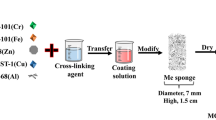
Abstract
The heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation overcome the shortage of traditional Fenton system, which got the high catalytic efficiency, good stability, wide pH working range, and so on. However, it is still challenging to develop highly efficient and recyclable solid catalysts in wastewater treatment. Herein, we employed melamine sponge (MS) as a base material to fabricate heterogeneous Fe/Cu-tannic acid (TA) coated MS (MS-Fe/Cu-TA) through the dip-coating method. The porous 3D structure of MS can enhance the catalyst loading, and expose more active catalytic sites to absorb dyes from solution. The loaded Fe/Cu weight ratio, pH value, H2O2 dosage, and initial MB concentration on the catalytic activity were optimized to get highest methylene blue (MB) degradation efficiency. The MS survived five times of cyclic MB degradation, and degradation efficiency for other dyes (methyl orange, rhodamine B, malachite green) kept above 65%. This work brings potential insights for development of enhanced heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation for wastewater treatment.
Graphical Abstract
Herein, we employed melamine sponge (MS) as a base material to fabricate heterogeneous Fe/Cu-tannic acid (TA) coated MS (MS-Fe/Cu-TA) through the dip-coating method. The porous 3D structure of MS can enhance the catalyst loading, and expose more active catalytic sites to absorb dyes from solution. This work brings potential insights for development of enhanced heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation for wastewater treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fenton HJH (1894) Oxidation of tartaric acid in presence of iron. J Chem Soc Trans 65:899–910
Qian X, Zhang J, Gu Z, Chen Y (2019) Nanocatalysts-augmented Fenton-like chemical reaction for nanocatalytic tumor therapy. Biomaterials 211:1
Hao Y, Dong Z, Chen M, Chao Y, Liu Z, Feng L (2018) Synthesis of hollow biomineralized CaCO3-polydopamine nanoparticles for multimodal imaging-guided cancer photodynamic therapy with reduced skin photosensitivity. J Am Chem Soc 140:77–2384
Herney-Ramirez J, Vicente MA, Madeira LM (2010) Heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like oxidation with pillared clay-based catalysts for wastewater treatment: a review. Appl Catal B-Environ 98:10–26
Kuznetsova EV, Savinov EN, Vostrikova LA, Parmon VN (2004) Heterogeneous catalysis in the Fenton-like-type system FeZSM-5/H2O2. Appl Catal B-Environ 51:165–170
Shi X, Tian A, You J, Yang H, Wang Y, Xue X (2018) Degradation of organic dyes by a new heterogeneous Fenton-like reagent-Fe2GeS4 nanoparticle. J Hazard Mater 353:182–189
Meyerstein D (2021) Re-examining Fenton and Fenton-like reactions. Nat Rev Chem 5:595–597
Wang N, Zheng T, Zhang G, Wang P (2016) A review on Fenton-like processes for organic wastewater treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 4(1):762–787
Priyadarshini M, Das I, Ghangrekar M, Blaney L (2022) Advanced oxidation processes: performance, advantages, and scale-up of emerging technologies. J Environ 316:115295
Chao Y (2020) Near-infrared light and glucose dual-responsive cascading hydroxyl radical generation for in situ gelation and effective breast cancer treatment. Biomaterials 228:119–568
Tang Z, Zhao P, Wang H, Liu Y, Bu W (2021) Biomedicine meets Fenton-like chemistry. Chem Rev 121:1981–2019
Huang X, Zhu N, Mao F, Ding Y, Zhang S, Liu H, Li F, Wu P, Dang Z, Ke Y (2020) Enhanced heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like catalytic degradation of tetracycline over yCeO2/Fh composites: performance, degradation pathways, Fe2+ regeneration and mechanism. Chem Eng J 392:123636
Bao W, Liu X, Lv Y, Lu GH, Li F, Zhang F et al (2019) Nanolongan with multiple on-demand conversions for ferroptosis-apoptosis combined anticancer therapy. ACS Nano 13:260–273
LiJ PAN, Dai R, Wang Z, David WT (2020) Recent advances in Cu-Fenton-like systems for the treatment of industrial wastewaters: role of Cu complexes and Cu composites. J Hazard Mater 392:122261
Gawande MB, Goswami A, Felpin FX, Asefa T, Huang X, Silva R et al (2016) Cu and Cu-based nanoparticles: synthesis and applications in catalysis. Chem Rev 116:3722–3811
Koo S, Park OK, Kim J, Han SI, Yoo TY et al (2022) Enhanced chemodynamic therapy by Cu−Fe peroxide nanoparticles: tumor microenvironment-mediated synergistic Fenton-like reaction. ACS Nano 16:2535–2545
Lin LS, Huang T, Song J, Ou XY, Wang Z et al (2019) Synthesis of copper peroxide nanodots for H2O2 self-supplying chemodynamic therapy. J Am Chem Soc 141:9937–9945
Ma B, Wang S, Liu F, Zhang S, Duan J et al (2019) Self-assembled copper-amino acid nanoparticles for in situ glutathione “AND” H2O2 sequentially triggered chemodynamic therapy. J Am Chem Soc 141:849–857
Zhang X, Zhang Q, Su H, Xu Y, Li L (2023) Nanoparticle-decorated and poly (dimethyl siloxane)-modified superhydrophobic melamine sponge for efficient oil/water separation. Mater Chem Phys 304:127909
Dong Z, Feng W, Huang C, Lin H, Jia C, Ren C (2023) Superhydrophobic melamine sponges with high performance in oil/organic solvent sorption. J Environ Chem Eng 11:110614
Lei Z, Deng Y, Wang C (2018) Multiphase surface growth of hydrophobic ZIF-8 on melamine sponge for excellent oil/water separation and effective catalysis in a knoevenagel reaction. J Mater Chem A 6:3258–3263
Feng Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhang XF, Yao J (2018) In-situ gelation of sodium alginate supported on melamine sponge for efficient removal of copper ions. J Colloid Interface Sci 512:7–13
Li B, Xu HY, Liu YL, Liu Y, Xu Y, Zhang SQ (2023) Unveiling the structure–activity relationships of ofloxacin degradation by Co3O4-activated peroxymonosulfate: from microstructures to exposed facets. Chem Eng J 467:143396
Xu HY, Xu Y, Zhang SQ, Dai LY, Wang Y (2023) Fabricating a Fe3O4@HNTs nanoreactor to expedite heterogeneous Fenton-like reactions. Mater Lett 337:133985
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their gratitude to Ms. XiaoXia Xu from Shiyanjia Lab (www.shiyanjia.com) for providing invaluable assistance with the EPR analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by Innovation Team project of Ningde Normal University (2022T03, 2023T05), Natural Science Foundation of the Fujian Province (2022J05277), and Scientific Research Fund project of Ningde Normal University (2018Y01, 2022Y13, 2022Y18).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, Y., Chen, Y., Reheman, A. et al. Enhanced Heterogeneous Fenton-Like Degradation by Fe/Cu-TA Encapsulated Melamine Sponge. Catal Lett (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-024-04594-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-024-04594-1