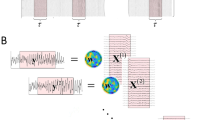
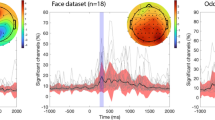
Abstract
We propose an alternative method to align the polarities of independent components (ICs) for group-level IC cluster analysis. Current methods are presently limited in how indeterminacy of IC polarities is handled, as when multiplying a weight matrix to a time-series IC activation, the result from 1 × 1 and − 1 × − 1 are indistinguishable. We first clarify the EEGLAB’s default solution and define it as the iterative correlation maximization as it maximizes the within-cluster correlations of the IC scalp topographies to the cluster mean. We then propose the covariance maximization method, which determines the polarity of ICs based on the sign of the largest eigenvalue of covariance matrix. We compared the two methods on datasets from a published visual event-related potential (ERP) study. The results were similar when both methods were applied to the IC scalp topographies. However, when the proposed method was applied to IC ERPs, the number of clusters that showed significant ERP amplitudes increased from 5 to 9 out of 9 due to minimization of within-cluster ERP amplitude cancellation. Our study confirm covariance maximization provides an alternative solution to post-ICA group-level analysis that can maximize sensitivity of IC ERPs.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bell AJ, Sejnowski TJ (1995) An information-maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution. Neural Comput 7:1129–1159. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1995.7.6.1129
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc 57:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x
Benjamini Y, Yekutieli D (2001) The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann Stat 29:1165–1188. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1013699998
Collins DL, Neelin P, Peters TM, Evans AC (1994) Automatic 3D intersubject registration of MR volumetric data in standardized Talairach space. J Comput Assist Tomogr 18:192–205. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004728-199403000-00005
Cong F, Kalyakin I, Ristaniemi T, Lyytinen H (2008) Drawback of ICA procedure on EEG: polarity indeterminacy at local optimization. In: Katashev A, Dekhtyar Y, Spigulis J (eds) 14th Nordic-Baltic conference on biomedical engineering and medical physics. Springer, Berlin, pp 202–205
Courellis H, Mullen T, Poizner H et al (2017) EEG-based quantification of cortical current density and dynamic causal connectivity generalized across subjects performing BCI-monitored cognitive tasks. Front Neurosci 11:180. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00180
Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods 134:9–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2003.10.009
Delorme A, Palmer J, Onton J et al (2012) Independent EEG sources are dipolar. PLoS ONE 7:e30135. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030135
Doualot A, Achim A (2021) A polarity alignment method for group-averaging of event-related neural signals at source level in MEG beamforming applications. Brain Topogr 34:269–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-021-00829-1
Evans AC, Collins DL, Mills SR, et al (1993) 3D statistical neuroanatomical models from 305 MRI volumes. In: 1993 IEEE conference record nuclear science symposium and medical imaging conference. IEEE, pp 1813–1817
Kothe CA, Makeig S (2013) BCILAB: a platform for brain-computer interface development. J Neural Eng 10:056014. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/10/5/056014
Kriegeskorte N, Simmons WK, Bellgowan PSF, Baker CI (2009) Circular analysis in systems neuroscience: the dangers of double dipping. Nat Neurosci 12:535–540. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2303
Makeig S, Bell A, Jung T-P, Sejnowski T (1996) Independent component analysis of electroencephalographic data. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 8:145–151
Miyakoshi M, Gehrke L, Gramann K et al (2021) The AudioMaze: an EEG and motion capture study of human spatial navigation in sparse augmented reality. Eur J Neurosci 54:8283–8307. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.15131
Miyakoshi M, Jurgiel J, Dillon A et al (2020) Modulation of frontal oscillatory power during blink suppression in children: effects of premonitory urge and reward. Cereb Cortex Commun. https://doi.org/10.1093/texcom/tgaa046
Miyakoshi M, Kanayama N, Iidaka T, Ohira H (2010) EEG evidence of face-specific visual self-representation. Neuroimage 50:1666–1675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.030
Onton J, Makeig S (2006) Information-based modeling of event-related brain dynamics. Prog Brain Res 159:99–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(06)59007-7
Oostenveld R, Fries P, Maris E, Schoffelen J-M (2011) FieldTrip: open source software for advanced analysis of MEG, EEG, and invasive electrophysiological data. Comput Intell Neurosci 2011:156869. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/156869
Palmer J, Kreutz-delgado K, Makeig S (2016) AMICA: an adaptive mixture of independent component analyzers with shared components
Piazza C, Miyakoshi M, Akalin-Acar Z et al (2016) An automated function for identifying EEG independent components representing bilateral source activity. In: Kyriacou E, Christofides S, Pattichis CS (eds) XIV Mediterranean conference on medical and biological engineering and computing 2016. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 105–109
Pion-Tonachini L, Kreutz-Delgado K, Makeig S (2019) ICLabel: an automated electroencephalographic independent component classifier, dataset, and website. Neuroimage 198:181–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.05.026
Acknowledgements
MM is supported by NSF 2011716 CRCNS US-Japan Research Proposal: A computational neuroscience approach to skill acquisition and transfer from visuo-haptic VR to the real-world and NINDS 5R01NS047293-16 ‘EEGLAB: Software for Analysis of Human Brain Dynamics’. MN and MM are supported by The Swartz Foundation (Old Field, New York). The authors express gratitude to Dr. Yash B. Joshi for encouraging the current study and revising the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.N. and M.M. wrote the main text. M.M. conducted data analyses and generated figures. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Bin He.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nakanishi, M., Miyakoshi, M. Revisiting Polarity Indeterminacy of ICA-Decomposed ERPs and Scalp Topographies. Brain Topogr 36, 223–229 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-023-00944-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-023-00944-1