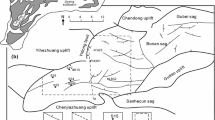
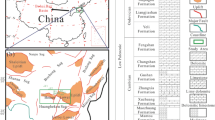
Medium-coarse-crystalline dolomite is a major variant of dolomite, and its structural heterogeneity inside and outside the crystals makes it an ideal vehicle for studies of dolomite genesis, fluid evolution and elemental migration. In this paper, the medium-coarse crystalline dolomite from the fifth section of the Majiagou Formation of the Lower Ordos Basin was systematically studied by petrographic, cathodoluminescence and related geochemical methods. The rock is developed in the context of mud powder crystal dolomite and granular dolomite, possessing significant ring band structure, fluorite and quartz intergrowth. Compared with other dolomites, it is characterized by Fe and Mn enrichment and low Na and Sr contents, as well as a negative δEu anomaly and a strong negative δ18 O offset. Combined with the evolutionary history of diagenesis, it is believed that the medium-coarse-crystal dolomite is the end product of a series of diagenetic effects such as early dolomitization-atmospheric freshwater leaching-secondary burial recrystallization-deep burial dissolution. Electron microprobe analysis reveals the structural and compositional heterogeneity inside and outside the crystals. The formation of mediumcoarse- crystalline dolomite is associated with an increase in Fe-Mn content, a rise in the Mn/Sr ratio, a decrease in Sr, and a first rise and then a fall in Na concentration. This study provides a valuable reference for further research on the genesis of the medium-coarse crystalline dolomite.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Warren, “Dolomite: occurrence, evolution and economically important associations,” Earth-Sci. Rev., 52(1-3), 1-81(2000).
D. F. Sibley, “Unstable to stable transformations during dolomitization,” J. Geol., 98(5), 739-748(1990).
S. E. Kaczmarek and D. F. Sibley, “On the evolution of dolomite stoichiometry and cation order during high-temperature synthesis experiments: an alternative model for the geochemical evolution of natural dolomites,” Sediment. Geol., 240(1-2), 30-40(2011).
S. E. Kaczmarek and D. F. Sibley, “Direct physical evidence of dolomite recrystallization,” Sedimentol., 61(6), 1862-1882(2014).
P. Mirti, M. C. Gennaro and C. Casalino, “Intramolecular exchange processes in cyclohexane-diaminetetraacetate complexes investigated by nuclear magnetic resonance technique,” Inorg. Chim. Acta, 53, L257-L259(1981).
P. W. Choquette and E. E. Hiatt, “Shallow-burial dolomite cement: a major component of many ancient sucrosic dolomites,” Sedimentol., 55(2), 423-460(2008).
X. Wang, Z. Jin, W. Hu, J. Zhang and Y. Qian, “Research on the ree partition characteristics and genesis of the lower Paleozoic dolomite micro-regions in the Tarim Basin,” Sci. China: Earth Sci., (06) , 721(2009).
B. J. Olanipekun and K. Azmy, “In situ characterization of dolomite crystals: evaluation of dolomitization process and its effect on zoning.” Sedimentol., 64(6), 1708-1730(2017).
J. Hu and Y. Zhao, “Dolomite Research Status and Development Trend Analysis. Urban Construction Theory Research,” Electron. Ed., 000(014), 1-5(2012).
L. B. Smith and G. R. Davies, “Structurally controlled hydrothermal alteration of carbonate reservoirs: introduction,” AAPG Bull., 90(11), 1635-1640(2006).
L. A. Melim, J. L. Masaferro, H. L. Vacher and T. M. Quinn, “Geology of the Bahamas: subsurface geology of the Bahamas banks,” Geology and Hydrogeology of Carbonate Islands. Elsevier, Amsterdam. dev. Sedimentol., 54, 161-182(1997).
J. A. Luczaj, “Evidence against the Dorag (mixing-zone) model for dolomitization along the Wisconsin arch-A case for hydrothermal diagenesis,” AAPG Bull., 90(11), 1719-1738(2006).
J. Zhao, H. Chen, J. Zhang and X. Liu, “Research on the genetic mechanism of dolomite in the 5th member of Ma in the central Ordos Basin,” Acta Petrolei Sin., 26(5), 38-41,47(2005).
Z. Su, H. Chen, F. Xu, et al. “Geochemical characteristics and dolomitization mechanism analysis of dolomites in Majiagou Formation, Ordos Basin,” Acta Petrolei Sin., 27(8), 2230-2238(2011).
F. Li, L. Du, J. Zhao and Y. Li, “Origin of dolomite in the fifth member of the Majiagou Formation, Sudong area, Ordos Basin,” Acta Petrolei Sin., 37(003), 328 -338(2016).
X. Gao, D. Zhang, Y. Shi, et al. “Structural characteristics and genesis of dolomite in the 5th sub-member of Ordovician in Ordos Basin,” J.Chengdu Univ.Technol., 045(005), 575-584(2018).
S. Huang, “The relationship between cathodoluminescence of marine carbonate minerals and diagenetic alteration,” Sediment. Tethyan Geol., 04:9-15(1990).
G. Shi, J. Tian, Y. Wu, et al., “Lower Paleozoic carbonate diagenesis and its influence on reservoirs in North China,” Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf., (02) , 10-15(2010).
J. L. Banner, G. N. Hanson and W. J. Meyers, “Rare earth element and Nd isotopic variations in regionally extensive dolomites from the Burlington-Keokuk Formation (Mississippian); implications for REE mobility during carbonate diagenesis,” J. Sediment. Res., 58(3), 415-432(1988).
K. Tachikawa, C. Jeandel, A. Vangriesheim et al., “Rare Earth elements and Nd isotopic composition distribution in suspended particles of the Tropical Atlantic Ocean (EUMELI site),” Deep-Sea Res., Part I, 46, 733-755(1999).
W. Hu, Q. Chen, X. Wang et al., “Rare earth element discrimination model of different fluids in the formation and evolution of dolomite reservoirs,” Pet. Nat. Gas Geol., ( 06), 810-818(2010).
D. Aubert, P. Stille, A. Probst et al., “Characterization and migration of atmospheric REE in soils and surface waters,” Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 66(19), 3339-3350(2002).
M. Huang, J. Liu, X. Shi et al., “The distribution characteristics of rare earth elements in the Pacific surface sediments and their resource significance,” J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.), (S1), 726(2015).
Z. Hu, R. Zheng, H. Wen et al., “Origin of dolomites from the Carboniferous Huanglong Formation in the Linshui-Yubei area of eastern Sichuan,” Acta Pet. Sinica, 24(006), 1369- 1378. 1378(2008).
B. N. Popp, T. F. Anderson and P. A. Sandberg, “Brachiopods as indicators of original isotopic compositions in some Paleozoic limestones,” Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 97(10), 1262-1269(1986).
Y. Wan, J. Wang, X. Fu et al., “The origin of fluid isotope geochemical tracing of dolomite reservoirs in the Buqu Formation of the Middle Jurassic in the South Depression of Qiangtang,” Pet. Nat. Gas Geol., v.41(01), 193-204(2020).
F. Li, L. Du, J. Zhao et al., “Origin of dolomite in sub-member 5, member 5, Majiagou Formation, Sudong area, Ordos Basin,” Acta Pet. Sinica, (03), 328-338 (2016).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China general project “ Spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of Neogene red clay detrital zircons in the Loess Plateau and their significance in indicating provenance areas” (41372036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 1, pp. 135–141, January–February, 2024
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, L., Jiaxuan, S., Yuwei, D. et al. Characterization of the Coarse-Crystalline Dolomite. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 60, 178–189 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-024-01669-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-024-01669-y