Abstract
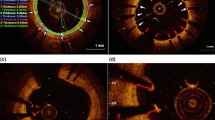
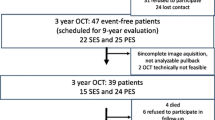
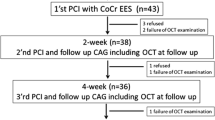
Long-term safety of second generation drug-eluting stents (DES) has not yet been evaluated. We sought to evaluate the very late phase (> 3 years) vascular response after second generation everolimus-eluting stent (EES) as compared with first generation sirolimus-eluting stent (SES) by using optical coherence tomography (OCT). We examined the vascular response in 39 patients with a total of 55 DESs [31 EESs (mean 54 months after stenting) and 24 first generation SES (mean 66 months after stenting)] by OCT. The frequency of lesions with any malapposed stent struts (19% vs. 46%, p = 0.035) and evagination (6% vs. 42%, p = 0.002) was significantly lower. Segments with malapposed stent struts were significantly shorter (0.4 ± 0.9 mm vs. 1.9 ± 3.5 mm, p = 0.024), maximal malapposition area and malapposition volume were significantly smaller (0.26 ± 0.38 mm2 vs. 0.95 ± 1.54 mm2, p = 0.019, and 0.78 ± 1.35 mm3 vs. 6.22 ± 15.76 mm3, p = 0.016, respectively) in EES. Compared with first generation SES, second generation EES showed more favourable vascular responses at the very late phase.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morice MC, Serruys PW, Sousa JE, Fajadet J, Ban Hayashi E, Perin M, Colombo A, Schuler G, Barragan P, Guagliumi G, RAVEL Study Group et al (2002) A randomized comparison of a sirolimus-eluting stent with a standard stent for coronary revascularization. N Engl J Med 346:1773–1780
Moses JW, Leon MB, Popma JJ, Fitzgerald PJ, Holmes DR, O'Shaughnessy C, Caputo RP, Kereiakes DJ, Williams DO, Teirstein PS, SIRIUS Investigators et al (2003) Sirolimus-eluting stents versus standard stents in patients with stenosis in a native coronary artery. N Engl J Med 349:1315–1323
Daemen J, Wenaweser P, Tsuchida K, Abrecht L, Vaina S, Morger C, Kukreja N, Jüni P, Sianos G, Hellige G et al (2007) Early and late coronary stent thrombosis of sirolimus-eluting and paclitaxel-eluting stents in routine clinical practice: data from a large two-institutional cohort study. Lancet 369:667–678
Kuriyama N, Kobayashi Y, Nakama T, Mine D, Nishihira K, Shimomura M, Nomura K, Ashikaga K, Matsuyama A, Shibata Y (2011) Late restenosis following sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 4:123–128
Nakazawa G, Finn AV, Joner M, Ladich E, Kutys R, Mont EK, Gold HK, Burke AP, Kolodgie FD, Virmani R (2008) Delayed arterial healing and increased late stent thrombosis at culprit sites after drug-eluting stent placement for acute myocardial infarction patients: an autopsy study. Circulation 118:1138–1145
Nakazawa G, Finn AV, Vorpahl M, Ladich ER, Kolodgie FD, Virmani R (2011) Coronary responses and differential mechanisms of late stent thrombosis attributed to first-generation sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents. J Am Coll Cardiol 57:390–398
Taniwaki M, Radu MD, Zaugg S, Amabile N, Garcia-Garcia HM, Yamaji K, Jørgensen E, Kelbæk H, Pilgrim T, Caussin C et al (2016) Mechanisms of very late drug-eluting stent thrombosis assessed by optical coherence tomography. Circulation 133:650–660
Guagliumi G, Sirbu V, Musumeci G, Gerber R, Biondi-Zoccai G, Ikejima H, Ladich E, Lortkipanidze N, Matiashvili A, Valsecchi O et al (2012) Examination of the in vivo mechanisms of late drug-eluting stent thrombosis: findings from optical coherence tomography and intravascular ultrasound imaging. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 5:12–20
Otsuka F, Byrne RA, Yahagi K, Mori H, Ladich E, Fowler DR, Kutys R, Xhepa E, Kastrati A, Virmani R et al (2015) Neoatherosclerosis: overview of histopathologic findings and implications for intravascular imaging assessment. Eur Heart J36:2147–2159
Park SJ, Kang SJ, Virmani R, Nakano M, Ueda Y (2012) In-stent neoatherosclerosis: a final common pathway of late stent failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 59:2051–2057
Ino Y, Kubo T, Kameyama T, Shimamura K, Terada K, Matsuo Y, Kitabata H, Shiono Y, Kashiwagi M, Kuroi A et al (2018) Clinical utility of combined optical coherence tomography and near-infrared spectroscopy for assessing the mechanism of very late stent thrombosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 11:772–775
Giglioli C, Formentini C, Romano SM, Cecchi E, Baldereschi GJ, Landi D, Chiostri M, Prati F, Marchionni N (2019) Vulnerable struts with CRE8, Biomatrix and Xience stents assessed with OCT and their correlation with clinical variables at 6-month follow-up: the CREBX-OCT study. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-019-01719-1
Sabate M, Cequier A, Iñiguez A, Serra A, Hernandez-Antolin R, Mainar V, Valgimigli M, Tespili M, den Heijer P, Bethencourt A et al (2012) Everolimus-eluting stent versus bare-metal stent in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (EXAMINATION): 1 year results of a randomized controlled trial. Lancet 380:1482–1490
Ino Y, Kubo T, Tanaka A, Liu Y, Tanimoto T, Kitabata H, Shiono Y, Shimamura K, Orii M, Komukai K et al (2015) Comparison of vascular response between everolimus-eluting stent and bare metal stent implantation in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction assessed by optical coherence tomography. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 16:513–520
Dangas GD, Serruys PW, Kereiakes DJ, Hermiller J, Rizvi A, Newman W, Sudhir K, Smith RS Jr, Cao S, Theodoropoulos K et al (2013) Meta-analysis of everolimus-eluting versus paclitaxel-eluting stents in coronary artery disease: final 3-year results of the SPIRIT clinical trials program (clinical evaluation of the Xience V everolimus-eluting coronary stent system in the treatment of patients with de novo native coronary artery lesions). JACC Cardiovasc Interv 6:914–922
Usui E, Yonetsu T, Kanaji Y, Hoshino M, Yamaguchi M, Hada M, Hamaya R, Kanno Y, Murai T, Lee T et al (2018) Prevalence of neoatherosclerosis in sirolimus-eluting stents in a very late phase after implantation. EuroIntervention. https://doi.org/10.4244/EIJ-D-18-00486
Ino Y, Kubo T, Matsuo Y, Yamaguchi T, Shiono Y, Shimamura K, Katayama Y, Nakamura T, Aoki H, Taruya A et al (2016) Optical coherence tomography predictors for edge restenosis after everolimus-eluting stent implantation. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 9:e004231
Uchimura Y, Itoh T, Oda H, Taguchi Y, Sasaki W, Kaneko K, Sakamoto T, Goto I, Sakuma M, Ishida M et al (2019) Cut-off value of mal-apposition volume and depth for resolution at early phase of acute incomplete stent apposition after CoCr-EES implantation. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 35:1979–1987
Galløe AM, Kelbæk H, Thuesen L, Hansen HS, Ravkilde J, Hansen PR, Christiansen EH, Abildgaard U, Stephansen G, Lassen JF, SORT OUT II Investigators et al (2017) 10 year clinical outcome after randomization to treatment by sirolimus- or paclitaxel-eluting coronary stents. J Am Coll Cardiol 69:616–624
Takano M, Yamamoto M, Mizuno M, Murakami D, Inami T, Kimata N, Murai K, Kobayashi N, Okamatsu K, Ohba T (2010) Late vascular responses from 2 to 4 years after implantation of sirolimus-eluting stents: serial observations by intracoronary optical coherence tomography. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 3:476–483
Kubo T, Akasaka T, Kozuma K, Kimura K, Kawamura M, Sumiyoshi T, Ino Y, Morino Y, Tanabe K, Kadota K, RESET Investigators et al (2015) Comparison of neointimal coverage between everolimus-eluting stents and sirolimus-eluting stents: an optical coherence tomography substudy of the RESET (randomized evaluation of sirolimus-eluting versus everolimus-eluting stent trial). EuroIntervention 11:564–571
Katayama Y, Kubo T, Akasaka T, Ino Y, Kimura K, Okura H, Shinke T, Igarashi K, Kadota K, Kozuma K, NEXT investigators et al (2017) Two-year vascular responses to drug-eluting stents with biodegradable polymer versus durable polymer: an optical coherence tomography sub-study of the NEXT. J Cardiol 70:530–536
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Kubo has received lecture fees from Abbott Vascular and Terumo. Dr. Akasaka has received lecture fees from Abbott Vascular and Terumo, and research grants from Abbott Vascular and Terumo. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalifa, A.K.M., Ino, Y., Kubo, T. et al. Very late-phase vascular response after everolimus-eluting stent implantation assessed by optical coherence tomography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 36, 1627–1635 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-020-01877-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-020-01877-7