK1 promotes EMT and drug resistance. 2019;38:3185-3200.
Wang YL, Faiola F, Xu M, Pan S, Martinez E. Human ATAC Is a GCN5/PCAF-containing acetylase complex with a novel NC2-like histone fold module that interacts with the TATA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:33808–15.
Xia ZP, Sun L, Chen X, Pineda G, Jiang X, Adhikari A, Zeng W, Chen ZJ. Direct activation of protein kinases by unanchored polyubiquitin chains. Nature. 2009;461:114–9.
Xiao Y, Jin J, Chang M, Nakaya M, Hu H, Zou Q, Zhou X, Brittain GC, Cheng X, Sun SC. TPL2 mediates autoimmune inflammation through activation of the TAK1 axis of IL-17 signaling. J Exp Med. 2014;211:1689–702.
Yu Y, Ge N, Xie M, Sun W, Burlingame S, Pass AK, Nuchtern JG, Zhang D, Fu S, Schneider MD, Fan J, Yang J. Phosphorylation of Thr-178 and Thr-184 in the TAK1 T-loop is required for interleukin (IL)-1-mediated optimal NFkappaB and AP-1 activation as well as IL-6 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:24497–505.
Zeng Z, Lei S, He Z, Chen T, Jiang J. YEATS2 is a target of HIF1alpha and promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236:2087–98.
Zhao D, Guan H, Zhao S, Mi W, Wen H, Li Y, Zhao Y, Allis CD, Shi X, Li H. YEATS2 is a selective histone crotonylation reader. Cell Res. 2016;26:629–32.
Zhao D, Li Y, Xiong X, Chen Z, Li H. YEATS domain-a histone acylation reader in health and disease. J Mol Biol. 2017;429:1994–2002.
Zheng H, Li Q, Chen R, Zhang J, Ran Y, He X, Li S, Shu HB. The dual-specificity phosphatase DUSP14 negatively regulates tumor necrosis factor- and interleukin-1-induced nuclear factor-κB activation by dephosphorylating the protein kinase TAK1. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:819–25.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the pzlink-yeats2 plasmid provided by Haitao Li at Tsinghua University.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (81502304, 81903873), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LQ19H160002, LQ18H160001), Medical and Health Technology Projects of Zhejiang Province (2017KY696, 2019PY089), Chinese Medicine Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (2021ZB328), Quzhou Technology Projects, China (2018K20).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Participated in research design: F. Zhang
Conducted experiments: H. Sheng, F. Zheng, H.F. Chen, C.Y. Xu, T. Lan, S.W. Wang, Y.Y. Weng
Performed data analysis: F. Zhang, H. Sheng
Wrote or contributed to the writing of the manuscript: F. Zhang, H. Sheng, T. Lan
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Animal Experiments of Quzhou People’s Hospital, China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• YEATS2 promotes pancreatic cancer progression.
• YEATS2 regulates NF-κB activity in pancreatic cancer cells.
• YEATS2 modulates TAK1 stability.
• YEATS2 is a transcriptional cofactor for NF-κB-mediated gene expression.
Supplementary Information

Supplemental Fig. 1
Knockdown efficiency of tested shRNA. The expression of shRNAs was delivered by lentiviruses. Cell lysates were collected 2 days after transduction and subjected to western blotting using YEATS2 specific antibody. (PNG 5361 kb)

Supplemental Fig. 2
Overexpression of YEATS2 enhances cell proliferation and colony formation in vitro. Overexpression of YEATS2 in MIA Paca-2 and PANC-1 PDCA cells was mediated by lentiviruses. Cell proliferation was measured by cell counting. Colonies was stained by crystal violet solution. At least 5 fields for each treatment were calculated in size and number. (PNG 13738 kb)

Supplemental Fig. 3
YEATS2 knockdown affects NF-κB pathway associated gene expression. RNA-seq was performed in MIA cells transduced with scramble (ctrl) or shRNA targeting YEATS2 (shY2). The altered mRNA expression of NF-κB pathway associated genes was shown as heatmap. (PNG 6761 kb)

Supplemental Fig. 4
The correlation of the expression of NF-κB target genes with YEATS2 in human PDAC samples. Eleven NF-κB target genes were analyzed using TCGA database. Among them, the expression of eight genes was significantly correlated with YEATS2 (p<0.01). (PNG 2949 kb)

Supplemental Fig. 5
YEATS2 interacts with p65 in vivo in multiple sites. FLAG-tagged YEATS2 variants with different section deletion were expressed in MIA PaCa2 cells. (A) The schematic diagram of the YEATS2 variants. Flag tags were fused in N-terminal of these variants. (B) Co-IP assay using the beads conjugated with antibody against Flag tag. (PNG 31517 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, H., Zheng, F., Lan, T. et al. YEATS2 regulates the activation of TAK1/NF-κB pathway and is critical for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell survival. Cell Biol Toxicol 39, 1–16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09671-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09671-4