Abstract
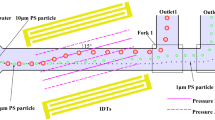
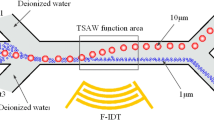
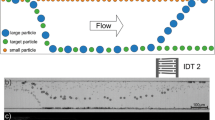
Particle/cell sorting has great potential in medical diagnosis and chemical analysis. Two kinds of microfluidic sorting chips (sequential sorting chip and direct sorting chip) are designed, which combine hydraulic force and acoustic radiation force to achieve continuous sorting of multiple particles. Firstly, the optimal values of the angle (α) between the interdigital transducer (IDT) and the main channel, the peak-to-peak voltage (Vpp), the main flow velocity (Vmax) and the flow ratio (A) are determined by simulation and experiments, the related optimal parameters were obtained that the α = 15°, Vpp = 25 V, Vmax = 4 mm/s, flow ratio A1 = 0.2, and A2 = 0.5, respectively. Then, the corresponding sorting experiments were carried out using two kinds of sorting chips to sort the polystyrene (PS) particles with diameters of 1 μm, 5 μm, and 10 μm, and the sorting rate and purity of particles were calculated and analyzed. Experimental results show that the two kinds of sorting chips can achieve continuous sorting of multiple particles, and the sorting effect of sequential sorting chip (control flow ratio) is better than that of direct sorting chip. In addition, the sorting chips in our research have the advantages of simple structure, high sorting efficiency, and the ability to sort multiple particles, which can be applied in medical and chemical research fields, such as cell sorting and chemical analysis.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. An, J. Lee, S.H. Lee, J. Park, B. Kim, Separation of malignant human breast cancer epithelial cells from healthy epithelial cells using an advanced dielectrophoresis-activated cell sorter (DACS). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 394(3), 801–809 (2009)
E. Berthier, E.W.K. Young, D. Beebe, Engineers are from PDMS-land, biologists are from Polystyrenia. Lab Chip 12, 1224–1237 (2012)
K. Chono, N. Shimizu, Y. Matsui, J. Kondoh, S. Shiokawa, Development of novel atomization system based on SAW streaming. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 43(5B), 2987–2991 (2004)
D.J. Collins, A. Tuncay, N. Adrian, Particle separation using virtual deterministic lateral displacement (vDLD). Lab Chip 14, 1595–1603 (2014)
D.J. Collins, B. Morahan, J. Garcia-Bustos, C. Doerig, M. Plebanski, A. Neild, Two-dimensional single-cell patterning with one cell per well driven by surface acoustic waves. Nat. Commun. 6, 8686 (2015)
G. Destgeer, K.H. Lee, J.H. Jung, A. Alazzam, H.J. Sung, Continuous separation of particles in a PDMS microfluidic channel via travelling surface acoustic waves (TSAW). Lab Chip 13(21), 4210–4216 (2013)
G. Destgeer, B.H. Ha, J.H. Jung, H.J. Sung, Submicron separation of microspheres via travelling surface acoustic waves. Lab Chip 14(24), 4665–4672 (2014)
G. Destgeer, B.H. Ha, J. Park, J.H. Jung, A. Alazzam, H.J. Sung, Microchannel anechoic corner for size-selective separation and medium exchange via traveling surface acoustic waves. Anal. Chem. 87(9), 4627–4632 (2015)
C. Devendran, N.R. Gunasekara, D.J. Collins, A. Neild, Batch process particle separation using surface acoustic waves (SAW): Integration of travelling and standing SAW. RSC Adv. 6(7), 5856–5864 (2016)
X. Ding, Z. Peng, S.C.S. Lin, M. Geri, S.X. Li, P. Li, Y.C. Chen, M. Dao, S. Suresh, H. TJl, Cell separation using tilted-angle standing surface acoustic waves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111(36), 12992–12997 (2014)
D.C. Duffy, J.C. Mcdonald, O.J. Schueller, G.M. Whitesides, Rapid prototyping of microfluidic Systems in Poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal. Chem. 70(23), 4974–4984 (1998)
J. Friend, L.Y. Yeo, Microscale acoustofluidics: Microfluidics driven via acoustics and ultrasonics. Review of Modern Physic 83(2), 647–704 (2011)
P.E. Furlani, Magnetophoretic separation of blood cells at the microscale. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 40(5), 1313–1319 (2007)
R. Guldiken, M.C. Jo, N.D. Gallant, U. Demirci, J. Zhe, Sheathless size-based acoustic particle separation. Sensors 12(12), 905–922 (2012)
L.R. Huang, Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement. Science 304(5673), 987–990 (2004)
H.M. Ji, V. Samper, Y. Chen, C.K. Heng, T.M. Lim, L. Yobas, Silicon-based microfilters for whole blood cell separation. Biomed. Microdevices 10(2), 251–257 (2008)
H. Li, J. Friend, L. Yeo, A. Dasvarma, K. Traianedes, Effect of surface acoustic waves on the viability, proliferation and differentiation of primary osteoblast-like cells. Biomicrofluidics 3(3), 034102 (2009)
S.X. Li, X.Y. Ding, Z.M. Mao, Y.C. Chen, N. Nama, F. Guo, P. Li, L. Wang, C.E. Cameron, T.J. Huang, Standing surface acoustic wave (SSAW)-based cell washing. Lab Chip 15(1), 331–338 (2015)
S.X. Li, F. Ma, H. Bachman, C.E. Cameron, X.Q. Zeng, T.J. Huang, Acoustofluidic bacteria separation. Journal of Micromechanics & Microengineering 27(1), 015031 (2017)
M.P. Macdonald, G.C. Spalding, K. Dholakia, Microfluidic sorting in an optical lattice. Nature 426(6965), 421–424 (2003)
S. Mashaghi, A. Abbaspourrad, D.A. Weitz, A.M. van Oijen, Droplet microfluidics: A tool for biology, chemistry and nanotechnology. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 82, 118–125 (2016)
J. Nam, H. Lim, C. Kim, J.Y. Kang, S. Shin, Density-dependent separation of encapsulated cells in a microfluidic channel by using a standing surface acoustic wave. Biomicrofluidics 6(2), 24120 (2012)
S.M. Naseer, A. Manbachi, M. Samandari, P. Walch, Y. Gao, Y.S. Zhang, F. Davoudi, W. Wang, K. Abrinia, J.M. Cooper, A. Khademhosseini, S.R. Shin, Surface acoustic waves induced micropatterning of cells in gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biofabrication 9(1), 015020 (2017)
J.W. Ng, D.J. Collins, C. Devendran, Y. Ai, A. Neild, Flow-rate-insensitive deterministic particle sorting using a combination of travelling and standing surface acoustic waves. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 20(11), UNSP 151 (2016)
A.M. Soliman, M.A. Eldosoky, T.E. Taha, The separation of blood components using standing surface acoustic waves (SSAWs) microfluidic devices: Analysis and simulation. Bioengineering 4(2), 4020028 (2017)
Z. Wu, B. Willing, J. Bjerketorp, J.K. Jansson, K. Hjort, Soft inertial microfluidics for high throughput separation of bacteria from human blood cells. Lab Chip 9, 1193 (2009)
M. Yamada, M. Seki, Hydrodynamic filtration for on-chip particle concentration and classification utilizing microfluidics. Lab Chip 5(11), 1233 (2005)
L.Y. Yeo, J.R. Friend, Ultrafast microfluidics using surface acoustic waves. Biomicrofluidics 3(1), 012002 (2009)
C.W. Yung, J. Fiering, A.J. Mueller, D.E. Ingber, Micromagnetic–microfluidic blood cleansing device. Lab Chip 9(9), 1171–1177 (2009)
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Jilin Province Natural Science Foundation Projects (No. 20170101136JC), the National Natural Science Foundation Projects (No. 51375207; 51875234), and the Jilin Provincial Department of Education Project (JJKH20190140KJ) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., He, F., Li, Y. et al. Effects of two surface acoustic wave sorting chips on particles multi-level sorting. Biomed Microdevices 21, 59 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0419-4
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0419-4