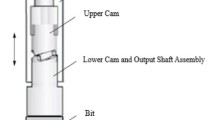
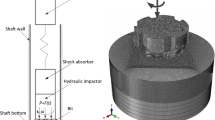
Friction between the drill string and the well wall is one of the key factors restricting the rate of penetration (ROP) in the process of sliding drilling in a horizontal well. The problem is effectively solved by applying the vibrating drag-reduction technology. In this paper, the authors propose a new type of mechanical rotary percussion tool driven by the positive displacement motor (PDM) and simulate the drag reduction effect of the tool in a horizontal well. The results show that the drag reduction effect depends on how the weight on the bit (WOB) is transmitted to the bit. When the excitation frequency is high, it causes severe fluctuation of the WOB. To maximize the overall WOB, the excitation frequency needs to be optimized. The WOB fluctuation contains not only the excitation frequency but also the double-excitation frequency and triple-excitation frequency. The research results can provide theoretical guidance for the application of the rotary percussion tool in horizontal wells.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. R. Newman, T. G. Burnett, J. C. Pursell, and O. Gouasmia, “Modeling the effect of a downhole vibrator,” SPE/ICoTA Coiled Tubing Well Intervention Conference and Exhibition, Woodlands, USA, 2009.
R. Gee, C. Hanley, R. Hussain, L. Canuel, and J. Martinez, “Axial oscillation tools vs. lateral vibration tools for friction reduction - what’s the best way to shake the pipe,” SPE/IADC Drilling Conference and Exhibition, London, UK, 2015.
P. J. Chen, D. L. Gao, Z. H. Wang, and W. J. Huang, “Study on aggressively working casing string in extended-reach well,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 157, 604-616 (2017).
Y. Z. Li, T. Chen, C. Jiang, and J. Du, “Key technologies of directional drilling in the Moxi-Gaoshiti area of the Sichuan Basin,” Pet. Drill. Tech., 49, 26-31 (2021).
L. R. Kong, Y. Wang, J. Zou, Z. Q. Wang, B. L. Liu, and B. R. Xia, “Development status and prospect of hydro-oscillation drag reduction drilling technology,” Oil Drill. Prod. Technol., 41, 23-30 (2019).
K. I. Sola and B. Lund, “New downhole tool for coiled tubing extended reach,” SPE/ICoTA Coiled Tubing Roundtable, Houston, Texas, USA (2000).
H. Zhang, Z. H. Wu, and W. J. Cai, “Development and field testing of hydraulic oscillator,” Chin. Pet. Machin., 43,12-14 (2015).
H. Z. Zhang, Z. C. Guan, Y. W Liu, and Y. L. Dou, “Development of drill string excitation drag reduction tool based on rotary excitation,” Chin. Pet. Machin., 43, 9-12 (2015).
J. C. Wang, C. M. Teng, H. P Zhang, R. L. Zhang, and L. C. Xuan, “Development and experiment of rotary percussion positive displacement motor,” Drill. Prod. Technol., 43, 68-71 (2020).
J. C. Wang, H. P Zhang, R. L. Zhang, and L. C. Xuan, “Field testing of rotary-percussive PDM in Linpan Oilfield,” Explor. Eng. (Rock Soil Drill. Tunnel.), 46, 44-49 (2019).
X. H Zhang, Z. G. Dong, X. Zhang, R. F. Wang, and W. K. Liu, “Gap element method for frictional resistance analysis of whole drill string in prospecting horizontal well,” ACTA Pet. Sin., 23, 105-109 (2002).
Y. H. Qin, S. L. Fu, and D. L. Gao, “A new model for analyzing torque and drag in extended reach wells,” Nat. Gas Ind., 26, 77-79 (2006).
T. Yan, Q. M. Li, Y. Wang, J. H. Li, and X. L. Bi, “Segmental calculation model for torque and drag of drill string in horizontal wells,” J. Daqing Pet. Inst., 35, 69-72 (2011).
Y. F. Guo, X. J. Jin, and S. R. Tan, “Forecasting drag and torque of string during drilling of a horizontal well in the South China Sea,” Chin. Offshore Oil Gas (Eng.), 12, 31-34 (2000).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the academic and technical support of the China University of Petroleum (East China). This paper is supported by the Major Science and Technology Project of CNPC “Research on efficient exploration and development theory and key technologies of deep oil and gas in the Tarim Basin” (No. ZD2019-183-005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 6, pp. 120–126, November-December, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, Z., Liang, D., Xu, Y. et al. Influence of Mechanical Rotary Percussion Tool on Friction Drag in Horizontal Wells. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 57, 1035–1043 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-022-01341-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-022-01341-3