Abstract
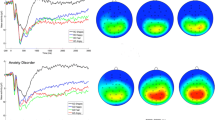
Patients with anxiety disorders (AnDs) have distinct patterns of threat-related emotional processing compared to healthy controls (HCs). The current study investigated the temporal course of emotional processing in AnDs by examining Event-related potential (ERP) components. Twenty-three AnDs and twenty-four age- and gender-matched HCs viewed emotional (fearful, happy) and neutral faces while their electroencephalograms were recorded. Early (P100, N170), middle (early posterior negativity; EPN), and late ERP components late positive potential were analyzed. To localize ERP source activity, standardized low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA) was used. AnDs displayed significantly enhanced mean amplitude of the EPN compared to HCs when fearful faces were presented. In addition, the EPN’s mean amplitude elicited by fearful faces was more pronounced than for happy and neutral faces in AnDs, whereas in HCs the EPN elicited by fearful faces was only augmented compared to neutral faces. Finally, sLORETA analysis revealed that the source activity of the EPN (fearful minus happy face condition) was increased in the cuneus and precuneus in AnDs compared to HCs. Our results indicate that the EPN is a distinct ERP component modulated by facial emotional processing in AnDs. Furthermore, the results show that anxiety symptoms enhance selective attention for fearful faces. Finally, it revealed that the cuneus and precuneus are involved in fearful face processing in AnDs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolphs R (2008) Fear, faces, and the human amygdala. Curr Opin Neurobiol 18:166–172
Armstrong T, Olatunji BO (2012) Eye tracking of attention in the affective disorders: a meta-analytic review and synthesis Clinical psychology review 32:704–723. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2012.09.004
Association AP, Association AP (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual-text revision (DSM-IV-TRim, 2000). American Psychiatric Association
Bar-Haim Y, Lamy D, Pergamin L, Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ, Van Ijzendoorn MH (2007) Threat-related attentional bias in anxious and nonanxious individuals: a meta-analytic study. Psychol Bull 133:1
Beck AT, Steer RA (1990) Manual for the Beck anxiety inventory. Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Beck AT, Steer RA, Carbin MG (1988) Psychometric properties of the Beck Depression Inventory: twenty-five years of evaluation. Clin Psychol Rev 8:77–100
Bediou B, Hénaff M-A, Bertrand O, Brunelin J, d’Amato T, Saoud M, Krolak-Salmon P (2007) Impaired fronto-temporal processing of emotion in schizophrenia. Neurophys Clin/Clin Neurophysiol 37:77–87
Bernard FA, Bullmore ET, Graham KS, Thompson SA, Hodges JR, Fletcher PC (2004) The hippocampal region is involved in successful recognition of both remote and recent famous faces. Neuroimage 22:1704–1714
Bishop SJ (2007) Neurocognitive mechanisms of anxiety: an integrative account. Trends Cognit Sci 11:307–316
Bishop S, Duncan J, Brett M, Lawrence AD (2004a) Prefrontal cortical function and anxiety: controlling attention to threat-related stimuli. Nat Neurosci 7:184–188
Bishop SJ, Duncan J, Lawrence AD (2004b) State anxiety modulation of the amygdala response to unattended threat-related stimuli. J Neurosci 24:10364–10368. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.2550-04.2004
Blau VC, Maurer U, Tottenham N, McCandliss BD (2007) The face-specific N170 component is modulated by emotional facial expression. Behav Brain Funct 3:1–13
Boutsen L, Humphreys GW, Praamstra P, Warbrick T (2006) Comparing neural correlates of configural processing in faces and objects: an ERP study of the Thatcher illusion. Neuroimage 32:352–367
Cavanna AE, Trimble MR (2006) The precuneus: a review of its functional anatomy and behavioural correlates. Brain 129:564–583
Dennis TA, Hajcak G (2009) The late positive potential: a neurophysiological marker for emotion regulation in children. J Child Psychol Psychiatr 50:1373–1383
Dolcos F, Cabeza R (2002) Event-related potentials of emotional memory: encoding pleasant, unpleasant, and neutral pictures. Cognit Affect Behav Neurosci 2:252–263
Dunning JP et al (2011) Motivated attention to cocaine and emotional cues in abstinent and current cocaine users—an ERP study. Eur J Neurosci 33:1716–1723
Etkin A, Wager T (2007) Functional neuroimaging of anxiety: a meta-analysis of emotional processing in PTSD, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobia. Am J Psychiatry 164:1476–1488
Eysenck MW, Byrne A (1992) Anxiety and susceptibility to distraction. Personal Individ Differ 13:793–798
Foa EB, Feske U, Murdock TB, Kozak MJ, McCarthy PR (1991) Processing of threat-related information in rape victims. J Abnorm Psychol 100:156
Frühholz S, Jellinghaus A, Herrmann M (2011) Time course of implicit processing and explicit processing of emotional faces and emotional words. Biol Psychol 87:265–274
Hajcak G, Nieuwenhuis S (2006) Reappraisal modulates the electrocortical response to unpleasant pictures Cognitive. Affect Behav Neurosci 6:291–297
Hajcak G, Olvet DM (2008) The persistence of attention to emotion: brain potentials during and after picture presentation. Emotion 8:250
Hajcak G, MacNamara A, Olvet DM (2010) Event-related potentials, emotion, and emotion regulation: an integrative review. Dev Neuropsychol 35:129–155
Hamilton M (1959) The assessment of anxiety states by rating British journal of medical psychology 32:50–55
Hamilton M (1986) The Hamilton rating scale for depression. In: Sartorious N, Ban T (eds) Assessment of depression. Springer, Berlin, pp 143–152
Herbert C, Junghofer M, Kissler J (2008) Event related potentials to emotional adjectives during reading. Psychophysiology 45:487–498
Herbert C, Deutsch R, Platte P, Pauli P (2013) No fear, no panic: probing negation as a means for emotion regulation. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci 8:654–661
Herrmann M, Ehlis A-C, Ellgring H, Fallgatter A (2005) Early stages (P100) of face perception in humans as measured with event-related potentials (ERPs). J Neural Transm 112:1073–1081
Holmes A, Nielsen MK, Green S (2008) Effects of anxiety on the processing of fearful and happy faces: an event-related potential study. Biol Psychol 77:159–173
Holmes A, Nielsen MK, Tipper S, Green S (2009) An electrophysiological investigation into the automaticity of emotional face processing in high versus low trait anxious individuals Cognitive. Affect Behav Neurosci 9:323–334
Johnson MH, Dziurawiec S, Ellis H, Morton J (1991) Newborns’ preferential tracking of face-like stimuli and its subsequent decline. Cognition 40:1–19
Kessels LT, Ruiter RA, Jansma BM (2010) Increased attention but more efficient disengagement: neuroscientific evidence for defensive processing of threatening health information. Health Psychol 29:346
Kim D-W, Kim H-S, Lee S-H, Im C-H (2013a) Positive and negative symptom scores are correlated with activation in different brain regions during facial emotion perception in schizophrenia patients: a voxel-based sLORETA source activity study. Schizophr Res 151:165–174
Kim PW, Kim SY, Shim M, Im C-H, Shon Y-M (2013b) The influence of an educational course on language expression and treatment of gaming addiction for massive multiplayer online role-playing game (MMORPG) players. Comput Educ 63:208–217
Kissler J, Herbert C, Peyk P, Junghofer M (2007) Buzzwords early cortical responses to emotional words during reading. Psychol Sci 18:475–480
Kissler J, Herbert C, Winkler I, Junghofer M (2009) Emotion and attention in visual word processing—An ERP study. Biol Psychol 80:75–83
Koenigsberg HW et al (2009) Neural correlates of emotion processing in borderline personality disorder. Psychiatry Res 172:192–199
Koster EH, Crombez G, Verschuere B, De Houwer J (2006) Attention to threat in anxiety-prone individuals: mechanisms underlying attentional bias. Cognit Ther Res 30:635–643
Krolak-Salmon P, Henaff MA, Vighetto A, Bertrand O, Mauguiere F (2004) Early amygdala reaction to fear spreading in occipital, temporal, and frontal cortex: a depth electrode ERP study in human. Neuron 42:665–676
Lang PJ, Bradley MM, Cuthbert BN (1997) International affective picture system (IAPS): Technical manual and affective ratings NIMH Center for the Study of Emotion and Attention, pp 39–58
Li W, Zinbarg RE, Boehm SG, Paller KA (2008) Neural and behavioral evidence for affective priming from unconsciously perceived emotional facial expressions and the influence of trait anxiety. J Cogn Neurosci 20:95–107
MacNamara A, Hajcak G (2010) Distinct electrocortical and behavioral evidence for increased attention to threat in generalized anxiety disorder. Depress Anxiety 27:234–243
Maurage P, Philippot P, Verbanck P, Noël X, Kornreich C, Hanak C, Campanella S (2007) Is the P300 deficit in alcoholism associated with early visual impairments (P100, N170)? An oddball paradigm. Clin Neurophysiol 118:633–644
McNally RJ, Kaspi SP, Riemann BC, Zeitlin SB (1990a) Selective processing of threat cues in posttraumatic stress disorder. J Abnorm Psychol 99:398
McNally RJ, Riemann BC, Kim E (1990b) Selective processing of threat cues in panic disorder. Behav Res Ther 28:407–412
Mocaiber I et al (2010) Fact or fiction? An event-related potential study of implicit emotion regulation. Neurosci Lett 476:84–88
Mogg K, Millar N, Bradley BP (2000) Biases in eye movements to threatening facial expressions in generalized anxiety disorder and depressive disorder. J Abnorm Psychol 109:695
Morel S, George N, Foucher A, Chammat M, Dubal S (2014) ERP evidence for an early emotional bias towards happy faces in trait anxiety. Biol Psychol 99:183–192. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2014.03.011
Morris JS, Frith CD, Perrett DI, Rowland D, Young AW, Calder AJ, Dolan RJ (1996) A differential neural response in the human amygdala to fearful and happy facial expressions. Nature 383:812–815
Moser JS, Huppert JD, Duval E, Simons RF (2008) Face processing biases in social anxiety: an electrophysiological study. Biol Psychol 78:93–103
Mueller E, Hofmann S, Santesso D, Meuret A, Bitran S, Pizzagalli DA (2009) Electrophysiological evidence of attentional biases in social anxiety disorder. Psychol Med 39:1141–1152
Mühlberger A, Wieser MJ, Herrmann MJ, Weyers P, Tröger C, Pauli P (2009) Early cortical processing of natural and artificial emotional faces differs between lower and higher socially anxious persons. J Neural Transm 116:735–746
Müsch K et al (2014) Selective attention modulates high-frequency activity in the face-processing network. Cortex 60:34–51
Norberg J, Wiens S (2013) Effects of attention manipulations on motivated attention to feared and nonfeared negative distracters in spider fear. BMC Neurosci 14:139
Olofsson JK, Nordin S, Sequeira H, Polich J (2008) Affective picture processing: an integrative review of ERP findings. Biol Psychol 77:247–265
Pandey AK et al (2012) Neurocognitive deficits in male alcoholics: an ERP/sLORETA analysis of the N2 component in an equal probability Go/NoGo task. Biol Psychol 89:170–182. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2011.10.009
Park J, Oh J, Kim S, Lee M, Lee C, Kim B (2011) Korean facial expressions of emotion (KOFEE) Seoul Korea: section of affect and neuroscience. Yonsei University College of Medicine, Institute of Behavioral Science in Medicine
Pascual-Marqui R (2002) Standardized low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA): technical details. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 24:5–12
Pastor MC, Bradley MM, Löw A, Versace F, Moltó J, Lang PJ (2008) Affective picture perception: emotion, context, and the late positive potential. Brain Res 1189:145–151
Ponz A, Montant M, Liegeois-Chauvel C, Silva C, Braun M, Jacobs AM, Ziegler JC (2014) Emotion processing in words: a test of the neural re-use hypothesis using surface and intracranial EEG. Soc Cognit Affect Neurosci 9:619–627. doi:10.1093/scan/nst034
Rahko J et al (2010) Functional mapping of dynamic happy and fearful facial expression processing in adolescents. Brain Imagin Behav 4:164–176
Rellecke J, Sommer W, Schacht A (2012) Does processing of emotional facial expressions depend on intention? Time-resolved evidence from event-related brain potentials. Biol Psychol 90:23–32
Reske M et al (2009) Differential brain activation during facial emotion discrimination in first-episode schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 43:592–599
Rossignol M, Philippot P, Douilliez C, Crommelinck M, Campanella S (2005) The perception of fearful and happy facial expression is modulated by anxiety: an event-related potential study. Neurosci Lett 377:115–120
Sander D, Grandjean D, Pourtois G, Schwartz S, Seghier ML, Scherer KR, Vuilleumier P (2005) Emotion and attention interactions in social cognition: brain regions involved in processing anger prosody. Neuroimage 28:848–858
Sass SM, Heller W, Stewart JL, Silton RL, Edgar JC, Fisher JE, Miller GA (2010) Time course of attentional bias in anxiety: emotion and gender specificity. Psychophysiology 47:247–259
Scharmüller W, Leutgeb V, Schäfer A, Köchel A, Schienle A (2011) Source localization of late electrocortical positivity during symptom provocation in spider phobia: an sLORETA study. Brain Res 1397:10–18
Schupp HT, Junghöfer M, Weike AI, Hamm AO (2004a) The selective processing of briefly presented affective pictures: an ERP analysis. Psychophysiology 41:441–449
Schupp HT, Öhman A, Junghöfer M, Weike AI, Stockburger J, Hamm AO (2004b) The facilitated processing of threatening faces: an ERP analysis. Emotion 4:189
Schupp HT, Flaisch T, Stockburger J, Junghöfer M (2006a) Emotion and attention: event-related brain potential studies. Prog Brain Res 156:31–51
Schupp HT, Stockburger J, Codispoti M, Junghofer M, Weike AI, Hamm AO (2006b) Stimulus novelty and emotion perception: the near absence of habituation in the visual cortex. NeuroReport 17:365–369. doi:10.1097/01.wnr.0000203355.88061.c6
Schupp HT, Stockburger J, Bublatzky F, Junghöfer M, Weike AI, Hamm AO (2007) Explicit attention interferes with selective emotion processing in human extrastriate cortex Bmc. Neuroscience 8:16
Schupp HT, Stockburger J, Schmälzle R, Bublatzky F, Weike AI, Hamm AO (2008) Visual noise effects on emotion perception: brain potentials and stimulus identification. NeuroReport 19:167–171
Semlitsch HV, Anderer P, Schuster P, Presslich O (1986) A solution for reliable and valid reduction of ocular artifacts, applied to the P300 ERP. Psychophysiology 23:695–703
Sheppes G, Luria R, Fukuda K, Gross JJ (2013) There’s more to anxiety than meets the eye: isolating threat-related attentional engagement and disengagement biases. Emotion 13:520
Skouras S, Gray M, Critchley H, Koelsch S (2014) Superficial amygdala and hippocampal activity during affective music listening observed at 3 T but not 1.5 T fMRI. NeuroImage 101:364–369
Spielberger CD, Gorsuch RL, Lushene RE (1970) Manual for the state-trait anxiety inventory. Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto
Turetsky BI, Kohler CG, Indersmitten T, Bhati MT, Charbonnier D, Gur RC (2007) Facial emotion recognition in schizophrenia: when and why does it go awry? Schizophr Res 94:253–263
Vuilleumier P, Pourtois G (2007) Distributed and interactive brain mechanisms during emotion face perception: evidence from functional neuroimaging. Neuropsychologia 45:174–194. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.06.003
Wagner M, Fuchs M, Kastner J (2004) Evaluation of sLORETA in the presence of noise and multiple sources. Brain Topogr 16:277–280
Walentowska W, Wronka E (2012) Trait anxiety and involuntary processing of facial emotions. Int J Psychophysiol 85:27–36
Wieser MJ, Pauli P, Reicherts P, Mühlberger A (2010) Don’t look at me in anger! Enhanced processing of angry faces in anticipation of public speaking. Psychophysiology 47:271–280
Zion-Golumbic E, Golan T, Anaki D, Bentin S (2008) Human face preference in gamma-frequency EEG activity. Neuroimage 39:1980–1987. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.10.025
Acknowledgments
We thank JC who supported all procedures in this study. This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (No. 2012R1A1A2043992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, S., Shim, M., Kim, H.S. et al. Enhanced Early Posterior Negativity to Fearful Faces in Patients with Anxiety Disorder. Brain Topogr 29, 262–272 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-015-0456-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-015-0456-0