Abstract
Background
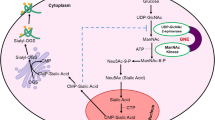
UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase/ManNAc 6-kinase (GNE) is a bifunctional enzyme responsible for the first committed steps in the synthesis of sialic acid, a common terminal monosaccharide in both protein and lipid glycosylation. GNE mutations are responsible for a rare autosomal recessive neuromuscular disorder, GNE myopathy (also called hereditary inclusion body myopathy). The connection between the impairment of sialic acid synthesis and muscle pathology in GNE myopathy remains poorly understood.
Methods
Glycosphingolipid (GSL) analysis was performed by HPLC in multiple models of GNE myopathy, including patients’ fibroblasts and plasma, control fibroblasts with inhibited GNE epimerase activity through a novel imino sugar, and tissues of GneM712T/M712T knock-in mice.
Results
Not only neutral GSLs, but also sialylated GSLs, were significantly increased compared to controls in all tested models of GNE myopathy. Treatment of GNE myopathy fibroblasts with N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc), a sialic acid precursor downstream of GNE epimerase activity, ameliorated the increased total GSL concentrations.
Conclusion
GNE myopathy models have increased total GSL concentrations. ManNAc supplementation results in decrease of GSL levels, linking abnormal increase of total GSLs in GNE myopathy to defects in the sialic acid biosynthetic pathway. These data advocate for further exploring GSL concentrations as an informative biomarker, not only for GNE myopathy, but also for other disorders of sialic acid metabolism.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2-AA:
-
Anthranilic acid
- CMP:
-
Cytidine monophosphate
- CMP-SA:
-
CMP-sialic acid
- CTP:
-
Cytidine triphosphate
- DMRV:
-
Distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles
- ECL:
-
Enhanced chemiluminescence
- FCS:
-
Fetal calf serum
- GlcNAc:
-
N-acetyl glucosamine
- GNE:
-
UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase/ManNAc 6-kinase
- GSL:
-
Glycosphingolipid
- HIBM:
-
Hereditary inclusion body myopathy
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- ManNAc:
-
N-acetylmannosamine
- MES:
-
2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid
- Neu5AC:
-
N-acetylneuraminic acid or sialic acid
- NP-HPLC:
-
Normal-phase HPLC
- OMIM:
-
Online mendelian inheritance in man
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene fluoride
- RP-HPLC:
-
Reverse-phase HPLC
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
- THF:
-
Tetrahydrofuran
- UDP:
-
Uridine diphosphate
- XMEA:
-
X-linked myopathy with excessive autophagy
References
Al-Rawi S, Hinderlich S, Reutter W, Giannis A (2004) Synthesis and biochemical properties of reversible inhibitors of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 43:4366–4370
Alonzi DS, Butters TD (2011) Therapeutic targets for inhibitors of glycosylation. Chimia (Aarau) 65:35–39
Amsili S, Zer H, Hinderlich S et al (2008) UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE) binds to alpha-actinin 1: novel pathways in skeletal muscle? PLoS One 3:e2477
Argov Z, Yarom R (1984) “Rimmed vacuole myopathy” sparing the quadriceps. A unique disorder in Iranian Jews. J Neurol Sci 64:33–43
Askanas V, Alvarez RB, Engel WK (1993) beta-Amyloid precursor epitopes in muscle fibers of inclusion body myositis. Ann Neurol 34:551–560
Askanas V, Engel WK (1995) New advances in the understanding of sporadic inclusion-body myositis and hereditary inclusion-body myopathies. Curr Opin Rheumatol 7:486–496
Butters TD, Dwek RA, Platt FM (2000) Inhibition of glycosphingolipid biosynthesis: application to lysosomal storage disorders. Chem Rev 100:4683–4696
Chou HH, Takematsu H, Diaz S et al (1998) A mutation in human CMP-sialic acid hydroxylase occurred after the Homo-Pan divergence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:11751–11756
Eisenberg I, Avidan N, Potikha T et al (2001) The UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase gene is mutated in recessive hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Nat Genet 29:83–87
Eisenberg I, Grabov-Nardini G, Hochner H et al (2003) Mutations spectrum of GNE in hereditary inclusion body myopathy sparing the quadriceps. Hum Mutat 21:99
Eskelinen EL (2006) Roles of LAMP-1 and LAMP-2 in lysosome biogenesis and autophagy. Mol Aspects Med 27:495–502
Galeano B, Klootwijk R, Manoli I et al (2007) Mutation in the key enzyme of sialic acid biosynthesis causes severe glomerular proteinuria and is rescued by N-acetylmannosamine. J Clin Invest 117:1585–1594
Ghaderi D, Strauss HM, Reinke S et al (2007) Evidence for dynamic interplay of different oligomeric states of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase by biophysical methods. J Mol Biol 369:746–758
Hinderlich S, Berger M, Keppler OT, Pawlita M, Reutter W (2001) Biosynthesis of N-acetylneuraminic acid in cells lacking UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase. Biol Chem 382:291–297
Hinderlich S, Stasche R, Zeitler R, Reutter W (1997) A bifunctional enzyme catalyzes the first two steps in N-acetylneuraminic acid biosynthesis of rat liver. Purification and characterization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase. J Biol Chem 272:24313–24318
Huizing M, Krasnewich DM (2009) Hereditary inclusion body myopathy: a decade of progress. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:881–887
Huwiler A, Kolter T, Pfeilschifter J, Sandhoff K (2000) Physiology and pathophysiology of sphingolipid metabolism and signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta 1485:63–99
Jones MB, Teng H, Rhee JK et al (2004) Characterization of the cellular uptake and metabolic conversion of acetylated N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) analogues to sialic acids. Biotechnol Bioeng 85:394–405
Kakani S, Yardeni T, Poling J et al (2012) The Gne M712T mouse as a model for human glomerulopathy. Am J Pathol 180:1431–1440
Keppler OT, Hinderlich S, Langner J et al (1999) UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase: a regulator of cell surface sialylation. Science 284:1372–1376
Kershaw DB, Beck SG, Wharram BL et al (1997) Molecular cloning and characterization of human podocalyxin-like protein. Orthologous relationship to rabbit PCLP1 and rat podocalyxin. J Biol Chem 272:15708–15714
Krause S, Hinderlich S, Amsili S et al (2005) Localization of UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase/ManAc kinase (GNE) in the Golgi complex and the nucleus of mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res 304:365–379
Li H, Marcelo F, Bello C et al (2009) Design and synthesis of acetamido tri- and tetra-hydroxyazepanes: potent and selective beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 17:5598–5604
Lucka L, Krause M, Danker K, Reutter W, Horstkorte R (1999) Primary structure and expression analysis of human UDP-N-acetyl-glucosamine-2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase, the bifunctional enzyme in neuraminic acid biosynthesis. FEBS Lett 454:341–344
Malicdan MC, Nishino I (2012) Autophagy in lysosomal myopathies. Brain Pathol 22:82–88
Malicdan MC, Noguchi S, Hayashi YK, Nonaka I, Nishino I (2009) Prophylactic treatment with sialic acid metabolites precludes the development of the myopathic phenotype in the DMRV-hIBM mouse model. Nat Med 15:690–695
Malicdan MC, Noguchi S, Nishino I (2007a) Autophagy in a mouse model of distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles or hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Autophagy 3:396–398
Malicdan MC, Noguchi S, Nonaka I, Hayashi YK, Nishino I (2007b) A Gne knockout mouse expressing human GNE D176V mutation develops features similar to distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles or hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Hum Mol Genet 16:2669–2682
Malicdan MC, Noguchi S, Nonaka I, Saftig P, Nishino I (2008) Lysosomal myopathies: an excessive build-up in autophagosomes is too much to handle. Neuromuscul Disord 18:521–529
Malicdan MC, Noguchi S, Tokutomi T et al (2012) Peracetylated N-acetylmannosamine, a synthetic sugar molecule, efficiently rescues muscle phenotype and biochemical defects in mouse model of sialic acid-deficient myopathy. J Biol Chem 287:2689–2705
Nemunaitis G, Jay CM, Maples PB et al (2011) Hereditary inclusion body myopathy: single patient response to intravenous dosing of GNE gene Lipoplex. Hum Gene Ther 22:1331–1341
Nemunaitis G, Maples PB, Jay C et al (2010) Hereditary inclusion body myopathy: single patient response to GNE gene Lipoplex therapy. J Gene Med 12:403–412
Neville DC, Alonzi DS, Butters TD (2012) Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography of anthranilic acid-labelled oligosaccharides with a 4-aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester-labelled dextran hydrolysate internal standard. J Chromatogr A 1233:66–70
Niethamer TK, Yardeni T, Leoyklang P et al (2012) Oral monosaccharide therapies to reverse renal and muscle hyposialylation in a mouse model of GNE myopathy. Mol Genet Metab 107:748–755
Nishino I (2006) Autophagic vacuolar myopathy. Semin Pediatr Neurol 13:90–95
Nishino I, Noguchi S, Murayama K et al (2002) Distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles is allelic to hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Neurology 59:1689–1693
Noguchi S, Keira Y, Murayama K et al (2004) Reduction of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase activity and sialylation in distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles. J Biol Chem 279:11402–11407
Nonaka I, Murakami N, Suzuki Y, Kawai M (1998) Distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles. Neuromuscul Disord 8:333–337
Nonaka I, Noguchi S, Nishino I (2005) Distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles and hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 5:61–65
Nonaka I, Sunohara N, Ishiura S, Satoyoshi E (1981) Familial distal myopathy with rimmed vacuole and lamellar (myeloid) body formation. J Neurol Sci 51:141–155
Paccalet T, Coulombe Z, Tremblay JP (2010) Ganglioside GM3 levels are altered in a mouse model of HIBM: GM3 as a cellular marker of the disease. PLoS One 5:e10055
Ramachandran N, Munteanu I, Wang P et al (2009) VMA21 deficiency causes an autophagic myopathy by compromising V-ATPase activity and lysosomal acidification. Cell 137:235–246
Schauer R (2009) Sialic acids as regulators of molecular and cellular interactions. Curr Opin Struct Biol 19:507–514
Schwarzkopf M, Knobeloch KP, Rohde E et al (2002) Sialylation is essential for early development in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:5267–5270
Sparks SE, Ciccone C, Lalor M et al (2005) Use of a cell-free system to determine UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase and N-acetylmannosamine kinase activities in human hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Glycobiology 15:1102–1110
Valles-Ayoub Y, Esfandiarifard S, Sinai P et al (2012) Serum neural cell adhesion molecule is hyposialylated in hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 16:313–317
Varki A (1997) Sialic acids as ligands in recognition phenomena. FASEB J 11:248–255
Varki A (2008) Sialic acids in human health and disease. Trends Mol Med 14:351–360
Wang Z, Sun Z, Li AV, Yarema KJ (2006) Roles for UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase/ManNAc 6-kinase outside of sialic acid biosynthesis: modulation of sialyltransferase and BiP expression, GM3 and GD3 biosynthesis, proliferation, and apoptosis, and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 281:27016–27028
Weidemann W, Stelzl U, Lisewski U et al (2006) The collapsin response mediator protein 1 (CRMP-1) and the promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein (PLZF) bind to UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE), the key enzyme of sialic acid biosynthesis. FEBS Lett 580:6649–6654
Wennekes T, van den Berg RJ, Boot RG et al (2009) Glycosphingolipids–nature, function, and pharmacological modulation. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 48:8848–8869
Yardeni T, Choekyi T, Jacobs K et al (2011) Identification, tissue distribution, and molecular modeling of novel human isoforms of the key enzyme in sialic acid synthesis, UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase/ManNAc kinase. Biochemistry 50:8914–8925
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Professor Raymond Dwek for his support (Oxford Glycobioloby Institute). We thank Shelley Hoogstraten-Miller and Theresa Calhoun (NHGRI, NIH) for their skilled assistance with mouse maintenance and thank Carla Ciccone (NHGRI, NIH) for her expert laboratory work. We thank the HIBM Research Group (Encino, CA, USA) for providing the Gne M712T knock-in mouse model.
Funding
This work was supported by the Oxford Glycobiology Institute, Oxford, UK (K.A.P., D.S.A., N.V.K., and T.D.B.), l’Association “Vaincre les maladies lysosomales” (Y.B.) and the Intramural Research Programs of the National Human Genome Research Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA (K.A.P., T.Y., P.L., H.D., W.A.G., and M.H.). The authors confirm independence from the sponsors; the content of the article has not been influenced by the sponsors.
Conflict of interests
Katherine A. Patzel, Tal Yardeni, Erell Le Poëc-Celic, Dominic S. Alonzi, Nikolay V. Kukushkin, Bixue Xu, Yongmin Zhang, Matthieu Sollogoub, Yves Blériot, and Terry D. Butters declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Marjan Huizing and William A. Gahl are co-inventors on patent PCT/US2008/006895 “N-acetyl mannosamine as a therapeutic agent”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by: Eva Morava
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 956 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patzel, K.A., Yardeni, T., Le Poëc-Celic, E. et al. Non-specific accumulation of glycosphingolipids in GNE myopathy. J Inherit Metab Dis 37, 297–308 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-013-9655-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-013-9655-6