Abstract
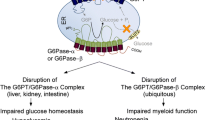
Disorders of the glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase)/glucose-6-phosphate transporter (G6PT) complexes consist of three subtypes: glycogen storage disease type Ia (GSD-Ia), deficient in the liver/kidney/intestine-restricted G6Pase-α (or G6PC); GSD-Ib, deficient in a ubiquitously expressed G6PT (or SLC37A4); and G6Pase-β deficiency or severe congenital neutropenia syndrome type 4 (SCN4), deficient in the ubiquitously expressed G6Pase-β (or G6PC3). G6Pase-α and G6Pase-β are glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) hydrolases with active sites lying inside the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen and as such are dependent upon the G6PT to translocate G6P from the cytoplasm into the lumen. The tissue expression profiles of the G6Pase enzymes dictate the disease's phenotype. A functional G6Pase-α/G6PT complex maintains interprandial glucose homeostasis, while a functional G6Pase-β/G6PT complex maintains neutrophil/macrophage energy homeostasis and functionality. G6Pase-β deficiency is not a glycogen storage disease but biochemically it is a GSD-I related syndrome (GSD-Irs). GSD-Ia and GSD-Ib patients manifest a common metabolic phenotype of impaired blood glucose homeostasis not shared by GSD-Irs. GSD-Ib and GSD-Irs patients manifest a common myeloid phenotype of neutropenia and neutrophil/macrophage dysfunction not shared by GSD-Ia. While a disruption of the activity of the G6Pase-α/G6PT complex readily explains why GSD-Ia and GSD-Ib patients exhibit impaired glucose homeostasis, the basis for neutropenia and myeloid dysfunction in GSD-Ib and GSD-Irs are only now starting to be understood. Animal models of all three disorders are now available and are being exploited to both delineate the disease more precisely and develop new treatment approaches, including gene therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annabi B, Hiraiwa H, Mansfield BC et al (1998) The gene for glycogen-storage disease type 1b maps to chromosome 11q23. Am J Hum Genet 62(2):400–405
Banka S, Newman WG (2013) A clinical and molecular review of ubiquitous glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency caused by G6PC3 mutations. Orphanet J Rare Dis 8:84
Boers SJ, Visser G, Smit PG, Fuchs SA (2014) Liver transplantation in glycogen storage disease type I. Orphanet J Rare Dis 9(1):47
Boztug K, Appaswamy G, Ashikov A et al (2009) A syndrome with congenital neutropenia and mutations in G6PC3. N Engl J Med 360(1):32–43
Chen LY, Shieh JJ, Lin B et al (2003) Impaired glucose homeostasis, neutrophil trafficking and function in mice lacking the glucose-6-phosphate transporter. Hum Mol Genet 12(19):2547–2558
Chen SY, Pan CJ, Nandigama K, Mansfield BC, Ambudkar SV, Chou JY (2008) The glucose-6-phosphate transporter is a phosphate-linked antiporter deficient in glycogen storage disease type Ib and Ic. FASEB J 22(7):2206–2213
Cheung YY, Kim SY, Yiu WH et al (2007) Impaired neutrophil activity and increased susceptibility to bacterial infection in mice lacking glucose-6-phosphatase-beta. J Clin Invest 117(3):784–793
Chou JY, Mansfield BC (2008) Mutations in the glucose-6-phosphatase-alpha (G6PC) gene that cause type Ia glycogen storage disease. Hum Mutat 29(7):921–930
Chou JY, Mansfield BC (2011) Recombinant AAV-directed gene therapy for type I glycogen storage diseases. Expert Opin Biol Ther 11(8):1011–1024
Chou JY, Mansfield BC (2014) The SLC37 family of sugar-phosphate/phosphate exchangers. Curr Top Membr 73:357–382
Chou JY, Matern D, Mansfield BC, Chen YT (2002) Type I glycogen storage diseases: disorders of the glucose-6-phosphatase complex. Curr Mol Med 2(2):121–143
Chou JY, Jun HS, Mansfield BC (2010) Glycogen storage disease type I and G6Pase-beta deficiency: etiology and therapy. Nat Rev Endocrinol 6(12):676–688
Ekstein J, Rubin BY, Anderson SL et al (2004) Mutation frequencies for glycogen storage disease Ia in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Am J Med Genet A 129A(2):162–164
Franco LM, Krishnamurthy V, Bali D et al (2005) Hepatocellular carcinoma in glycogen storage disease type Ia: a case series. J Inherit Metab Dis 28(2):153–162
Gerin I, Veiga-da-Cunha M, Achouri Y, Collet JF, Van Schaftingen E (1997) Sequence of a putative glucose 6-phosphate translocase, mutated in glycogen storage disease type Ib. FEBS Lett 419(2–3):235–238
Ghosh A, Shieh JJ, Pan CJ, Sun MS, Chou JY (2002) The catalytic center of glucose-6-phosphatase. HIS176 is the nucleophile forming the phosphohistidine-enzyme intermediate during catalysis. J Biol Chem 277(36):32837–32842
Ghosh A, Shieh JJ, Pan CJ, Chou JY (2004) Histidine 167 is the phosphate acceptor in glucose-6-phosphatase-beta forming a phosphohistidine enzyme intermediate during catalysis. J Biol Chem 279(13):12479–12483
Hiraiwa H, Pan CJ, Lin B, Moses SW, Chou JY (1999) Inactivation of the glucose 6-phosphate transporter causes glycogen storage disease type 1b. J Biol Chem 274(9):5532–5536
Jun HS, Lee YM, Cheung YY et al (2010) Lack of glucose recycling between endoplasmic reticulum and cytoplasm underlies cellular dysfunction in glucose-6-phosphatase-beta-deficient neutrophils in a congenital neutropenia syndrome. Blood 116(15):2783–2792
Jun HS, Lee YM, Song KD, Mansfield BC, Chou JY (2011) G-CSF improves murine G6PC3-deficient neutrophil function by modulating apoptosis and energy homeostasis. Blood 117(14):3881–3892
Jun HS, Cheung YY, Lee YM, Mansfield BC, Chou JY (2012) Glucose-6-phosphatase-beta, implicated in a congenital neutropenia syndrome, is essential for macrophage energy homeostasis and functionality. Blood 119(17):4047–4055
Jun HS, Weinstein DA, Lee YM, Mansfield BC, Chou JY (2014) Molecular mechanisms of neutrophil dysfunction in glycogen storage disease type Ib. Blood in press
Kilpatrick L, Garty BZ, Lundquist KF et al (1990) Impaired metabolic function and signaling defects in phagocytic cells in glycogen storage disease type 1b. J Clin Invest 86(1):196–202
Kim SY, Jun HS, Mead PA, Mansfield BC, Chou JY (2008) Neutrophil stress and apoptosis underlie myeloid dysfunction in glycogen storage disease type Ib. Blood 111(12):5704–5711
Koeberl DD, Pinto C, Sun B et al. (2008) AAV vector-mediated reversal of hypoglycemia in canine and murine glycogen storage disease type Ia. Mol Ther 16(4):665–672
Kishnani PS, Faulkner E, VanCamp S et al (2001) Canine model and genomic structural organization of glycogen storage disease type Ia (GSD Ia). Vet Pathol 38(1):83–91
Koeberl DD, Kishnani PS, Bali D, Chen YT (2009) Emerging therapies for glycogen storage disease type I. Trends Endocrinol Metab 20:252–258
Kuijpers TW, Maianski NA, Tool AT et al (2003) Apoptotic neutrophils in the circulation of patients with glycogen storage disease type 1b (GSD1b). Blood 101(12):5021–5024
Lee YM, Jun HS, Pan CJ et al (2012) Prevention of hepatocellular adenoma and correction of metabolic abnormalities in murine glycogen storage disease type Ia by gene therapy. Hepatology 56(5):1719–1729
Lee YM, Pan CJ, Koeberl DD, Mansfield BC, Chou JY (2013) The upstream enhancer elements of the G6PC promoter are critical for optimal G6PC expression in murine glycogen storage disease type Ia. Mol Genet Metab 110(3):275–280
Lei KJ, Shelly LL, Pan CJ, Sidbury JB, Chou JY (1993) Mutations in the glucose-6-phosphatase gene that cause glycogen-storage-disease type-1a. Science 262(5133):580–583
Lei KJ, Chen H, Pan CJ et al (1996) Glucose-6-phosphatase dependent substrate transport in the glycogen storage disease type-1a mouse. Nat Genet 13(2):203–209
Lin B, Pan CJ, Chou JY (2000) Human variant glucose-6-phosphate transporter is active in microsomal transport. Hum Genet 107(5):526–529
Martin CC, Oeser JK, Svitek CA, Hunter SI, Hutton JC, O'Brien RM (2002) Identification and characterization of a human cDNA and gene encoding a ubiquitously expressed glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit-related protein. J Mol Endocrinol 29(2):205–222
Matern D, Seydewitz HH, Bali D, Lang C, Chen YT (2002) Glycogen storage disease type I: diagnosis and phenotype/genotype correlation. Eur J Pediatr 161(Suppl 1):S10–S19
McCawley LJ, Korchak HM, Cutilli JR et al (1993) Interferon-gamma corrects the respiratory burst defect in vitro in monocyte-derived macrophages from glycogen storage disease type 1b patients. Pediatr Res 34(3):265–269
McDermott DH, De Ravin SS, Jun HS et al (2010) Severe congenital neutropenia resulting from G6PC3 deficiency with increased neutrophil CXCR4 expression and myelokathexis. Blood 116(15):2793–2802
Michelfelder S, Trepel M (2009) Adeno-associated viral vectors and their redirection to cell-type specific receptors. Adv Genet 67:29–60
Mutel E, Abdul-Wahed A, Ramamonjisoa N et al (2011) Targeted deletion of liver glucose-6 phosphatase mimics glycogen storage disease type 1a including development of multiple adenomas. J Hepatol 54(3):529–537
Pan CJ, Lei KJ, Annabi B, Hemrika W, Chou JY (1998) Transmembrane topology of glucose-6-phosphatase. J Biol Chem 273(11):6144–6148
Pan CJ, Lin B, Chou JY (1999) Transmembrane topology of human glucose 6-phosphate transporter. J Biol Chem 274(20):13865–13869
Peng WT, Pan CJ, Lee EJ, Westphal H, Chou JY (2009) Generation of mice with a conditional allele for G6pc. Genesis 47(9):590–594
Pierre G, Chakupurakal G, McKiernan P et al (2008) Bone marrow transplantation in glycogen storage disease type 1b. J Pediatr 152(2):286–288
Rake JP, Visser G, Labrune P, Leonard JV, Ullrich K, Smit GP (2002) Glycogen storage disease type I: diagnosis, management, clinical course and outcome. Results of the European Study on Glycogen Storage Disease Type I (ESGSD I). Eur J Pediatr 161(Suppl 1):S20–S34
Rocca CJ, Ur SN, Harrison F, Cherqui S (2014) rAAV9 combined with renal vein injection is optimal for kidney-targeted gene delivery: conclusion of a comparative study. Gene Ther 21(6):618–628
Shah KK, O'Dell SD (2013) Effect of dietary interventions in the maintenance of normoglycaemia in glycogen storage disease type 1a: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hum Nutr Diet 26(4):329–339
Shieh JJ, Terzioglu M, Hiraiwa H et al (2002) The molecular basis of glycogen storage disease type 1a: structure and function analysis of mutations in glucose-6-phosphatase. J Biol Chem 277(7):5047–5053
Shieh JJ, Pan CJ, Mansfield BC, Chou JY (2003) A glucose-6-phosphate hydrolase, widely expressed outside the liver, can explain age-dependent resolution of hypoglycemia in glycogen storage disease type Ia. J Biol Chem 278(47):47098–47103
Visser G, Rake JP, Labrune P et al (2002) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in glycogen storage disease type 1b. Results of the European Study on Glycogen Storage Disease Type 1. Eur J Pediatr 161(Suppl 1):S83–S87
Weinstein DA, Correia CE, Conlon T et al (2010) Adeno-associated virus-mediated correction of a canine model of glycogen storage disease type Ia. Hum Gene Ther 21(7):903–910
Yiu WH, Lee YM, Peng WT et al (2010) Complete normalization of hepatic G6PC deficiency in murine glycogen storage disease type Ia using gene therapy. Mol Ther 18(6):1076–1084
Zincarelli C, Soltys S, Rengo G, Rabinowitz JE (2008) Analysis of AAV serotypes 1–9 mediated gene expression and tropism in mice after systemic injection. Mol Ther 16(6):1073–1080
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institutes of Health.
Compliance with ethics guidelines
ᅟ
Conflict of Interest
Janice Y. Chou, Hyun Sik Jun, and Brian C. Mansfield declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects performed by any of the authors.
Animal Rights
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Alberto B Burlina
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chou, J.Y., Jun, H.S. & Mansfield, B.C. Type I glycogen storage diseases: disorders of the glucose-6-phosphatase/glucose-6-phosphate transporter complexes. J Inherit Metab Dis 38, 511–519 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-014-9772-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-014-9772-x