Abstract
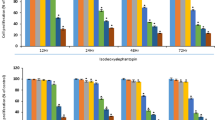
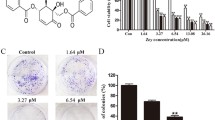
Deoxyelephantopin, a sesquiterpene lactone extracted and purified from Elephantopus scaber, has been shown to exhibit antitumor and hepatoprotective activities. The purpose of this study was to investigate the antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing properties of deoxyelephantopin in SiHa cells and to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms. Deoxyelephantopin inhibited growth of SiHa cells and triggered apoptosis. Apoptosis was accompanied by sequential activation of caspases (8, 9, 3, and 7) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Downregulation of antiapoptotic proteins (Bcl2 and Bcl-xL) and upregulation of apoptotic protein (bax) were also detected. Our results demonstrated that deoxyelephantopin-induced G2/M phase arrest was associated with a marked increase in the levels of p53 and p21 and a decrease in phospho-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (pSTAT3-Tyr705), cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (cdc2), and cyclin B1. The expression of p-Akt and p-mTOR was downregulated. p-ERK was inhibited while p-JNK and p-p38 was activated on deoxyelephantopin treatment. Our findings provided the first evidence that STAT3/p53/p21 signaling, MAPK pathway, PI3k/Akt/mTOR pathway, caspase cascades, and ROS play critical roles in deoxyelephantopin-induced G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis of SiHa cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan LA, Morrice N, Brady S, Magee G, Pathak S, Clarke PR. Inhibition of caspase-9 through phosphorylation at Thr 125 by ERK MAPK. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:647–54.
Balachandran P, Govindarajan R. Cancer-an ayurvedic perspective. Pharmacol Res. 2005;51:19–30.
Bertelsen BI, Steine SJ, Sandvei R, Molven A, Laerum O. Molecular analysis of the PI3K-AKT pathway in uterine cervical neoplasia: frequent PIK3CA amplification and AKT phosphorylation. Int J Cancer. 2006;118(8):1877–83.
Bunz F, Dutriaux A, Lengauer C, Waldman T, Zhou S. Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage. Science. 1998;282:1497–501.
Catlett-Falcone R, Dalton WS, Jove R. STAT proteins as novel targets for cancer therapy. Signal transducer an activator of transcription. Curr Opin Oncol. 1999;11:490–6.
Chadwick M, Trewin H, Gawthrop F, Wagstaff C. Sesquiterpenoids lactones: benefits to plants and people. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:12780–805.
Chen CL. Stat3 activation in human endometrial and cervical cancers. Br J Cancer. 2007;96:591–9.
Circu ML, Aw TY. Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Rad Biol Med. 2010;48:749–62.
Courtney KD, Corcoran RB, Engelman JA. The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1075–83.
Daisy P, Rayan NA, Rajathi D. Hypoglycemic and other related effects of Elephantopus scaber extracts on alloxan induced diabetic rats. J Biol Sci. 2007;7:433–7.
Davis Jr W, Ronai Z, Tew KD. Cellular thiols and reactive oxygen species in drug-induced apoptosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;296:1–6.
Deacon K, Mistry P, Chernoff J. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates cell death and p21-activated kinase mediates cell survival during chemotherapeutic drug-induced mitotic arrest. Mol Biol Cell. 2003;14:2071–87.
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3279–90.
Frenkel K, Gleichauf C. Hydrogen peroxide formation by cells treated with a tumor promoter. Free Radic Res Commun. 1991;2:783–94.
Geetha BS, Nair MS, Latha PG, Remani P. Sesquiterpene lactones isolated from Elephantopus scaber L. inhibits human lymphocyte proliferation and the growth of tumour cell lines and induces apoptosis in vitro. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012; 1–6
Germain D, Frank DA. Targeting the cytoplasmic and nuclear functions of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:5665–9.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70.
Hsu YL, Kuo PL, Tzeng WS, Lin CC. Chalcone inhibits the proliferation of human breast cancer cell by blocking cell cycle progression and inducing apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol. 2006;44(5):704–13.
Huang CC, Lo CP, Chiu CY, Shayur LF. Deoxyelephantopin, a novel multifunctional agent, suppresses mammary tumour growth and lung metastasis and doubles survival time in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;159:856–71.
Innocente SA, Abrahamson JL, Cogswell JP, Lee JM. p53 regulates a G2 checkpoint through cyclin B1. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1999;96:2147–52.
Janicke RU, Ng P, Sprengart ML, Porter AG. Caspase-3 is required for alpha-fodrin cleavage but dispensable for cleavage of other death substrates in apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:15540–5.
Kabeer FA, Sreedevi GB, Nair MS, Rajalekshmi DS, Gopalakrishnan LP, Kunjuraman S, et al. Antineoplastic effects of deoxyelephantopin, a sesquiterpene lactone from Elephantopus scaber, on lung adenocarcinoma (A549) cells. J Integr Med. 2013;11:269–77.
Kauffmann-Zeh A, Rodriguez-Viciana P, Ulrich E. Suppression of c-Myc-induced apoptosis by Ras signalling through PI(3)K and PKB. Nature. 1997;385:544–8.
Kawabe T. G2 checkpoint abrogators as anticancer drugs. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004;3:513–9.
Kim MJ, Choi SM, Park IC, Hwang SG, Kim C, Choi YH, et al. Opposing roles of c-jun NH2-terminal kinase andp38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in the cellular response to ionizing radiation in human cervical cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2008;6:1718–31.
Lin J. p53 regulates Stat3 phosphorylation and DNA binding activity in human prostate cancer cells expressing constitutively active Stat3. Oncogene. 2002;21:3082–8.
Mashima T, Tsuruo T. Defects of the apoptotic pathway as therapeutic target against cancer. Drug Resist Updat. 2005;8:339–43.
Mbazima VG, Mokgotho MP, February F, Rees DJG, Mampuru LJM. Alteration of Bax-to-Bcl-2 ratio modulates the anticancer activity of methanolic extract of Commelina benghalensis (Commelinaceae) in Jurkat T cells. Afr J Biotechnol. 2008;7:3569–76.
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 1993;74:609e19.
Orrenius S. Mitochondrial regulation of apoptotic cell death. Toxicol Lett. 2004;149:19–23.
Pathak S, Bhatla N, Singh N. Cervical cancer pathogenesis is associated with one carbon metabolism. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;369:1–7.
Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kacmaz K, Linn S. Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the DNA damage checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:39–85.
Scheffner M. The state of the p53 and retinoblastoma genes in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88:5523–7.
Sebolt-Leopold JS, Herrera R. Targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade to treat cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:937–47.
Seger R, Krebs EG. The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J. 1995;9:726–35.
Singh SV, Zeng Y, Xiao D, Vogel VG, Nelson JB, Dhir R, et al. Caspase-dependent apoptosis induction by guggulsterone, a constituent of Ayurvedic medicinal plant Commiphora mukul, in PC-3 human prostate cancer cells is mediated by Bax and Bak. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4:1747–54.
Su M, Chung HY, Li Y. Deoxyelephantopin from Elephantopus scaber L. induces cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in the human nasopharyngeal cancer CNE cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;41:342–7.
Xiao D, Zeng Y, Prakash L, Badmaev V, Majeed M, Singh SV. Reactive oxygen species dependant apoptosis by gugalipid extract of ayurvedic medicine plant Commiphora mukul in human prostate cancer cells is regulated by c-Jun N terminal kinase. Mol Pharmacol. 2011;79:499–507.
Xu G, Liang Q, Gong Z, Yu W, He S, Xi L. Antitumor activities of the four sesquiterpene lactones from Elephantopus scaber L. Exp Oncol. 2006;28:106–9.
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:798–809.
Zamzami N, Kroemer G. Apoptosis: mitochondrial membrane permeabilization—the whole story. Curr Biol. 2003;13:R71–3.
Zur Hausen H. Papillomavirus and cancer: from basic studies to clinical application. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:342–50.
Acknowledgments
The first author would like to express gratitude to University Grant Commission (UGC) for financial support. This research work was supported by Indian Council for Medical Research, New Delhi, India (grant no. 59/47/2011/BMS/TRM).'
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farha, A.K., Dhanya, S.R., Mangalam, S.N. et al. Deoxyelephantopin impairs growth of cervical carcinoma SiHa cells and induces apoptosis by targeting multiple molecular signaling pathways. Cell Biol Toxicol 30, 331–343 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-014-9288-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-014-9288-z