Abstract
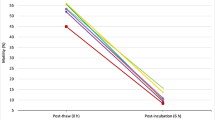
Oxidative damage of sperm by means of reactive oxygen species generated by the cellular components of semen is one of the main reason of declined motility and fertility of sperm during the freeze-thawing process. This study was conducted to determine the influence of vitamin C and vitamin E on rooster post-thawed sperm motility, viability and malondialdehyde (MDA) level. Semen samples from 10 sexually-mature Ross 308 breeder roosters were collected and pooled, divided into nine equal parts and diluted with modified Beltsville extender containing with no antioxidants (control), or containing 100 (C100), 200 (C200), 400 (C400), 800 (C800) µg/mL vitamin C, and 2 (E2), 5 (E5), 10 (E10) and 15 (E15) µg/mL vitamin E. After thawing, total and progressive sperm motility, sperm viability and semen MDA level were assessed. The results shown that C200 and E5 extenders resulted in higher total motility (p < 0.05) compared to other extenders, with exception of E10 extender. Progressive motility was higher in E5 extender (p < 0.05) compared to other extenders, with exception of C200 and E10 extenders. Also, C200 and E5 extenders resulted in higher viability of post-thawed spermatozoa (p < 0.05) compared to other extenders. Finally, the results showed that MDA level was lower in C100 and C200 extenders compared to other extenders (p < 0.05), with exception of E5 extender. In conclusion, the results of the present study demonstrate that C200 and E5 can improve the function of post-thawed rooster spermatozoa.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal A, Nallella KP, Allamaneni SS, Said TM (2004) Role of antioxidants in treatment of male infertility: an overview of the literature. Reprod Biomed Online 8:616–627
Akhlaghi A, Jafari Ahangari Y, Zhandi M, Peebles ED (2014) Reproductive performance, semen quality, and fatty acid profile of spermatozoa in senescent broiler breeder roosters as enhanced by the long-term feeding of dried apple pomace. Anim Reprod Sci 147:64–73
Amini MR, Kohram H, Zare Shahaneh A, Zhandi M, Sharideh H, Nabi MM (2015) The effects of different levels of catalase and superoxide dismutase in modified Beltsville extender on rooster post-thawed sperm quality. Cryobiology. doi:10.1016/j.cryobiol.2015.03.001
Asadpour R, Jafari R, Tayefi-Nasrabad H (2012) Influence of added vitamin C and vitamin E on frozen-thawed bovine sperm cryopreserved in citrate and tris-based extenders. Vet Res Forum 2:37–44
Bell M, Wang R, Hellstrom WJ, Sikka SC (1993) Effect of cryoprotective additives and cryopreservation protocol on sperm membrane lipid peroxidation and recovery of motile human sperm. J Androl 14:472–478
Branco CS, Garcez ME, Pasqualotto FF, Erdtman B, Salvador M (2010) Resveratrol and ascorbic acid prevent DNA damage induced by cryopreservation in human semen. Cryobiology 60:235–237
Breininger E, Beorlegui NB, O’Flaherty CM, Beconi MT (2005) Alpha-tocopherol improves biochemical and dynamic parameters in cryopreserved boar semen. Theriogenology 63:2126–2135
Burrows WH, Quinn JP (1937) The collection of spermatozoa from the domestic fowl and turkey. Poult Sci 16:19–24
Cerolini S, Kelso KA, Noble RC, Speake BK, Pizzi F, Cavalchini LG (1997) Relationship between spermatozoan lipid composition and fertility during aging of chickens. Biol Reprod 57:976–980
Donoghue AM, Donoghue DJ (1997) Effects of water- and lipid-soluble antioxidants on turkey sperm viability, membrane integrity, and motility during liquid storage. Poult Sci 76:1440–1445
Esterbauer H, Cheeseman KH (1990) Determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation products: malonaldehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal. Methods Enzymol 186:407–421
Foote RH, Brockett CC, Kaproth MT (2002) Motility and fertility of bull sperm in whole milk extender containing antioxidants. Anim Reprod Sci 71:13–23
Hu JH, Tian WQ, Zhao XL, Zan LS, Wang H, Li QW, Xin YP (2010) The cryoprotective effects of ascorbic acid supplementation on bovine semen quality. Anim Reprod Sci 121:72–77
Jenkins TG, Aston KI, Carrell DT (2011) Supplementation of cryomedium with ascorbic acid–2-glucoside (AA2G) improves human sperm post-thaw motility. Fertil Steril 95:2001–2004
Jeong YJ, Kim MK, Song HJ, Kang EJ, Ock SA, Kumar BM, Balasubramanian S, Rho GJ (2009) Effect of alpha-tocopherol supplementation during boar semen cryopreservation on sperm characteristics and expression of apoptosis related genes. Cryobiology 58:181–189
Lenzi A, Picardo M, Gandini L, Dondero F (1996) Lipids of the sperm plasma membrane: from polyunsaturated fatty acids considered as markers of sperm function to possible scavenger therapy. Hum Reprod Update 2:246–256
Li Z, Lin Q, Liu R, Xiao W, Liu W (2010) Protective effects of ascorbate and catalase on human spermatozoa during cryopreservation. J Androl 31:437–444
Luck MR, Jeyaseelan I, Scholes RA (1995) Ascorbic acid and fertility. Biol Reprod 52:262–266
Malo C, Gil L, Gonzalez N, Martinez F, Cano R, de Blas I, Espinosa E (2010) Anti-oxidant supplementation improves boar sperm characteristics and fertility after cryopreservation: comparison between cysteine and rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis). Cryobiology 61:142–147
Martinez-Paramo S, Diogo P, Dinis MT, Herraez MP, Sarasquete C, Cabrita E (2012) Incorporation of ascorbic acid and alpha-tocopherol to the extender media to enhance antioxidant system of cryopreserved sea bass sperm. Theriogenology 77:1129–1136
Michael AJ, Alexopoulos C, Pontiki EA, Hadjipavlou-Litina DJ, Saratsis P, Ververidis HN, Boscos CM (2008) Quality and reactive oxygen species of extended canine semen after vitamin C supplementation. Theriogenology 70:827–835
Partyka A, Łukaszewicz E, Niżański W (2012) Effect of cryopreservation on sperm parameters, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes activity in fowl semen. Theriogenology 77:1497–1504
Partyka A, Niżański W, Bajzert J, Łukaszewicz E, Ochota M (2013) The effect of cysteine and superoxide dismutase on the quality of post-thawed chicken sperm. Cryobiology 67:132–136
Peruma P, Chamuah JK, Rajkhowa C (2013) Effect of catalase on the liquid storage of mithun (Bos frontalis) semen. Asian Pac J Reprod 2:209–214
Sierens J, Hartley JA, Campbell MJ, Leathem AJ, Woodside JV (2001) Effect of phytoestrogen and antioxidant supplementation on oxidative DNA damage assessed using the comet assay. Mutat Res 485:169–176
Silva SV, Soares AT, Batista AM, Almeida FC, Nunes JF, Peixoto CA, Guerra MM (2013) Vitamin E (Trolox) addition to Tris-egg yolk extender preserves ram spermatozoon structure and kinematics after cryopreservation. Anim Reprod Sci 137:37–44
Song GJ, Norkus EP, Lewis V (2006) Relationship between seminal ascorbic acid and sperm DNA integrity in infertile men. Int J Androl 29:569–575
Surai P, Kostjuk I, Wishart G, Macpherson A, Speake B, Noble R, Ionov I, Kutz E (1998) Effect of vitamin E and selenium supplementation of cockerel diets on glutathione peroxidase activity and lipid peroxidation susceptibility in sperm, testes, and liver. Biol Trace Elem Res 64:119–132
Thuwanut P, Chatdarong K, Techakumphu M, Axner E (2008) The effect of antioxidants on motility, viability, acrosome integrity and DNA integrity of frozen-thawed epididymal cat spermatozoa. Theriogenology 70:233–240
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amini, M.R., Kohram, H., Zare Shahaneh, A. et al. The effects of different levels of vitamin E and vitamin C in modified Beltsville extender on rooster post-thawed sperm quality. Cell Tissue Bank 16, 587–592 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-015-9506-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-015-9506-9